Abstract
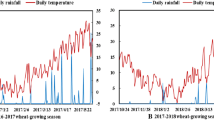
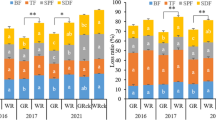
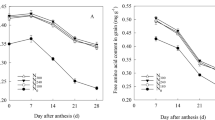
A rational nitrogen (N) application strategy effectively improves grain yield and N use efficiency (NUE) in the production of super rice (Oryza sativa L.). This study explored the effects of different N management strategies on N leaching loss in paddy soil and N use characteristics in different kinds of super hybrid rice cultivars. Two rice cultivars, Zhongzheyou 1 (ZZY1, a super rice of hybrid indica) and Yongyou 12 (YY12, a super rice of hybrid japonica), were chosen as representatives, and four N input levels (CK-0, N135-135, N195-195 and N255-255 kg N ha-1) with three application strategies (P1-60%:30%:10%, P2-50%:30%:20% and P3-40%:30%:30% with split N applied proportionally at the basal, tillering and panicle initiation stages, respectively) were set as treatments. An increase in the total N application rate and split proportion of basal fertilization resulted in higher N loss via leaching during the early growing stage of rice. Improving the split proportion of the second topdressing applied at the panicle initiation stage was beneficial to promoting the total N uptake and the amount of biomass accumulation, which ultimately enhanced the grain yield and NUE. YY12 obtained a 0.4–10.0% higher grain yield and 3.6–18.7% higher N recovery efficiency (REN) than that of ZZY1. Furthermore, YY12 showed greater adaptation at the high N level than did ZZY1, and allocating more N during the mid–late stage had a significant advantage in achieving high yield potential and improving NUE for YY12 compared to ZZY1. Thus, the results suggested that the N255 level with the P3 strategy was the optimal N management strategy that could optimize trade-offs between grain yield and NUE for YY12, while the N195 level with the P2 or P3 strategy was more appropriate for ZZY1.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao YS, Tian YH, Yin B, Zhu ZL (2014) Improving agronomic practices to reduce nitrate leaching from the rice–wheat rotation system. Agric Ecosyst Environ 195:61–67
Cassman KG, Dobermann A, Walters DT (2002) Agro-ecosystems, nitrogen-use efficiency, and nitrogen management. AMBIO A J Hum Environ 31(2):132–140
Cataldo DA, Maroon M, Schrader LE, Youngs VL (1975) Rapid colorimetric determination of nitrate in plant tissue by nitration of salicylic acid. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 6(1):71–80
Chen XP, Cui ZL, Fan MS, Vitousek P, Zhao M, Ma WQ, Wang ZL, Zhang WJ, Yan XY, Yang JC, Deng XP, Gao Q, Zhang Q, Guo SW, Ren J, Li SQ, Ye YL, Wang ZH, Huang JL, Tang QY, Sun YX, Peng XL, Zhang JW, He MR, Zhu YJ, Xue JQ, Wang GL, Wu L, An N, Wu LQ, Ma L, Zhang WF, Zhang FS (2014) Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature 514:486–489
Chen G, Chen Y, Zhao GH, Cheng WD, Guo SW, Zhang HL, Shi WM (2015) Do high nitrogen use efficiency rice cultivars reduce nitrogen losses from paddy fields? Agr Ecosyst Environ 209:26–33
Cheng SH, Cao LY, Zhuang JY, Chen SG, Zhan XD, Fan YY, Zhu DF, Min SK (2007) Super hybrid rice breeding in China: achievements and prospects. J Integr Plant Biol 49(6):805–810
Choudhury ATMA, Kennedy IR (2005) Nitrogen fertilizer losses from rice soils and control of environmental pollution problems. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 36:1625–1639
Das S, Adhya TK (2014) Effect of combine application of organic manure and inorganic fertilizer on methane and nitrous oxide emissions from a tropical flooded soil planted to rice. Geoderma 213:185–192
Deng F, Wang L, Ren WJ, Mei XF (2014) Enhancing nitrogen utilization and soil nitrogen balance in paddy fields by optimizing nitrogen management and using polyaspartic acid urea. Field Crops Res 169:30–38
Fageria NK, Carvalho MCS (2014) Comparison of conventional and polymer coated urea as nitrogen sources for lowland rice production. J Plant Nutr 37:1358–1371
Fu J, Yang JC (2012) Research advances in high-yielding cultivation and physiology of super rice. Rice Sci 19(3):177–184
Fu J, Huang ZH, Wang ZQ, Yang JC, Zhang JH (2011) Pre-anthesis non-structural carbohydrate reserve in the stem enhances the sink strength of inferior spikelets during grain filling of rice. Field Crops Res 123:170–182
Garnett T, Conn V, Kaiser BN (2009) Root based approaches to improving nitrogen use efficiency in plants. Plant, Cell Environ 32:1272–1283
Haefele SM, Jabbar SMA, Siopongco JDLC, Padre AT, Amarante ST, Sta Cruz PC, Cosico WC (2008) Nitrogen use efficiency in selected rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes under different water regimes and nitrogen levels. Field Crops Research 107:137–146
Hofman G, Cleemput OV (2004) Soil and plant nitrogen. 1st version, published by International Fertilizer Industry Association, Paris, France
Jin JY (2012) Changes in the efficiency of fertilizer use in China. J Sci Food Agric 92:1006–1009
Ju XT, Xing GX, Chen XP, Zhang SL, Zhang LJ, Liu XJ, Cui ZL, Yin B, Christie P, Zhu ZL, Zhang FS (2009) Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. PNAS. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0813417106
Kato T, Shinmura D, Taniguchi A (2007) Activities of enzymes for sucrose-starch conversion in developing endosperm of rice and their association with grain filling in extra-heavy panicle types. Plant Prod Sci 10(4):442–450
Kaur B, Kaur G, Asthir B (2017) Biochemical aspects of nitrogen use efficiency: an overview. J Plant Nutr 40(4):506–523
Li XL, Zhang GB, Xu H, Cai ZC, Yagi K (2009) Effect of timing of joint application of hydroquinone and dicyandiamide on nitrous oxide emission from irrigated lowland rice paddy field. Chemosphere 75:1417–1422
Neilen AD, Chen CR, Faggotter SJ, Ellison TL, Burford MA (2016) Biotic and abiotic controls on nitrogen leaching losses into waterways during successive bovine urine application to soil. J Environ Manag 176:11–20
Pan SG, Cao CG, Cai ML, Zhai J, Wang RH, Huang SQ, Gao GL (2009) Effects of nitrogen management on rice nitrogen uptake and nitrogen concentrations in the leachate from rice field (in Chinese with English abstract). J Agro-Environ Sci 28(10):2145–2150
Pan SG, Huang SQ, Zhai J, Wang JP, Cao CG, Cai ML, Zhan M, Tang XR (2012) Effects of N management on yield and N uptake of rice in central China. J Integr Agric 11(12):1993–2000
Peng SB, Buresh RJ, Huang JL, Yang JC, Zou YB, Zhong XH, Wang GH, Zhang FS (2006) Strategies for overcoming low agronomic nitrogen use efficiency in irrigated rice systems in China. Field Crops Res 96:37–47
Peng SB, Buresh RJ, Huang JL, Zhong XH, Zou YB, Yang JC, Wang GH, Liu YY, Hu RF, Tang QY, Cui KH, Zhang FS, Dobermann A (2010) Improving nitrogen fertilization in rice by site-specific N management. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 30:649–656
Santoni S, Bonifacio E, Zanini E (2001) Indophenol blue colorimetric method for measuring cation exchange capacity in sandy soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 32(15&16):2519–2530
Sui B, Feng XM, Tian GL, Hu XY, Shen QR, Guo SW (2013) Optimizing nitrogen supply increases rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency by regulating yield formation factors. Field Crops Research 150:99–107
Sun L, Lu YF, Yu FW, Kronzucker HJ, Shi WM (2016) Biological nitrification inhibition by rice root exudates and its relationship with nitrogen-use efficiency. New Phytol. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14057
Wang F, Peng SB (2017) Yield potential and nitrogen use efficiency of China’s super rice. J Integr Agric 16(5):1000–1008
Wei HY, Zhang HC, Blumwald E, Li HL, Cheng JQ, Dai QG, Huo ZY, Xu K, Guo BW (2016) Different characteristics of high yield formation between inbred japonica super rice and inter-sub-specific hybrid super rice. Field Crops Res 198:179–187
Wei HH, Meng TY, Li C, Xu K, Huo ZY, Wei HY, Guo BW, Zhang HC, Dai QG (2017) Comparisons of grain yield and nutrient accumulation and translocation in high-yielding japonica/indica hybrids, indica hybrids, and japonica conventional varieties. Field Crops Res 204:101–109
Xu GH, Fan XR, Miller AJ (2012) Plant nitrogen assimilation and use efficiency. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:153–182
Yang JC, Zhang JH (2006) Grain filling of cereals under soil drying. New Phytol 169:223–236
Yu WX, Hu XC, Wang XX (2016) Analysis on yield formation and cultivation techniques of Yongyou 12 with yield of 15.44 t/hm2 (in Chinese with English abstract). China Rice 22(4):77–80
Zhang WF, Dou ZX, He P, Ju XT, Powlson D, Chadwick D, Norse D, Lu YL, Zhang Y, Wu L, Chen XP, Cassman KG, Zhang FS (2013a) New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China. PNAS 110:8375–8380
Zhang ZJ, Chu G, Liu LJ, Wang ZQ, Wang XM, Zhang H, Yang JC, Zhang JH (2013b) Mid-season nitrogen application strategies for rice varieties differing in panicle size. Field Crops Research 150:9–18
Zhang BG, Li Q, Cao J, Zhang CY, Song Z, Zhang FS, Chen XP (2017) Reducing nitrogen leaching in a subtropical vegetable system. Agric Ecosyst Environ 241:133–141
Zhou W, Lv TF, Zhang PP, Huang Y, Chen Y, Ren WJ (2016) Regular nitrogen application increases nitrogen utilization efficiency and grain Yield in indica hybrid rice. Agron J 108:1951–1961
Acknowledgements
We thank National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0200801), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872857), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY16C130007), Science and Technology project in Zhejiang province (2015C26005) and Project of State Key Laboratory of Rice Biology (2017ZZKT10404) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Z., Huang, J., Zhu, L. et al. Effects of N application strategies on N leaching loss in paddy soil and N use characteristics in different super hybrid rice cultivars. Paddy Water Environ 18, 27–41 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-019-00762-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-019-00762-x