Abstract
Purpose
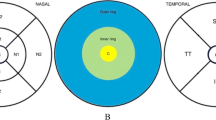
The present study was designed to investigate the influence of axial length on macular ganglion cell complex (GCC) thickness and two ratio parameters—the GCC thickness to macular total retinal thickness (G/T) ratio and the GCC thickness to macular outer retinal thickness (G/O) ratio—using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Methods
In this prospective case series, 74 eyes of 74 healthy Japanese study participants with varying degrees of myopia were recruited. GCC, outer retinal, and total retinal thicknesses were measured with the RTVue-100 system. The G/T and G/O ratios were also calculated. The axial length was determined using the IOLMaster. The correlation between the OCT measurements and axial length was evaluated.
Results
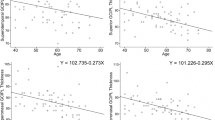
The average axial length was 25.05 ± 1.38 mm. The GCC thickness was significantly correlated with axial length (r = −0.384, P = 0.001). The outer retinal thickness and the total retinal thickness were significantly correlated with axial length (r = −0.444, P < 0.001 and r = −0.493, P < 0.001, respectively), but the G/T and G/O ratios were not (r = −0.093, P = 0.428 and r = −0.091, P = 0.440, respectively).
Conclusions
GCC thickness is affected by axial length. Because the prevalence of myopia is high in Japan, when determining the GCC thickness of Japanese individuals, it seems necessary to consider the axial length as well. To take account of individual variation in axial length, we propose the ratio parameters as a suitable parameter.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shimizu N, Nomura H, Ando F, Niino N, Miyake Y, Shimokata H. Refractive errors and factors associated with myopia in an adult Japanese population. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2003;47:6–12.
Mitchell P, Hourihan F, Sandbach J, Wang JJ. The relationship between glaucoma and myopia: the Blue Mountains Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 1999;106:2010–5.
Kanamori A, Nakamura M, Escano MF, Seya R, Maeda H, Negi A. Evaluation of the glaucomatous damage on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;135:513–20.
Wollstein G, Ishikawa H, Wang J, Beaton SA, Schuman JS. Comparison of three optical coherence tomography scanning areas for detection of glaucomatous damage. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;139:39–43.
Ojima T, Tanabe T, Hangai M, Yu S, Morishita S, Yoshimura N. Measurement of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and macular volume for glaucoma detection using optical coherence tomography. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2007;51:197–203.
Wollstein G, Schuman JS, Price LL, Aydin A, Beaton SA, Stark PC, et al. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) macular and peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer measurements and automated visual fields. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004;138:218–25.
Leung CK, Chan WM, Yung WH, Ng AC, Woo J, Tsang MK, et al. Comparison of macular and peripapillary measurements for the detection of glaucoma: an optical coherence tomography study. Ophthalmology. 2005;112:391–400.
Medeiros FA, Zangwill LM, Bowd C, Vessani RM, Susanna R Jr, Weinreb RN. Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer, optic nerve head, and macular thickness measurements for glaucoma detection using optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;139:44–55.
Vajaranant TS, Anderson RJ, Zelkha R, Zhang C, Wilensky JT, Edward DP, et al. The relationship between macular cell layer thickness and visual function in different stages of glaucoma. Eye. 2011;25:612–8.
Leung CK, Yu M, Weinreb RN, Mak HK, Lai G, Ye C, et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: interpreting the RNFL maps in healthy myopic eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53:7194–200.
Kim NR, Lee ES, Seong GJ, Kang SY, Kim JH, Hong S, et al. Comparing the ganglion cell complex and retinal nerve fiber layer measurements by Fourier domain OCT to detect glaucoma in high myopia. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011;95:1115–21.
Shoji T, Sato H, Ishida M, Takeuchi M, Chihara E. Assessment of glaucomatous changes in subjects with high myopia using spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:1098–102.
Budenz DL, Anderson DR, Varma R, Schuman J, Cantor L, Savell J, et al. Determinants of normal retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Stratus OCT. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:1046–52.
Leung CK, Mohamed S, Leung KS, Cheung CY, Chan SL, Cheng DK, et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer measurements in myopia: an optical coherence tomography study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47:5171–6.
Rauscher FM, Sekhon N, Feuer WJ, Budenz DL. Myopia affects retinal nerve fiber layer measurements as determined by optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma. 2009;18:501–5.
Wang G, Qiu KL, Lu XH, Sun LX, Liao XJ, Chen HL, et al. The effect of myopia on retinal nerve fiber layer measurement: a comparative study of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography and scanning laser polarimetry. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011;95:255–60.
Kang SH, Hong SW, Im SK, Lee SH, Ahn MD. Effect of myopia on the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer measured by Cirrus HD optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:4075–83.
Savini G, Barboni P, Parisi V, Carbonelli M. The influence of axial length on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and optic-disc size measurements by spectral-domain OCT. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012;96:57–61.
Öner V, Aykut V, Taş M, Alakuş MF, İşcan Y. Effect of refractive status on peripapillary retinal nerve fibre layer thickness: a study by RTVue spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013;97:75–9.
Kim NR, Kim JH, Lee J, Lee ES, Seong GJ, Kim CY. Determinants of perimacular inner retinal layer thickness in normal eyes measured by Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:3413–8.
Zhao Z, Jiang C. Effect of myopia on ganglion cell complex and peripapillary retinal nerve fibre layer measurements: a Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography study of young Chinese persons. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013;41:561–6. doi:10.1111/ceo.12045.
Kita Y, Kita R, Takeyama A, Takagi S, Nishimura C, Tomita G. Ability of optical coherence tomography-determined ganglion cell complex thickness to total retinal thickness ratio to diagnose glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2012;. doi:10.1097/IJG.0b013e31825af58a.
Kita Y, Kita R, Takeyama A, Anraku A, Tomita G, Goldberg I. Relationship between macular ganglion cell complex thickness and macular outer retinal thickness: a spectral-domain optical coherence tomography study. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013;41:674–82. doi:10.1111/ceo.12089.
Tan O, Li G, Lu AT, Varma R, Huang D. Mapping of macular substructures with optical coherence tomography for glaucoma diagnosis. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:949–56.
Tan O, Chopra V, Lu AT, Schuman JS, Ishikawa H, Varma R, et al. Detection of macular ganglion cell loss in glaucoma by Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2009;116:2305–14.
Kita Y, Kita R, Nitta A, Nishimura C, Tomita G. Glaucomatous eye macular ganglion cell complex thickness and its relation to temporal circumpapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2011;55:228–34.
Kim NR, Lee ES, Seong GJ, Kim JH, An HG, Kim CY. Structure–function relationship and diagnostic value of macular ganglion cell complex measurement using Fourier-domain OCT in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:4646–51.
Rao HL, Zangwill LM, Weinreb RN, Sample PA, Alencar LM, Medeiros FA. Comparison of different spectral domain optical coherence tomography scanning areas for glaucoma diagnosis. Ophthalmology. 2010;117:1692–9.
Seong M, Sung KR, Choi EH, Kang SY, Cho JW, Um TW, et al. Macular and peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer measurements by spectral domain optical coherence tomography in normal-tension glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:1446–52.
Schulze A, Lamparter J, Pfeiffer N, Berisha F, Schmidtmann I, Hoffmann EM. Diagnostic ability of retinal ganglion cell complex, retinal nerve fiber layer, and optic nerve head measurements by Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2011;249:1039–45.
Mori S, Hangai M, Sakamoto A, Yoshimura N. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography measurement of macular volume for diagnosing glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2010;19:528–34.
Girkin CA, McGwin G Jr, Sinai MJ, Sekhar GC, Fingeret M, Wollstein G, et al. Variation in optic nerve and macular structure with age and race with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology. 2011;118:2403–8.
Hoh ST, Lim MC, Seah SK, Lim AT, Chew SJ, Foster PJ, et al. Peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness variations with myopia. Ophthalmology. 2006;113:773–7.
Apple DJ, Fabb MF. Clinico-pathologic correlation of ocular disease: a text and stereoscopic atlas. St. Louis: CV Mosby; 1978. p. 39–44.
Yanoff M, Fine BS. Ocular pathology: a text and atlas. Philadelphia: Harper & Row; 1982. p. 513–4.
Kanamori A, Escano MF, Eno A, Nakamura M, Maeda H, Seya R, et al. Evaluation of the effect of aging on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmologica. 2003;217:273–8.
Hirasawa H, Tomidokoro A, Araie M, Konno S, Saito H, Iwase A, et al. Peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness determined by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in ophthalmologically normal eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010;128:1420–6.
Iwase A, Tomidokoro A, Araie M, Shirato S, Shimizu H, Kitazawa Y, Tajimi Study Group. Performance of frequency-doubling technology perimetry in a population-based prevalence survey of glaucoma: the Tajimi study. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:27–32.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) 24592656 from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, and Technology of the Japanese Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Takeyama, A., Kita, Y., Kita, R. et al. Influence of axial length on ganglion cell complex (GCC) thickness and on GCC thickness to retinal thickness ratios in young adults. Jpn J Ophthalmol 58, 86–93 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-013-0292-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-013-0292-2