Abstract
The infrastructure construction in tectonically active mountainous areas is faced with the threat of earthquake-induced rockslide-avalanches. We took the Woqian rockslide-avalanche induced by the Wenchuan earthquake near the Qinchuan active fault, Southwestern China as an instance to elucidate a unique initiation mechanism of the inward inclined bedding slope, which had a characteristic of twice destabilization in succession. The high-resolution satellite images, UAV aerial photography, field investigation, and numerical simulation were conducted to reveal the failure processes. The results suggested that (1) the long-term headward erosion of the gully runoff had locally exposed the unconformity contact plane within the strata, which evolved as a part of the sliding plane; (2) the seismic loading produced a rapid shear strain increment on the unconformity plane; (3) the brittle rupture occurred along the sliding plane at the bottom of the sliding source I developed at 6 s after the seismic wave arrival; (4) as a “resistance barrier”, the sliding source I first collapsed and most of it accumulated at a short distance; (5) the sliding source II subsequently slid along the apparent dip of the bedding plane and then entrained the deposits of the source I into a catastrophic rock avalanche. The failure mechanism of such carbonaceous bedding slopes with similar geological conditions could provide an insight into the early risk recognition of potential rockslides and the safe site selection of infrastructures.



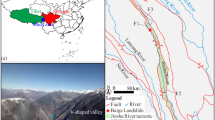
© Google Earth). a. initial topography of linear fault valley and compressive ridges before the WRA, joint set J1 (dip 40°, dip direction 80°) subparallel to the N-S mountain ridge became the rear boundary of the sliding source. b. distribution characteristics of the deposits of the WRA and two lateral deep-cutting grooves along the gully showing two sliding paths


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang M, Cui P, Xu L, Zhou Y (2021) The spatial distribution characteristics of coseismic landslides triggered by the Ms7.0 Lushan earthquake and Ms7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake in southwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(16):20549–20569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11826-5
Chang WB, Xu Q, Dong XJ, Zhuang Y, Xing AG, Wang Q, Kong., X.Z. (2022) Dynamic process analysis of the Xinmo landslide via seismic signal and numerical simulation. Landslides 19(6):1463–1478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-022-01876-w
Cui SH, Pei XJ, Jiang Y, Wang GH, Fan XM, Yang QW, Huang RQ (2021) Liquefaction within a bedding fault: understanding the initiation and movement of the Daguangbao landslide triggered by the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake (Ms=8.0). Eng Geol 295:106–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106455
Dai FC, Tu XB, Xu C, Gong QM, Yao X (2011) Rock avalanches triggered by oblique-thrusting during the 12 May 2008 Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, China. Geomorphology 132:300–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.05.016
Fan XM, Scaringi G, Korup O, West AJ, Westen CJ, Tanyas H, Hovius N, Hales TC, Jibson RW, Allstadt KE, Zhang LM, Evans SG, Xu C, Li G, Pei XJ, Xu Q, Huang RQ (2019) Earthquake-induced chains of geologic hazards: patterns, mechanisms, and impacts. Rev Geophys 57(2):421–503. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018RG000626
Gombert B, Duputel Z, Shabani E, Rivera L, Jolivet R, Hollingsworth J (2019) Impulsive source of the 2017 Mw= 7.3 Ezgeleh, Iran, earthquake. Geophys Res Lett 46(10):5207–5216. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL081794
Gong B (2021) Study of PLSR-BP model for stability assessment of loess slope based on particle swarm optimization. Sci Rep 11(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41598-021-97484-0
Gong B, Tang CA (2017) Slope-slide simulation with discontinuous deformation and displacement analysis. Int J Geomech 17(5):E4016017
Gorum T, Fan XM, Van Western CJ, Huang RQ, Xu Q, Tang C, Wang GH (2011) Distribution pattern of earthquake-induced landslides triggered by the 12 May 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Geomorphology 133:152–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2010.12.030
He K, Ma G, Hu X (2021) Formation mechanisms and evolution model of the tectonic-related ancient giant basalt landslide in Yanyuan County, China. Nat Hazards 106:2575–2597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04555-6
He K, Liu B, Hu X, Zhou R, Xi C, Ma G, Han M, Li Y, Luo G (2022) Rapid characterization of landslide-debris flow chains of geologic hazards using multi-method investigation: case study of the Tiejiangwan LDC. Rock Mech Rock Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02905-9
Huang Y, Zhang B, Zhu CQ (2021) Computational assessment of baffle performance against rapid granular flows. Landslides 18:485–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01511-6
Hungr O (2006) Rock avalanche occurrence, process and modelling. Landslides from massive rock slope failure. Landslides 49:243–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-4037-5_14
Hungr O, Leroueil S, Picarelli L (2014) The Varnes classification of landslide types, an update. Landslides 11:167–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0436-y
Itasca Consulting Group, Inc (2018) Fast Lagrangian Analysis of Continua, ver. 6.0 Manual. Itasca, Minneapolis
Kargel JS, Leonard GJ, Shugar DH (2016) Geomorphic and geologic controls of geo-hazards induced by Nepal’s 2015 Gorkha earthquake. Science 351(6269):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aac8353
Keefer DK (1984) Landslides caused by earthquakes. Geol Soc Am Bull 95(4):406–421. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1984)95%3c406:LCBE%3e2.0.CO
Liu B, Hu X, He K, He S, Shi H, Liu D (2020) The starting mechanism and movement process of the coseismic rockslide: a case study of the Laoyingyan rockslide induced by the “5.12” Wenchuan earthquake. J Mt Sci 17(5):1188–1205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-019-5775-2
Lin C, Pastor M, Li T, Liu X, Qi H, Lin C (2019) A SPH two-layer depth-integrated model for landslide-generated waves in reservoirs: application to Halaowo in Jinsha River (China). Landslides 16(11):2167–2185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01204-9
Lin F, Wu LZ, Huang RQ, Zhang H (2018) Formation and characteristics of the Xiaoba landslide in Fuquan, Guizhou, China. Landslides 15:669–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0897-5
Mahani AB, Kazemian J (2018) Strong ground motion from the November 12, 2017, M7.3 Kermanshah earthquake in western Iran. J Seismol 22(6):1339–1358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-018-9761-x
Matsuoka N (2019) A multi-method monitoring of timing, magnitude and origin of rockfall activity in the Japanese Alps. Geomorphology 336:65–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.03.023
Oswald P, Strasser M, Hammerl C, Moernaut J (2021) Seismic control of large prehi-storic rockslides in the Eastern Alps. Nat Commun 12(1):1059–1066. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21327-9
Petley DN (2013) Characterizing giant landslides. Science 339(6126):1395–1396. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1236165
Pudasaini SP, Miller SA (2013) The hypermobility of huge landslides and avalanches. Eng Geol 157:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.01.012
Qi SW, Xu Q, Lan HX, Zhang B, Liu JY (2010) Spatial distribution analysis of landslides triggered by 2008.5.12 Wenchuan earthquake, China. Eng Geol 116:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.07.011
Roback K, Clark MK, West AJ, Zekkos D, Li G, Gallen SF, Chamlagain D, Godt JW (2018) The size, distribution, and mobility of landslides caused by the 2015 Mw7.8 Gorkha earthquake. Nepal Geomorphology 301:121–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.01.030
Stead D, Wolter A (2015) A critical review of rock slope failure mechanisms: the importance of structural geology. J Struct Geol 74:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2015.02.002
Sun HY, He HL, Ikeda Y, Kano K, Shi F, Gao W, Echigo T, Okada S (2015) Holocene paleoearthquake history on the Qingchuan fault in the northeastern segment of the Longmenshan thrust zone and its implications. Tectonophysics 660:92–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2015.08.022
Sun P, Zhang YS, Shi JS, Chen LW (2011) Analysis on the dynamical process of Donghekou rockslide-debris flow triggered by 5.12 Wenchuan earthquake. J Mt Sci 8:140–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-011-2112-9
Tang MG, Xu Q, Zhang W (2011) Discuss on failure mechanism and geologic characteristic of Woqian landslide triggered by Wenchuan earthquake. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 30(S2):3491–3502 (in Chinese)
Vanani AAG, Shoaei G, Zare M (2021) Statistical analyses of landslide size and spat-ial distribution triggered by 1990 Rudbar-Manjil (Mw 7.3) earthquake, northern Iran: revised inventory, and controlling factors. Bull Eng Geol Env 80:3381–3403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02106-8
Wang GH, Huang RQ, Chigira M, Wu XY, Lourenço SD (2013) Landslide amplification by liquefaction of runout-path material after the 2008 Wenchuan (M 8·0) earthquake, China. Earth Surf Process Landf 38(3):265–274. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3277
Wang HL, Liu SQ, Xu WY, Yan L, Qu X, Xie WC (2020) Numerical investigation on the sliding process and deposit feature of an earthquake-induced landslide: a case study. Landslides 17:2671–2682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01446-y
Wang T, Wu SR, Shi JS, Xin P, Wu LZ (2018) Assessment of the effects of historical strong earthquakes on large-scale landslide groupings in the Wei River midstream. Eng Geol 235:11–19
Wang WP, Yin YP, Zhu SN, Wang LC, Zhang N, Zhao RX (2019a) Investigation and numerical modeling of the overloading-induced catastrophic rockslide avalanche in Baige, Tibet, China. Bull Eng Geol Env 79(4):1765–1779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01664-2
Wang XL, Clague JJ, Crosta GB, Sun JJ, Stead D, Qi SW, Zhang LQ (2021) Relationship between the spatial distribution of landslides and rock mass strength, and implications for the driving mechanism of landslides in tectonically active mountain ranges. Eng Geol 292:106281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106281
Wang YF, Cheng QG, Zhu Q (2015) Surface microscopic examination of quartz grains from rock avalanche basal facies. Can Geotech J 52(2):167–181. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2013-0284
Wang YS, Wu LZ, Gu J (2019b) Process analysis of the Moxi earthquake-induced Lantianwan landslide in the Dadu River, China. Bull Eng Geol Env 78:4731–4742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-01438-2
Xu C, Xu XW (2014) Statistical analysis of landslides caused by the Mw 6.9 Yushu, China, earthquake of April 14, 2010. Nat Hazards 72(2):871–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1038-2
Xu C, Xu XW, Yao X, Dai FC (2014) Three (nearly) complete inventories of landslides triggered by the May 12, 2008 Wenchuan Mw 7.9 earthquake of China and their spatial distribution statistical analysis. Landslides 11(3):441–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0404-6
Yin YP, Li B, Wang WP (2015) Dynamic analysis of the stabilized Wangjiayan land-slide in the Wenchuan Ms 8.0 earthquake and aftershocks. Landslides 12:537–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-014-0497-6
Zhang M, Yin YP, Mcsaveney M (2016) Dynamics of the 2008 earthquake-triggered Wenjiagou Creek rock avalanche, Qingping, Sichuan, China. Eng Geol 200:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.12.008
Zhang M, Wu LZ, Zhang JC, Li LP (2019) The 2009 Jiweishan rock avalanche, Wulong, China: deposit characteristics and implications for its fragmentation. Landslides 16:893–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01142-6
Zhang SL, Yin YP, Hu XW, Wang WP, Li ZL, Wu XM, Luo G, Zhu SN (2021) Geostructures and deformation-failure characteristics of rockslide areas near the Baige landslide scar in the Jinsha River tectonic suture zone. Landslides 18(11):3577–3597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01741-2
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Sichuan Province Science and Technology Support Program (2021YJ0033) and the research project of the Department of Natural Resources of Sichuan Province (Kj-2022-29) for their strong support for this topic. The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to Professor Bernd Wünnemann of Southwest Jiaotong University for discussing the academic ideas and improving the quality of the paper. Further, the authors also thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable time and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, G., Chen, X., Zhang, Q. et al. Failure mechanism and sedimentary characteristics of a catastrophic rockslide avalanche induced by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Landslides 20, 25–38 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-022-01955-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-022-01955-y