Abstract
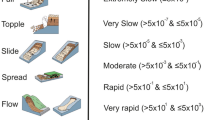
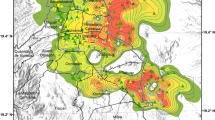
In Emilia-Romagna, over 32,000 landslide bodies cover one-fifth of the hilly and mountainous territory. The majority of them originated as earth-flows after the last glacial maximum and grew during the rainiest periods of the Holocene through the superimposition of new earth-flows. Reactivation of these large landslides is the main problem the geologists of Emilia-Romagna are facing now. Intense and/or prolonged precipitation play a major role as triggering factors in reactivating landslide bodies, but also the importance of snowmelt is suggested by the monthly distribution of landslide events. Almost all the present-day landslide activity is due to the reactivation of pre-existing landslide bodies. Consequently, territorial planning and geo-thematic cartography are fundamental tools for the reduction of risk. The Emilia-Romagna geo-thematic cartography (1:10,000) is legally binding and regulates land use in regional, municipal and basin plans.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basenghi R, Bertolini G (2001) Ricorrenza e caratteristiche delle frane riattivate durante in XX secolo nella Provincia di Reggio Emilia (Appennino Settentrionale). Quad Geol Appl 8, Pitagora Ed, Bologna, Italy
Bertolini G (1994) Note Illustrative della Carta del Dissesto Geologico Attuale, Foglio 218 SE, Carpineti (Scala 1:25.000). Geological Survey of the Emilia-Romagna Region, S.EL.C.A. Ed, Florence, Italy
Bertolini G (2005) Monitoraggio di frane in area appenninica. In: Proceeding of the Congress “Il monitoraggio e l’assetto idrogeologico: stato dell’arte e prospettive professionali, Milano, 9–10 ottobre 2003”, Ordine dei Geologi della Lombardia, pp 125–136
Bertolini G, Canuti P, Casagli N, De Nardo MT, Egidi D, Mainetti M, Pignone R, Pizziolo M (2002) Carta della Pericolosità Relativa da Frana della Regione Emilia-Romagna. SystemCart, Rome, Italy
Bertolini G, Gorgoni C (2001) La lavina di Roncovetro (Vedriano, Comune di Canossa, Provincia di Reggio Emilia). Quad Geol Appl 8, Pitagora Ed, Bologna, Italy
Bertolini G, Pellegrini M (2001) The landslides of the Emilia Apennines (northern Italy) with reference to those which resumed activity in the 1994–1999 period and required Civil Protection interventions. Quad Geol Appl 8, Pitagora Ed, Bologna, Italy
Bertolini G, Sartini G (2001) La frana di Valestra (Comune di Carpineti, Provincia di Reggio Emilia). Quad Geol Appl 8, Pitagora Ed, Bologna, Italy
Bertolini G, Tellini C (2001) New radiocarbon dating for landslide occurrences in the Emilia Apennines (Northern Italy). Trans Jpn Geom Un 22(4):C-23
Bertolini G, Casagli N, Ermini L, Malaguti C (2003) Radiocarbon data on Late Glacial and Holocene Landslides in the Northern Apennines (Italy). Nat Hazards 31:645–662, Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands
Bertolini G, De Nardo MT, Larini G, Pizziolo M (2004) Landslides of the Emilia Apennines. Field Trip Guide Book of the 32nd International Geological Congress, August 20–28, 2004, Florence (Italy). Edited by APAT, Rome, Italy
Bettelli G, De Nardo MT (2001) Geological outlines of Emilia Apennines (Italy) and introduction to the rock units cropping out in the areas of landslides reactivated in the 1994–1999 period. Quad Geol Appl 8:1–26, Pitagora Ed, Bologna, Italy
Cancelli A, Pellegrini M (1987) Deep seated gravitational slope deformations in the Northern Apennines (Italy). In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference and Field Workshop on Landslides, Australia and New Zealand, pp 171–178
Cancelli A, Casagli N (1995) Classificazione e modellazione di fenomeni di instabilità in ammassi rocciosi sovrapposti ad argiliti o argille sovraconsolidate. Mem Soc Geol It 50:83–100, Rome, Italy
Cancelli A, Pellegrini M, Tosatti G, with a contribution by Bertolini G (1987) Alcuni esempi di deformazioni gravitative profonde di versante nell’Appennino Settentrionale. Mem Soc Geol It 39:447–466, Rome, Italy
Carboni R, Casagli N, Iotti A, Monti l, Tarchiani U (2001) La frana di Cà di Sotto (San Benedetto Val di Sambro, Bologna): caratteri geomorfologici, analisi geotecniche ed interventi di mitigazione del rischio. Quad Geol Appl 8, Pitagora Ed, Bologna, Italy
Casagli N, Ermini L (1999) Geomorphic analysis of landslide dams in the Northern Apennines. Transactions of the Japanese Geomorphological Union, 20(3):219–249, Kyoto
Catenacci V (1992) Il dissesto geologico e ambientale in Italia dal dopoguerra al 1990. Mem Descr Carta Geol D’It 47, Rome, Italy
Clerici A, Mandrone G, Tellini C, Vescovi P (2002) Simulation of the Ceno R. blockage by the Anzola landslide (Northern Apennines, Italy). In: Rybar, Stemberk and Wagner (eds) Landslides, Proceedings of the 1st European Conference on Landslides, Prague, Rep. Czech, June 24–26, 2002, pp 137–142
Colombetti A, Moratti L, Tosatti G (1989) Una frana di scivolamento con formazione di un lago di sbarramento: il caso di Cerredolo (Appennino Reggiano). Le Strade, 91(1257):471–482, Milan, Italy
Cruden DM, Varnes DJ (1996) Landslide types and processes. In: Turner AK, Shuster RL (eds) Landslides: investigation and mitigation. Transportation Research Board, National Research Council, Special Report 247, pp 36–75. National Academy Press, Washington DC, USA
Galliani G, Pomi L, Zinoni F, Casagli N (2001) Analisi meteoclimatologica e soglie di innesco delle frane nella Regione Emilia-Romagna negli anni 1994–1996. Quad Geol Appl 8:59–114, Pitagora Ed, Bologna, Italy
Larini G, Malaguti C, Pellegrini M, Tellini C (2001) “La Lama” di Corniglio (Appennino Parmense), riattivata negli anni 1994–1999. Quad Geol Appl 8:59–114, Pitagora Ed, Bologna, Italy
Leheman EL (1959) Testing Statistical Hypotheses. John Wiley, New York
Lollino G, Brunamonte F, Larini G, Malaguti C (2001) La sperimentazione del Sistema Inclinometrico Automatizzato nel monitoraggio in continuo della frana di Corniglio (Parma) e ricerca di correlazioni significative fra le precipitazioni e la riattivazione del novembre 1994. Quad Geol Appl 8:59–114, Pitagora Ed, Bologna, Italy
Pizziolo M (1996) Carta Inventario del Dissesto. Regione Emilia-Romagna, Bologna, Italy
Pini GA (1999) Tectosomes and olistostromes in the Argille Scagliose of the northern Apennines, Italy. Geol Soc Am Special Paper, 335
Sorriso Valvo M. (ed) (1984) Atti del I° Seminario sul tema “Deformazioni Gravitative Profonde di Versante”. Boll Soc Geol It 103:667–729
Sorriso Valvo M, Ibsen ML (1994) Statistical methods. In: Casale R, Fantechi R, Flageollet JC (eds) Temporal occurrence and forecasting of landslides in the European Community, Final Report. 1, Eur, 15805en, Strasbourg, France
Tellini C (2004) Le grandi frane dell’Appennino Emiliano quali indicatori geomorfologici di variazioni climatiche. Rassegna Frignanese, XXXIII, Accademia del Frignano “Lo Scoltenna”, Pievepelago, Modena, Italy
Ter-Stephanian G (1966) Types of depth creep of slopes in rocky masses. In: Proceedings of the 1st Conf. Int. Soc. Rock. Mech., Lisbon, Sect. 2, pp 157–160
WPL/WLI Working Party on the World Landslide Inventory and Canadian Geotechnical Society (1993) Multilingual Landslide Glossary, BiTech Publishers, Richmond, BC
Wu TH, Tang WH, Einstein HH (1996) Landslide hazard and risk assessment. In: Turner AK, Shuster RL (eds) Landslides: Investigation and Mitigation. Transportation Research Board, National Research Council, Special Report 247, pp 106–118. National Academy Press, Washington DC, USA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertolini, G., Guida, M. & Pizziolo, M. Landslides in Emilia-Romagna region (Italy): strategies for hazard assessment and risk management. Landslides 2, 302–312 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-005-0020-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-005-0020-1