Abstract
Objective
The aim of the research was to study peptidylarginine deiminase type 4 (PAD4/PADI4) expression and its tumorigenic mechanism in hepatocellular carcinomas.
Methods
Expressions of PADI4 and p53 were investigated in tumors and non-tumor tissues by Western blot in patients with hepatocellular carcinomas. We constructed plasmid of PADI4-Flag and transfected it in Hela cells to investigate the mechanism.
Results
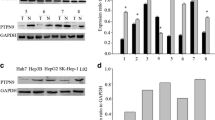
Western blot analysis showed higher PADI4 expression in hepatocellular carcinomas than in the surrounding healthy tissues. Furthermore, by Western blot, we detected decreased p53 levels in the tumor tissues of patients with hepatocellular carcinomas compared to surrounding healthy tissues. In Hela cells transfected with PcDNA3.0-Flag-PADI4 plasmid, the expression of p53 decreased obviously.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that PADI4 elevated in the tissues of hepatocellular carcinomas and induced tumorigenic by down-regulating p53 expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaibori M, Matsui K, Saito T, et al. Risk factors for early death due to recurrence after resection of large hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatogastroenterology, 2008, 55: 2151–2156.
Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F, et al. Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in 1990. Int J Cancer, 1999, 83: 18–29.
Tang ZY. Hepatocellular carcinoma — cause, treatment and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol, 2001, 7: 445–454.
Chang X, Han J. Expression of peptidylarginine deiminase type 4 (PAD4) in various tumors. Mol Carcinog, 2006, 45: 183–196.
Li P, Yao H, Zhang Z, et al. Regulation of p53 target gene expression by peptidylarginine deiminase 4. Mol Cell Biol, 2008, 28: 4745–4758.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin, 2005, 55: 74–108.
Bruix J, Boix L, Sala M, et al. Focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell, 2004, 5: 215–219.
Nakashima K, Hagiwara T, Ishigami A, et al. Molecular characterization of peptidylarginine deiminase in HL-60 cells induced by retinoic acid and 1alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3). J Biol Chem, 1999, 274:27786–27792.
Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, et al. Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Genome Res, 2000, 10: 1546–1560.
Chari NS, Pinaire NL, Thorpe L, et al. The p53 tumor suppressor network in cancer and the therapeutic modulation of cell death. Apoptosis, 2009, 14: 336–347.
Yao H, Li P, Venters BJ, et al. Histone Arg modifications and p53 regulate the expression of OKL38, a mediator of apoptosis. J Biol Chem, 2008, 283: 20060–20068.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Y., Xia, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Expression of PADI4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 8, 453–455 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-009-0058-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-009-0058-y