Abstract
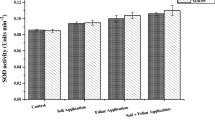
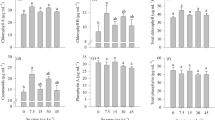
Iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn) are essential nutrients for plant growth and development. Therefore, a pot experiment was conducted to examine the role of Zn and Fe on vegetative growth, photosynthetic pigments, soluble sugars, soluble protein, nitrate reductase (NR), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), catalase (CAT), minerals content, amino acid composition fraction, isozymes, and protein electrophoresis in faba bean plants foliar sprayed with FeSO4 and ZnSO4. The results revealed that foliar spray with 1 or 3 g/L of FeSO4 and ZnSO4 significantly increased all the abovementioned parameters compared to control plants. The activity of esterase increased with increasing concentration of Fe and Zn as compared to control plants. The most pronounced increase was found in plants treated with 3 g/L ZnSO4. Three bands of peroxidase isozyme were exhibited with different densities and intensities in all treatments. Three types of modification were observed in the protein patterns of faba bean leaves. Some protein bands disappeared, while other increased and synthesis of a new set of proteins was induced. It could be concluded that foliar spray with the two concentrations (1 or 3 g/L) of ZnSO4 and FeSO4 helped faba bean plants to overcome the deficiency in these minerals by producing antioxidant enzymes. Improved faba bean growth through adequate Fe and Zn foliar spray is likely a promising strategy to improve Vicia faba plants.
Zusammenfassung
Eisen (Fe) und Zink (Zn) sind essenzielle Nährstoffe für das Wachstum und die Entwicklung von Pflanzen. Es wurde ein Topfexperiment durchgeführt, um die Rolle von Zn und Fe im vegetativen Wachstum, im Gehalt an Photosynthesepigmenten, an löslichen Zuckern und Proteinen, an Nitratreduktase, Ascorbatperoxidase, Katalase und Mineralstoffen sowie an der Zusammensetzung im Aminosäureanteil, im Gehalt an Isoenzymen und in der Proteinelektrophorese von Ackerbohnenpflanzen (Vicia faba) zu untersuchen. Hierfür wurden deren Blätter mit FeSO4 und ZnSO4 besprüht. Die Ergebnisse haben gezeigt, dass das Besprühen der Blätter mit 1 bzw. 3 g/l FeSO4 und ZnSO4 alle o. g. Parameter im Vergleich zu den Kontrollpflanzen signifikant erhöhte. Die Aktivität der Esterase nahm mit steigender Behandlungskonzentration mit Fe und Zn im Vergleich zu den Kontrollpflanzen zu. Der deutlichste Anstieg wurde bei Pflanzen beobachtet, die mit 3 g/l ZnSO4 behandelt wurden. Bei allen Behandlungen wurden drei Peroxidaseisoenzymbänder mit unterschiedlicher Dichte und Intensität ausgebildet. Drei Arten von Veränderungen im Proteinmuster von Ackerbohnenblättern wurden beobachtet. Manche Proteinbänder verschwanden, während andere vermehrt auftraten. Außerdem wurde die Synthese neuer Proteine eingeleitet. Daraus lässt sich schlussfolgern, dass das Besprühen der Blätter mit zwei Konzentrationen (1 und 3 g/l) ZnSO4 und FeSO4 den Ackerbohnenpflanzen dabei hilft, ein Defizit an diesen Mineralstoffen durch Produktion antioxidativer Enzyme zu überwinden. Das Besprühen der Blätter mit Fe und Zn ist wahrscheinlich eine vielversprechende Strategie, um das Wachstum von Vicia faba zu verbessern.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen S, Grimshay HM, Parkinson JA, Quarmby C (1974) Chemical analysis of ecological materials vol. 565. Black well Scientific Publications, Oxford, London
AOAC (2005) Association of official agricultural chemists. In: Hortwitz W, Latimer GW (eds) Official methods of analysis, 16th edn. Association of Official Agricultural Chemists, Washington
Aslam W, Arfan M, Shahid SA, Anwar F, Mahmood Z, Rashid U (2014) Effects of exogenously applied Zn on the growth, yield, chlorophyll contents and nutrient accumulation in wheat line L‑5066. Inter J Chem Bioch Sci 5:11–15
AOAC (1995) Association of official agricultural chemists. – official methods of analysis, 16th edn. AOAC, Washington
Balashouri P (1995) Effect of zinc on germination, growth and pigment content and phytomass of Vigna radiata and Sorghum bicolor. J Ecobiol 7:109–114
Beers RF Jr, Sizer IW (1952) A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem 195:133–140
Briat JF, Curie C, Gaymard F (2007) Iron utilization and metabolism in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:276–282
Broadly MR, White PJ, Hammond JP, Zelko I, Lux A (2007) Zinc in plants. New Phytol 173(4):677–702
Cakmak I (2000) Possible role of zinc in protecting plant cells from damage by reactive oxygen species. New Phytol 146:185–205
Cakmak I (2008) Enrichment of cereal grains with zinc: agronomic or genetic biofortification? Plant Soil 302:1–17
Chaoui A, Jarrar B, Ferjani EE (2004) Effects of cadmium and copper on peroxidase, NADH oxidase and IAA oxidase activities in cell wall, soluble and microsomal membrane fractions of pea roots. J Plant Physiol 161:1225–1234
Charest C, Pan T (1990) Cold acclimation of wheat properties of enzymes involved in proline metabolism. Physiol Plant 80:159–168
Coleman JE (1992) Zinc proteins: enzymes, storage proteins, transcription factors, and replication proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 61:897–946
Cooper T (1977) The tools of biochemistry. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Costa PHA, da Neto ADA, Bezerra MA, Prisco JT, Gomes-Filho E (2005) Antioxidant enzymatic system of two sorghum genotypes differing in salt tolerance. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:353–361
Cuypers A, Vangronsveld J, Clijsters H (2002) Peroxidases in roots and primary leaves of phaseolus vulgaris copper and zinc phytotoxicity: a comparison. J Plant Physiol 159:869–876
Dillon KS, Yagodeen BA, Vernichenko VA (1987) Micronutrients and nitrogen metabolism. II. Effect of micronutrients on the assimilation of ammonium and nitrate ions by maize (Zea mays L). Plant Soil 103:51–55
Dubey RS (1994) Protein synthesis by plants under stressful conditions. In: Pessarakli M (ed) Handbook of plant and crop stress. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, pp 277–299
Dubey RS, Rani M (1990) Influence of NaCl salinity on the behavior of rotease. Amino peptidase and carboxy peptidase in rice seedlings in relation to salt tolerance. Aust J Plant Physiol 17:215–221
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Dwived P (2005) Physiology of abiotic stress in plants. Agrobios, Jodhpur
El-Baz FK, Mohamed AA (2002) Some biochemical parameters to evaluate iron deficiency in bean plants. Phaseolus vulgaris L. Abstract of XI International Symposium on iron nutrition and interaction in plants, Universität Udine. p 45
El-Beltagi HS, Mohamed HI (2013) Alleviation of cadmium toxicity in Pisum sativum L. seedlings by calcium chloride. Not Bot Horti Agrobot 41(1):1–12
El-Gala A, Amberger A (1988) Root exudate and the ability of corn to utilize insoluble sources of iron. J Plant Nutr 11:677–690
El-Habbasha SF, Abd El-Salam MS (2010) Response of two canola varieties (Brassica napus L.) to nitrogen fertilizer levels and zinc foliar application. Int J Acad Res 2(2):60–66
El-Tohamy WA, Khalid A, Kh, El-Abagy HM, Abou-Hussein SD (2009) Essential oil, growth and yield of onion (Allium cepa L.) in response to foliar application of some micronutrients. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 3(1):201–205
Fang WC, Wang JW, Lin CC, Kao CH (2001) Iron induction of lipid peroxidation and effects on antioxidative enzyme activities in rice leaves. Plant Growth Regul 35:75–80
Gaber AM, Mostafa HAM, Ramadan AA (2000) Effect of gamma irradiation of faba beans (Vica faba) plant on its chemical composition, favism causative agent and hormonal level. Egypt J Physiol Sci 24:1–16
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research. John Wiley & Sons, Singapore, p 680
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM (1987) Protection against oxidants in biological system: the superoxide theory of oxygen toxicity. In: Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM (eds) Free radicals biol Med. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 86–123
Hao MD, Wei XR, Dang DH (2003) Effect of long-term applying zinc fertilizer on wheat yield and content of zinc in dry land. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 9(3):377–380
Jaworski EG (1971) Nitrate reductase assay in intact plant tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 43:1274–1279
Jeong J, Connolly EL (2009) Iron uptake mechanisms in plants: functions of the FRO family of ferric reductases. Plant Sci 176:709–714
Jeong J, Guerinot ML (2009) Homing in on iron homeostasis in plants. Trends Plant Sci 14:280–285
Kazemi M (2013) Effects of Zn, Fe and their Combination Treatments on the growth and yield of tomato. Bull Environ Pharmacol Life Sci 3(1):109–114
Khanna S (1998) Regulation of K+ uptake by exogenous amino acids, glycine betaine and abscisic acid in turgid and stressed Raphanus sativus L seedlings. Ph. D. Thesis. H.P. University, Shimla.
Al Khateeb W, Al-Qwasemeh H (2014) Cadmium, copper and zinc toxicity effects on growth, proline content and genetic stability of Solanum nigrum L., a crop wild relative for tomato; comparative study. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 20(1):31–39
Kong J, Dong Y, Xu L, Liu S, Bai X (2014) Effects of foliar application of salicylic acid and nitric oxide in alleviating iron deficiency induced chlorosis of Arachis hypogaea L. Bot Stud 55(9):1–12
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of head bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Larsen AL, Benson WC (1970) Variety specific variants of oxidative enzymes from soybean seeds. Crop Sci 10:493–495
Lowry OH, Rosembrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:267–275
Madan S, Nainawatee H, Jain R, Chowdhury J (1995) Proline and proline metabolising enzymes in in-vitro selected NaCl-tolerant Brassica juncea L. under salt stress. Ann Bot 76:51–57
Mahboobi H, Yucel M, Oktem HA (2002) Nitrate reductase and glutamate delydrogenase activities of resistant and sensitive cultivars of wheat and barley under boron toxicity. J Plant Nutr 25:1829–1837
Manthey JA, Crowley DE (1997) Leaf and root responses to iron deficiency in avocado. J Plant Nutr 20:683–693
Marschner H (1986) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, Orlando
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrient of higher plants, 2nd edn. Academic Press Limited. Harcourt Brace and Company, Publishers, London, pp 347–364
Metzener H, Rau H, Senger H (1965) Untersuchungen zur Synchronisierbarkeit einzelner Pigmentmangel-Mutanten von Chlorella. Planta 65:186
Miller GW, Huang IJ, Welkie GW, Pushmik JC (1995) Function of iron in plants with special emphasis on chloroplasts and photosynthetic activity. In: Abadia J (ed) Iron nutrition in soils and Plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordecht, pp 19–28
Mishra S, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD, Kumar R, Seth CS, Gupta DK (2006) Lead detoxification by coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum L.) involves induction of phytochelatins and antioxidant system in response to its accumulation. Chemosphere 65:1027–1039
Mohamed HI (2011) Molecular and biochemical studies on the effect of gamma rays on lead toxicity in cowpea (Vigna sinensis) plants. Biol Trace Elem Res 144:1205–1218
Van de Mortel JE, Villanueva LA, Schat H, Kwekkeboom J, Coughlan S, Moerland PD, Van Themaat EVL, Koornneef M, Aarts MGM (2006) Large expression differences in genes for iron and zinc homeostasis, stress response, and lignin biosynthesis distinguish roots of Arabidopsis thaliana and the related metal hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Physiol 142:1127–1147
Naghavi F (2014) Effect of zinc and lead toxicity on some physiological parameters of Glycine max L. J Biomed Environ Sci 4(4):192–201
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinash chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Pooladvand S, Ghorbanli M, Farzami Sepehr M (2012) Effect of various levels of iron on morphological, biochemical, and physiological properties of Glycine max var. Pershing. Iran J Plant Physiol 2(4):531–538
Qureshi MI, Abdin MZ, Qadir S, Iqbal M (2007) Lead induced oxidative stress and metabolic alterations in Cassia angustifolia Vahl. Biol Plant 51:121–128
Rengel Z, Hawkesford MJ (1997) Biosynthesis of a 34-Kda polypeptide in the root-cell plasma membrane of a Zn-efficient wheat genotype increases upon Zn deficiency. Aust J Plant Physiol 24:307–315
Robello E, Galatro A, Puntarulo S (2007) Iron role in oxidative metabolism of soybean axes upon growth effect of iron overload. Plant Sci 172:939–947
Rout GR, Das P (2003) Effect of metal toxicity on plant growth and metabolism: I. Zinc. Agronomie 23:3–11
Samreen T, Humaira Shah HU, Ullah S, Javid M (2013) Zinc effect on growth rate, chlorophyll, protein and mineral contents of hydroponically grown mungbeans plant (Vigna radiata). Arab J Chem. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.07.005
Scandalios JG (1964) Tissue specific isozyme variation in maize. Heredity (Edinb) 55:281–285
Schmidt A, Buchout TH (1997) The response of tomato roots (Lycopersicon esculentum mill.) to iron stress: alteration in the pattern of protein synthesis. J Exp Bot 48:1909–1918
Stoyanova Z, Doncheva S (2002) The effect of zinc supply and succinate treatment on plant growth and mineral uptake in pea plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 14(2):1–9
Suzuki K, Itali R, Suzuki K, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa NK, Yoshimura E, Mori S (1998) Formate dehydrogenase, an enzyme of anaerobic metabolism is induced by iron deficiency in barley roots. Plant Physiol 116:725–732
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Mazumdar P, Kumar D, Sharma GD, Sahoo L, Panda SK (2012) Excess copper induced oxidative stress and response of antioxidants in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 53:33–39
Veliksar SG, Toma SI, Zemshman AI (1997) Free amino acids content in grape leaves in relation to iron nutrition. Abstract of 9th International Symposium on Iron Nutrition and Interactions in Plants, Hohenheim University, Stuttgart. pp 42–46
Wang C, Zhang SH, Wang PF, Hou J, Zhang WJ, Li W, Lin ZP (2009) The effect of excess Zn on mineral nutrition and antioxidative response in rapeseed seedlings. Chemosphere 75:1468–1476
Wu G, Kang H, Zhang X, Shao H, Chu L, Ruan C (2010) A critical review on the bio-removal of hazardous heavy metals from contaminated soils: issues, progress, eco-environmental concerns and opportunities. J Hazard Mater 174(1–3):1–8
Zhang J, Wu L, Xi K, Wu S, Li Y, Zhao Y (2006) Effect of foliar application of iron, zinc mixed fertilizers on the content of iron, zinc, soluble sugar and Vitamin C in green pea seeds. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 12(2):245–249
Zhang XW, Dong YJ, Qiu XK, Hu GQ, Wang YH, Wang QH (2012) Exogenous nitric oxide alleviates iron-deficiency chlorosis in peanut growing on calcareous soil. Plant Soil Environ 58:111–120
Zhou ZS, Wang SJ, Yang ZM (2008) Biological detection and analysis of mercury toxicity to alfalfa (Medicago sativa) plants. Chemosphere 70:1500–1509
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, H.I., Elsherbiny, E.A. & Abdelhamid, M.T. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Vicia Faba Plants to Foliar Application of Zinc and Iron. Gesunde Pflanzen 68, 201–212 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-016-0378-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-016-0378-0