Abstract
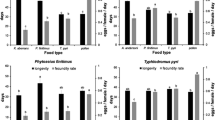
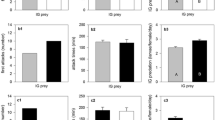
A laboratory study revealed that females of the phytoseiid mite, Amblyseius swirskii Athias-Henriot, fed on protonymphs of their own species or of other predatory mites i.e. Agistemus exsertus Gonzales and Euseius scutalis Athias-Henriot exhibited a marked decline in their fecundity and a shortening in their longevity. Moreover, the rate of predation was also reduced. When A. swirskii females were fed on nymphs of the two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae Koch after having been fed previously on protonymphs of either A. swirskii or A. exsertus increases in the rates of oviposition and consumption were observed, although these rates were lower than those of conspecific females reared continuously on the two-spotted spider mite only.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Awad BA, Reda AS, el-Sawi SA (1992) Effects of artificial and natural diets on the development and reproduction of two phytoseiid mite Amblyseius gossipi and Amblyseius swirskii. Insect Sci Appl 13:441–445
Castagnoli M, Simoni S (1999) Effect of long-term nutritional history on functional and numerical response of Neoseiulus californicus. Exp Appl Acarol 23:217–234
Castagnoli M, Liguori M, Simoni S (2002) Interspecific competition and cannibalism in four phytoseiid species of the Mediterranean area. In: Bernini F, Nannelli R, Nuzzaci G, de Lillo E (eds) Acarid phylogeny and evolution. Adaptations in mites and ticks, Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 321–349
Kabicek J (1995) Development and predation by Amblyseius barkeri on the mite Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Ochrana-Rostlin 31:57–62
McRae IV, Croft BA (1997) Intra- and inter-specific predation by adult females of Metaseiulus occidentalis and Typhlodromus pyri when provisioned with varying densities and ratios of Tetranychus urticae and phytoseiid larvae. Exp Appl Acarol 21:235–245
Rasmy AH, El-Banhawy EM (1975) Biology and predatory efficiency of two phytoseiid mites as affected by long term pollen feeding. Entomophaga 20:93–95
Schausberger P (1999) Juvenile survival and development in Euseius finlandicus, Typhlodromus pyri and Kampimodromus aberrans (Acari: Phytoseiidae) feeding on conspecific and heterospecific immatures. Exp Appl Acarol 23:297–307
Walzer A, Schausberger A (1999a) Cannibalism and interspecific predation in the phytoseiid mites Phytoseiulus persimilis and Neoseiulus californicus: predation rates and effects on production and juvenile development. Biocontrol 43:457–468
Walzer A, Schausberger P (1999b) Predation preference and discrimination between con- and hetero-specific prey by the phytoseiid mites Phytoseiulus persimilis and Neoseiulus californicus. Biocontrol 43:469–478
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasmy, A.H., Abou-El-Ella, G.M. & Hussein, H.E. Cannibalism and interspecific predation of the phytoseiid mite, Amblyseius swirskii . J Pest Sci 77, 23–25 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-003-0022-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-003-0022-5