Abstract
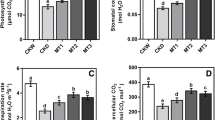
Flooding stress is an important abiotic stress factor, restricting agricultural production and causing yield and quality losses. This study was carried out to measure the effects of melatonin (MEL) applications on plant growth and the physiological and biochemical changes associated with flooding stress in seedling cauliflower plants. Approximately one-month-old cauliflower seedlings were subjected to flooding stress (Flo) and compared with fully irrigated control plants. Three doses (0, 50, and 100 µM) of MEL were applied to the seedlings in the form of a spray, and the plants were harvested 10, 15, and 20 days after Flo and MEL treatments. Agronomic, physiological, and biochemical measurements were made from the plant samples taken after each harvest. The Flo applied to the cauliflower seedlings significantly restricted their growth, causing reductions in aboveground fresh and dry weight, under-ground fresh and dry weight, and leaf area of 68%, 58%, 45%, 62%, and 40%, respectively. Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that the most important factor of the study was Flo. Plant growth parameters, leaf relative water content, chlorophyll b, stomatal conductance, actual photosynthetic efficiency, and chlorophyll fluorescence values gave the best results under full irrigation conditions; while under Flo conditions, malondialdehyde, peroxidase, hydrogen peroxidase, chlorophyll a, carotenoid, catalase, and leaf temperature exhibited significant changes. The MEL treatments had little effect in ameliorating stress conditions. In conclusion, the exposure of agricultural lands to flood stress is an important consideration when determining where cauliflower will be grown.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Pandey V (2004) Antioxidant enzyme responses to NaCl stress in Cassia angustifolia. Biol plant 48(4):555–560. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOP.0000047152.07878.e7
Ahmad S, Kamran M, Ding R, Meng X, Wang H, Ahmad I, Fahad S, Han Q (2019) Exogenous melatonin confers drought stress by promoting plant growth, photosynthetic capacity and antioxidant defense system of maize seedlings. Peer J 7:e7793. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7793
Ali M, Kamran M, Abbasi GH, Saleem MH, Ahmad S, Parveen A, Fahad S (2021) Melatonin-induced salinity tolerance by ameliorating osmotic and oxidative stress in the seedlings of two tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) cultivars. J Plant Growth Regul 40(5):2236–2248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10273-3
Altaf MA, Shahid R, Ren MX, Altaf MM, Khan LU, Shahid S, Jahan MS (2021) Melatonin alleviates salt damage in tomato seedling: a root architecture system, photosynthetic capacity, ion homeostasis, and antioxidant enzymes analysis. Sci Hortic 285:110145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110145
Altaf MA, Shahid R, Ren MX, Naz S, Altaf MM, Khan LU, Ahmad P (2022) Melatonin improves drought stress tolerance of tomato by modulating plant growth, root architecture, photosynthesis, and antioxidant defense system. Antioxidants 11(2):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020309
Angelini R, Federico R (1989) Histochemical evidence of polyamine oxidation and generation of hydrogen peroxide in the cell wall. J Plant Physiol 135(2):212–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(89)80179-8
Bailey-Serres J, Fukao T, Ronald P, Ismail A, Heuer S, Mackill D (2010) Submergence tolerant rice: SUB1’s journey from landrace to modern cultivar. Rice 3:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12284-010-9048-5
Barickman TC, Simpson CR, Sams CE (2019) Waterlogging causes early modification in the physiological performance, carotenoids, chlorophylls, proline, and soluble sugars of cucumber plants. Plants 8:160. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8060160
Bartley GE, Scolnik PA (1995) Plant carotenoids: pigments for photo protection, visual attraction, and human health. Plant Cell 7:1027–1038. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.7.7.1027
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare I (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39(1):205–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018060
Bhatt RM, Upreti KK, Divya MH, Bhat S, Pavithra CB, Sadashiva AT (2015) Interspecific grafting to enhance physiological resilience to flooding stress in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Sci Hortic 182:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.10.043
Bidabadi SS, Van der Weide J, Sabbatini P (2020) Exogenous melatonin improves glutathione content, redox state and increases essential oil production in two Salvia species under drought stress. Sci Rep 10:6883. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63986-6
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Cao Y, Ma C, Chen G, Zhang J, Xing B (2017) Physiological and biochemical responses of Salix integra Thunb. under copper stress as affected by soil flooding. Environ Pollut 225:644–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.040
Cardinif F, Bonzi LM (2005) Carotenoid composition and its chemotaxonomic significance in leaves of ten species of the genus Ceratozamia (Cycads). J Plant Physiol 162:517–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2004.06.007
Chance B (1955) Assay of catalase and peroxidase. Meth Enzymol 2:765–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(55)02300-8
Chen H, Feng C, Kong J, Wang L, Wang N, Zheng X, Chan D (2015) Use of product containing melatonin as effective component for improving waterlogging stress resistance in plants CN105076136‑A, CN105076136‑B, CN105076136‑A. 25 Nov 2015 (A01N-043/38 201612)
Chen HJ, Qualls RG, Miller GC (2002) Adaptive responses of Lepidium latifolium to soil flooding: biomass allocation adventitious rooting aerenchyma formation and ethylene production. Environ Exp Bot 48:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0098-8472(02)00018-7
Chen Z, Cao X, Niu J (2021) Effects of melatonin on morphological characteristics, mineral nutrition, nitrogen metabolism, and energy status in alfalfa under high-nitrate stress. Front Plant Sci 12:694179. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.694179
Dai L, Li J, Harmens H, Zheng X, Zhang C (2020) Melatonin enhances drought resistance by regulating leaf stomatal behaviour, root growth and catalase activity in two contrasting rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) genotypes. Plant Physiol Biochem 149:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.01.039
Damanik RI, Maziah M, Ismail MR, Ahmad S, Zain A (2010) Responses of the antioxidative enzymes in Malaysian rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars under submergence condition. Acta Physiol Plant 32:739–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0456-3
Das K, Roychoudhury A (2014) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front Environ Sci 2:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2014.00053
Ezin V, Pena RDL, Ahanchede A (2010) Flooding tolerance of tomato genotypes during vegetative and reproductive stages. Braz J Plant Physiol 22:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-04202010000200007
FAO (2022) Food and agriculture organization, crop production statistics. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC. Accessed 17 June 2022
Gholami R, Hoveizeh NF, Zahedi SM, Gholami H, Carillo P (2022) Melatonin alleviates the adverse effects of water stress in adult olive cultivars (Olea europea cv. Sevillana & Roughani) in field condition. Agric Water Manag 269:107681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107681
Gray SB, Brady SM (2016) Plant developmental responses to climate change. Dev Biol 419(1):64–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.07.023
Greenway H, Armstrong W, Colmer TD (2006) Conditions leading to high CO2 (.5 kPa) in waterlogged-flooded soils and possible effects on root growth and metabolism. Ann Bot 98:9–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcl076
Grichko VP, Glick BR (2001) Amelioration of flooding stress by ACC deaminasecontaining plant growth-promoting bacteria. Plant Physiol Biochem 39(1):11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0981-9428(00)01212-2
Gu X, Xue L, Lu L, Xiao J, Song G, Xie M, Zhang H (2021) Melatonin enhances the waterlogging tolerance of Prunus persica by modulating antioxidant metabolism and anaerobic respiration. J Plant Growth Regul 40(5):2178–2190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10263-5
Hashimoto T, Mustafa G, Nishiuchi T, Komatsu S (2020) Comparative analysis of the effect of inorganic and organic chemicals with silver nanoparticles on soybean under flooding stress. IJMS 21(4):1300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041300
Hattori Y, Nagai K, Ashikari M (2011) Rice growth adapting to deepwater. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2010.09.008
Havir EA, McHale NA (1987) Biochemical and developmental characterization of multiple forms of catalase in tobacco leaves. Plant Physiol 84(2):450–455. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.84.2.450
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125(1):189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(68)90654-1
Hossain MA, Bhattacharjee S, Armin SM, Qian P, Xin W, Li HY, Burritt DJ, Fujita M, Tran LS (2015) Hydrogen peroxide priming modulates abiotic oxidative stress tolerance: insights from ROS detoxification and scavenging. Front Plant Sci 6:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00420
Hossain Z, Lopez-Climent MF, Arbona V, Perez-Clemente RM, Gomez-Cadenas A (2009) Modulation of the antioxidant system in citrus under waterlogging and subsequent drainage. J Plant Physiol 166:1391–1404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2009.02.012
Ipek M, Pirlak L, Esitken A, Dönmez FM, Turan M (2014) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) increase yield, growth and nutrition of strawberry under high-calcareous soil conditions. J of Plant Nutrition 37(7):990–1001. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2014.881857
Jia W, Ma M, Chen J, Wu S (2021) Plant morphological, physiological and anatomical adaption to flooding stress and the underlying molecular mechanisms. IJMS 22(3):1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031088
Kayak N, Kal Ü, Dal Y, Yavuz D, Seymen M (2022) Do proline and glycine betaine mitigate the adverse effects of water stress in spinach? Gesunde Pflanz. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00675-6
Kumar S (2020) Abiotic stresses and their effects on plant growth, yield and nutritional quality of agricultural produce. Int J Food Sci Agric 4:367–378. https://doi.org/10.26855/ijfsa.2020.12.002
Li C, Wang P, Wei ZW, Liang D, Liu CH, Yin LH, Jia DF, Fu MY, Ma FW (2012) The mitigation effects of exogenous melatonin on salinity-induced stress in Malus hupehensis. J Pineal Res 53:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.00999.x
Liang B, Ma C, Zhang Z, Wei Z, Gao T, Zhao Q, Ma F, Li C (2018) Long-term exogenous application of melatonin improves nutrient uptake fluxes in apple plants under moderate drought stress. Environ Exp Bot 155:650–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.08.016
Liang D, Ni Z, Xia H, Xie Y, Lv X, Wang J, Lin L, Deng Q, Luo X (2019) Exogenous melatonin promotes biomass accumulation and photosynthesis of kiwifruit seedlings under drought stress. Sci Hortic 246:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.10.058
Lichtenthaler H, Buschmann C (2001) Chlorophylls and Carotenoids: measurement and characterization by UV-VIS spectroscopy. Curr Protoc Food Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142913.faf0403s01
Loreti E, van Veen H, Perata P (2016) Plant responses to flooding stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 33:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2016.06.005
Lutts S, Kinet J, Bouharmont J (1996) NaCl-induced senescence in leaves of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity resistance. Ann Bot 78(3):389–398. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.1996.0134
Mohammadi SA, Prasanna BM (2003) Analysis of genetic diversity in crop plants salient statistical tools and considerations. Crop Sci 43(4):1235–1248. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2003.1235
Mozafari AA, Ghaderi N, Havas F, Dedejani S (2019) Comparative investigation of structural relationships among morpho-physiological and biochemical properties of strawberry (Fragaria×ananassa Duch.) under drought and salinity stresses: A study based on in vitro culture. Sci Hortic 256:108601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108601
Mutava RN, Prince SJK, Syed NH, Song L, Valliyodan B, Chen W, Nguyen HT (2015) Understanding abiotic stress tolerance mechanisms in soybean: a comparative evaluation of soybean response to drought and flooding stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 86:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.11.010
Najeeb U, Tan DKY, Bange MP, Atwell BJ (2018) Protecting cotton crops under elevated CO2 from waterlogging by managing ethylene. Fun Plant Biol 45:340. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP17184
Patel PK, Singh AK, Tripathi N, Yadav D, Hemantaranjan A (2014) Flooding: abiotic constraint limiting vegetable productivity. Adv Plants Agric Res 1(3):96–103. https://doi.org/10.15406/apar.2014.01.00016
Radmann EB, Klumb EK, Deuner S, Bianchi VJ (2018) Antioxidant capacity in leaf and root tissues of Prunus spp under flooding. J Exp Agric Int. https://doi.org/10.9734/JEAI/2018/43650
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Sharma R (2018) Historical perspective and evaluation of the mechanisms by which melatonin mediates seasonal reproduction in mammals. Melatonin Res 1:59–77. https://doi.org/10.32794/mr11250004
Romero-Oliva CS, Contardo-Jara V, Pflugmacher S (2015) Antioxidative response of the three macrophytes Ceratophyllum demersum, Egeria densa, and Hydrilla verticillata to a time dependent exposure of cell-free crude extracts containing three microcystins from cyanobacterial blooms of Lake Amatitlan, Guatemala. Aquat Toxicol 163:130–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.04.001
Roy R, Sultana S, Begum N, Fornara D, Barmon M, Zhang R, Sarker T, Rabbany MG (2022) Exogenous melatonin reduces water deficit-induced oxidative stress and improves growth performance of Althaea rosea grown on coal mine spoils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(41):61550–61560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14671-2
Sairam RK, Kumutha D, Ezhilmathi K, Chinnusamy V, Meena RC (2009) Waterlogging induced oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme activities in pigeon pea. Biol plant 53:493–504
Sasidharan R, Hartman S, Liu Z, Martopawiro S, Sajeev N, Van Veen H, Voesenek LA (2018) Signal dynamics and interactions during flooding stress. Plant Physiol 176(2):1106–1117. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01232
Seymen M (2021) How does the flooding stress occurring in different harvest times affect the morpho-physiological and biochemical characteristics of spinach? Sci Hortic 275:109713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109713
Seymen M, Yavuz D, Dursun A, Kurtar ES, Türkmen Ö (2019) Identification of drought-tolerant pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) genotypes associated with certain fruit characteristics, seed yield, and quality. Agric Water Manag 221:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.05.009
Shao GC, Lan JJ, Yu SE, Liu N, Guo RQ, She DL (2013) Photosynthesis and growth of winter wheat in response to waterlogging at different growth stages. Photosynt 51:429–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-013-0039-9
Teklić T, Parađiković N, Špoljarević M, Zeljković S, Lončarić Z, Lisjak M (2021) Linking abiotic stress, plant metabolites, biostimulants and functional food. Ann Appl Biol 178(2):169–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/aab.12651
Velikova V, Yordanov I, Edreva A (2000) Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants: protective role of exogenous polyamines. Plant Science 151(1):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(99)00197-1
Wang X, Li F, Chen Z, Yang B, Komatsu S, Zhou S (2021) Proteomic analysis reveals the effects of melatonin on soybean root tips under flooding stress. J Proteomics 232:104064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2020.104064
Witham FH, Blaydes DF, Devlin RM (1971) Experiments in plant physiology. Van Nostrand Reinhold Compan, New York, pp 55–56
Xu W, Cai SY, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Ahammed GJ, Xia XJ, Shi K, Zhou YH, Yu JQ, Reiter RJ, Zhou J (2016) Melatonin enhances thermotolerance by promoting cellular 787 protein protection in tomato plants. J Pineal Res 61:457–469. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12359
Yadav DK, Hemantaranjan A (2017) Mitigating effects of paclobutrazol on flooding stress damage by shifting biochemical and antioxidant defense mechanisms in mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) at pre-flowering stage. Legum Res Int J 40(3):453–461. https://doi.org/10.18805/lr.v0i0.7593
Yakupoğlu G, Köklü Ş, Korkmaz A (2018) Phytomelatonin and Its Roles in Plants. J Agric Nat 21(2):264–276. https://doi.org/10.18016/ksudobil.320180
Yavuz D, Seymen M, Süheri S, Yavuz N, Türkmen Ö, Kurtar ES (2020) How do rootstocks of citron watermelon (Citrullus lanatus var. citroides) affect the yield and quality of watermelon under deficit irrigation? Agric Water Manag 241:106351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106351
Yavuz D, Kılıç E, Seymen M, Dal Y, Kayak N, Kal Ü, Yavuz N (2022) The effect of irrigation water salinity on the morph-physiological and biochemical properties of spinach under deficit irrigation conditions. Sci Hortic 304:111272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111272
Yavuz N, Seymen M, Kal Ü (2021) Impacts of water stress and harvest tıme on physıo-bıochemıcal characterıstıcs of lettuce. Int J Agric Nat Sci 14(2):61–77
Zandalinas SI, Mittler R, Balfagón D, Arbona V, Gómez-Cadenas A (2018) Plant adaptations to the combination of drought and high temperatures. Physiol Plantarum 162(1):2–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12540
Zhang Q, Liu X, Zhang Z, Liu N, Li D, Hu L (2019) Melatonin improved waterlogging tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) by reprogramming polyamine and ethylene metabolism. Front Plant Sci 10:44. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00044
Zheng X, Zhou J, Tan DX, Wang N, Wang L, Shan D, Kong J (2017) Melatonin improves waterlogging tolerance of Malus baccata (Linn.) Borkh. Seedlings by maintaining aerobic respiration, photosynthesis and ROS migration. Front Plant Sci 8:483. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00483
Zuo ZY, Sun LY, Wang TY, Miao P, Zhu XC, Liu SQ, Song FB, Mao HP, Li XN (2017) Melatonin improves the photosynthetic carbon assimilation and antioxidant capacity in wheat exposed to nano-ZnO stress. Molecules 22:1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101727
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. Seymen writing- original draft, data curation, ınvestigation, methodology, validation, B. Çiçek Arı original draft, data curation, Ü. Kal writing-original draft, methodology, ınvestigation, N. Issı formal analysis, data curation, Z. Atakul formal analysis, data curation, D. Yavuz writing-original draft, ınvestigation, formal analysis, data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
M. Seymen, B. Çiçek Arı, Ü. Kal, N. Issı, Z. Atakul and D. Yavuz declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Seymen, M., Çiçek Arı, B., Kal, Ü. et al. Mitigation Effects of Melatonin Applied to Cauliflower Seedlings Under Different Flooding Durations. Gesunde Pflanzen 75, 1031–1045 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00797-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00797-x