Abstract
Object
The aim of this study was to demonstrate the feasibility of MR microimaging on a conventional 9.4 T horizontal animal MRI system using commercial available microcoils in combination with only minor modifications to the system, thereby opening this field to a larger community.
Materials and methods
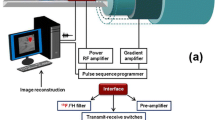
Commercially available RF microcoils designed for high-resolution NMR spectrometers were used in combination with a custom-made probehead. For this purpose, changes within the transmit chain and modifications to the adjustment routines and image acquisition sequences were made, all without requiring expensive hardware. To investigate the extent to which routine operation and high-resolution imaging is possible, the quality of phantom images was analysed. Surface and solenoidal microcoils were characterized with regard to their sensitive volume and signal-to-noise ratio. In addition, the feasibility of using planar microcoils to achieve high-resolution images of living glioma cells labelled with MnCl2 was investigated.
Results
The setup presented in this work allows routine acquisition of high-quality images with high SNR and isotropic resolutions up to 10 μm within an acceptable measurement time.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that MR microscopy can be applied at low cost on animal MR imaging systems, which are in widespread use. The successful imaging of living glioma cells indicates that the technique promises to be a useful tool in biomedical research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SNR:
-
Signal-to-noise ratio
- SNR/mm3 :
-
Signal-to-noise ratio per unit volume
- SGU:
-
Signal generation unit
- FA:
-
Flip angle
- SE:
-
Spin echo
- GE:
-
Gradient echo
- MGE:
-
Multi gradient echo
References
Eccles CD, Callaghan PT (1986) High resolution imaging: the NMR microscope. J Magn Reson 68: 393–398
Aguayo JB, Blackband SJ, Schoeniger J, Mattingly MA, Hintermann M (1986) Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of a single cell. Nature 322: 190–191
Ciobanu L, Pennington CH (2004) 3D micron-scale MRI of single biological cells. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson 25: 138–141
Lee SC, Kim K, Kim J, Lee S, Yi JH, Kim SW, Ha KS, Cheong C (2001) One micrometer resolution NMR microscopy. J Magn Reson 150: 207–213
Grant SC, Buckley DL, Gibbs S, Webb AG, Blackband SJ (2001) MR microscopy of multicomponent diffusion in single neurons. Magn Reson Med 46: 1107–1112
Meadowcroft MD, Connor JR, Smith MB, Yang QX (2009) MRI and histological analysis of beta-amyloid plaques in both human Alzheimer’s disease and APP/PS1 transgenic mice. J Magn Reson Imaging 29: 997–1007
Flint JJ, Lee CH, Hansen B, Fey M, Schmidig D, Bui JD, King MA, Vestergaard-Poulsen P, Blackband SJ (2009) Magnetic resonance microscopy of mammalian neurons. Neuroimage 46: 1037– 1040
Blackwell ML, Farrar CT, Fischl B, Rosen BR (2009) Target-specific contrast agents for magnetic resonance microscopy. Neuroimage 46: 382–393
Hoult DI, Richards RE (1976) The signal-to-noise ratio of the nuclear magnetic resonance experiment. J Magn Reson 24: 71–85
Hoult DI, Lauterbur PC (1979) The sensitivity of the zeugmatographic experiment involving human samples. J Magn Reson 34: 425–433
Ciobanu L, Seeber DA, Pennington CH (2002) 3D MR microscopy with resolution 3.7 μm by 3.3 μm by 3.3 μm. J Magn Reson 158: 178–182
Eroglu S, Gimi B, Friedman BRG, Magin RL (2003) NMR spiral surface microcoils: design, fabrication and imaging. Concept Magn Reson B 17: 1–10
Dechow J, Lanz T, Stumber M, Forchel A, Haase A (2003) Preamplified planar microcoils on GaAs substrates for microspectroscopy. Rev Sci Instrum 74(11): 4855–4857
Baxan N, Rabeson H, Pasquet G, Châteaux J-F, Briguet A, Morin P, Graveron-Demilly D, Fakri-Bouchet L (2008) Limit of detection of cerebral metabolites by localized NMR spectroscopy using microcoils. CR Chim 11: 448–456
Weiger M, Schmidig D, Denoth S, Massin C, Vincent F, Schenkel M, Fey M (2008) NMR microscopy with isotropic resolution of 3.0 μm using dedicated hardware and optimized methods. Concept Magn Reson B 33: 84–93
Anders J, Chiaramonte G, Sangiorgio P, Boero G (2009) A single-chip array of NMR receivers. J Magn Reson 201(2): 239–249
Nema (2001) Determination of Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) in Diagnostic Magnetic Resonance Imaging. NEMA Standards Publication MS 1-2001
Hemmati HD, Nakano I, Lazareff JA, Masterman-Smith M, Geschwind DH, Bronner-Fraser M, Kornblum HI (2003) Cancerous stem cells can arise from pediatric brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 15178–15183
Maclaren JR, Bones PJ, Millane RP, Watts R (2008) MRI with TRELLIS: a novel approach to motion correction. Magn Reson Imaging 26: 474–483
Olson DL, Peck TL, Webb AG, Magin RL, Sweedler JV (1995) High-resolution microcoil 1H-NMR for mass-limited, nanoliter-volume samples. Science 270: 1967–1970
Mispelter J, Lupu M, Briguet A (2006) NMR probeheads for biophysical and biomedical experiments. Imperial College Press, London
Gimi B (2006) Magnetic resonance microscopy: concepts, challenges, and state-of-the-art. Methods Mol Med 124: 59–84
Badilita V, Kratt K, Baxan N, Mohmmadzadeh M, Burger T, Weber H, Elverfeldt DV, Hennig J, Korvink JG, Wallrabe U (2010) On-chip three dimensional microcoils for MRI at the microscale. Lab Chip 10: 1387–1390
Lin YJ, Koretsky AP (1997) Manganese ion enhances T1-weighted MRI during brain activation: an approach to direct imaging of brain function. Magn Reson Med 38: 378–388
Callaghan PT (2006) Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance microscopy. Oxford Science Publications, Oxford
Neuberger T, Webb A (2008) Radiofrequency coils for magnetic resonance microscopy. NMR Biomed 22: 975–981
Webb AG (2004) Optimizing the point spread function in phase-encoded magnetic resonance microscopy. Concept Magn Reson A 22: 25–36
Einstein A (1905) Über die von der molekularkinetischen Theorie der Wärme geforderte Bewegung von in ruhenden Flüssigkeiten suspendierten Teilchen. Ann Phys-Berlin 17: 549–560
Aoki I, Takahashi Y, Chuang K-H, Silva AC, Igarashi T, Tanaka C, Childs RW, Koretsky AP (2006) Cell labeling for magnetic resonance imaging with the T1 agent manganese chloride. NMR Biomed 19: 50–59
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weber, H., Baxan, N., Paul, D. et al. Microcoil-based MRI: feasibility study and cell culture applications using a conventional animal system. Magn Reson Mater Phy 24, 137–145 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-011-0244-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-011-0244-0