Abstract
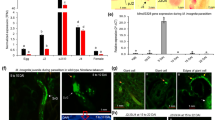
Root-knot nematodes are economically important plant pathogens that cause considerable damage to agricultural crops worldwide. They secrete a range of effector proteins from their specialized gland cells to modify host cell physiology to favour parasitism of the host tissue. A deeper understanding of the roles of effectors in nematode parasitism is necessary to unravel the mysteries of plant–nematode interactions. Herein, mRNAs of Mi-msp-1 (or Mi-vap-1), a gene encoding venom allergen-like effector protein, was localized to the subventral esophageal glands of Meloidogyne incognita. Mi-msp-1 was highly transcribed in the pre- and post-parasitic juveniles of M. incognita, suggesting the association of this effector gene during early stage infection behaviour of nematode. The targeted knockdown of Mi-msp-1 using in vitro RNAi rendered the nematode less successful in penetrating the tomato root. Silencing of Mi-msp-1 also interfered with the development and reproduction of M. incognita in adzuki bean. Intriguingly, induced suppression of Mi-msp-1 significantly altered the transcription of cell-wall-modifying enzymes (CWMEs, effectors involved in early parasitic process) and vice versa in M. incognita, indicating a possible interaction among msp-1 and CWMEs during the early stage of nematode–plant interaction. Our results showed that Mi-msp-1 could be a potential target/choke point for developing anti-nematode strategies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanc-Mathieu R, Perfus-Barbeoch L, Aury JM, Da Rocha M, Gouzy J, Sallet E, Martin-Jimenez C, Bailly-Bechet M, Castagnone-Sereno P, Flot JF, Kozlowski DK, Cazareth J, Couloux A, Da Silva C, Guy J, Kim-Jo YJ, Rancurel C, Schiex T, Abad P, Wincker P, Danchin EGJ (2017) Hybridization and polyploidy enable genomic plasticity without sex in the most devastating plant-parasitic nematodes. PLoS Genet 13:e1006777
Byrd DW, Kirkpatrick T, Barker KR (1983) An improved technique for clearing and staining plant tissues for detection of nematodes. J Nematol 15:142–143
Chi Y, Wang X, Le X, Ju Y, Guan T, Li H (2016) Exposure to double-stranded RNA mediated by tobacco rattle virus leads to transcription up-regulation of effector gene Mi-vap-2 from Meloidogyne incognita and promotion of pathogenicity in progeny. Int J Parasitol 46:105–113
Dalzell JJ, McMaster S, Johnston MJ, Kerr R, Fleming CC, Maule AG (2009) Non-nematode-derived double-stranded RNAs induce profound phenotypic changes in Meloidogyne incognita and Globodera pallida infective juveniles. Int J Parasitol 39:1503–1516
Dash M, Dutta TK, Phani V, Papolu PK, Shivakumara TN, Rao U (2017) RNAi-mediated disruption of neuropeptide genes, nlp-3 and nlp-12, cause multiple behavioral defects in Meloidogyne incognita. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 490:933–940
Ding X, Shields J, Allen R, Hussey R (2000) Molecular cloning and characterisation of a venom allergen AG5-like cDNA from Meloidogyne incognita. Int J Parasitol 30:77–81
Duarte A, Curtis R, Maleita C, Tiago I, Abrantes I (2014) Characterization of the venom allergen-like protein (vap-1) and the fatty acid and retinol binding protein (far-1) genes in Meloidogyne hispanica. Eur J Plant Pathol 139:825–836
Duarte A, Maleita C, Egas C, Abrantes I, Curtis R (2017) Significant effects of RNAi silencing of the venom allergen-like protein (Mhi-vap-1) of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne hispanica in the early events of infection. Plant Pathol 66:1329–1337
Dutta TK, Powers SJ, Kerry BR, Gaur HS, Curtis RHC (2011) Comparison of host recognition, invasion, development and reproduction of Meloidogyne graminicola and M. incognita on rice and tomato. Nematol 13:509–520
Dutta TK, Banakar P, Rao U (2015a) The status of RNAi-based transgenic in plant nematology. Front Microbiol 5:760
Dutta TK, Papolu PK, Banakar P, Choudhary D, Sirohi A, Rao U (2015b) Tomato transgenic plants expressing hairpin construct of a nematode protease gene conferred enhanced resistance to root-knot nematodes. Front Microbiol 6:260
Dutta TK, Banakar P, Rao U (2016) Standardization of an in vitro feeding protocol for rice root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne graminicola. Ind J Nematol 46:73–74
Elling AA (2013) Major emerging problems with minor Meloidogyne species. Phytopathol 103:1092–1102
Gao B, Allen R, Maier T, Davis EL, Baum TJ, Hussey RS (2001) Molecular characterisation and expression of two venom allergen-like protein genes in Heterodera glycines. Int J Parasitol 31:1617–1625
Gheysen G, Mitchum MG (2011) How nematodes manipulate plant development pathways for infection. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:415–421
Haegeman A, Mantelin S, Jones JT, Gheysen G (2012) Functional roles of effectors of plant-parasitic nematodes. Gene 492:19–31
Huang G, Gao B, Maier T, Allen R, Davis EL, Baum TJ, Hussey RS (2003) A profile of putative parasitism genes expressed in the esophageal gland cells of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 16:376–381
Huang G, Dong R, Maier T, Allen R, Davis EL, Baum TJ, Hussey RS (2004) Use of solid-phase subtractive hybridization for the identification of parasitism gene candidates from the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Mol Plant Pathol 5:217–222
Huang G, Allen R, Davis EL, Baum TJ, Hussey RS (2006) Engineering broad root-knot resistance in transgenic plants by RNAi silencing of a conserved and essential root-knot nematode parasitism gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14302–14306
Kang JS, Koh YH, Moon YS, Lee SH (2012) Molecular properties of a venom allergen-like protein suggest a parasitic function in the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Int J Parasitol 42:63–70
Kumari C, Dutta TK, Banakar P, Rao U (2016) Comparing the defence related gene expression changes upon root-knot nematode attack in susceptible versus resistant cultivars of rice. Sci Rep 6:22846
Kumari C, Dutta TK, Chaudhary S, Banakar P, Papolu PK, Rao U (2017) Molecular characterization of FMRFamide-like peptides in Meloidogyne graminicola and analysis of their knockdown effect on nematode infectivity. Gene 619:50–60
Lilley CJ, Davies LJ, Urwin PE (2012) RNA interference in plant parasitic nematodes: a summary of the current status. Parasitology 139:630–640
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lozano-Torres JL, Wilbers RHP, Gawronski P, Boshoven JC, Finkers-Tomczak A, Cordewener JHG, America AH, Overmars HA, Van‘t Klooster JW, Baranowski L, Sobczak M, Muhammad L, van der Hoorn RAL, Schots A, de Wit PJGM, Bakker J, Goverse A, Smant G (2012) Dual disease resistance mediated by the immune receptor Cf-2 in tomato requires a common virulence target of a fungus and a nematode. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:10119–10124
Lozano-Torres JL, Wilbers RHP, Warmerdam S, Finkers-Tomczak A, Diaz-Granados A, van Schaik CC, Helder J, Bakker J, Goverse A, Schots A, Smant G (2014) Apoplastic venom allergen-like proteins of cyst nematodes modulate the activation of basal plant innate immunity by cell surface receptors. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004569
Mantelin S, Thorpe P, Jones JT (2017) Translational biology of nematode effectors. Or, to put it another way, functional analysis of effectors—what’s the point? Nematol 19:251–261
Mitchum MG, Hussey RS, Baum TJ, Wang X, Elling AA, Wubben M, Davis EL (2013) Nematode effector proteins: an emerging paradigm of parasitism. New Phytol 199:879–894
Naito Y, Yamada T, Matsumiya T, Ui-Tei K, Saigo K, Morishita S (2005) dsCheck: highly sensitive off-target search software for double-stranded RNA-mediated RNA interference. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W589–W591
Niu JH, Jian H, Xu J, Chen C, Guo Q, Liu Q, Guo Y (2012) RNAi silencing of the Meloidogyne incognita Rpn7 gene reduces nematode parasitic success. Eur J Plant Pathol 134:131–144
Palomares-Rius JE, Escobar C, Cabrera J, Vovlas A, Castillo P (2017) Anatomical alterations in plant tissues induced by plant-parasitic nematodes. Front Plant Sci 8:1987
Papolu PK, Gantasala NP, Kamaraju D, Banakar P, Sreevathsa R, Rao U (2013) Utility of host delivered RNAi of two FMRF amide like peptides, flp-14 and flp-18, for the management of root knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. PLoS ONE 8:e80603
Rosso M-N, Dubrana MP, Cimbolini N, Jaubert S, Abad P (2005) Application of RNA interference to root-knot nematode genes encoding esophageal gland proteins. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 18:615–620
Rosso M-N, Jones JT, Abad P (2009) RNAi and functional genomics in plant parasitic nematodes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 47:207–232
Satoh H, Hiyama K, Takeda M, Awaya Y, Watanabe K, Ihara Y, Maeda H, Ishioka S, Yamakido M (1996) Telomere shortening in peripheral blood cells was related with aging but not with white blood cell count. Jpn J Hum Genet 41:413–417
Sharp PA (2001) RNA interference—2001. Genes Dev 15:485–490
Shivakumara TN, Papolu PK, Dutta TK, Kamaraju D, Chaudhary S, Rao U (2016) RNAi-induced silencing of an effector confers transcriptional oscillation in another group of effectors in the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. Nematol 18:857–870
Shivakumara TN, Chaudhary S, Kamaraju D, Dutta TK, Papolu PK, Banakar P, Sreevathsa R, Singh B, Manjaiah KM, Rao U (2017) Host-induced silencing of two pharyngeal gland genes conferred transcriptional alteration of cell wall-modifying enzymes of Meloidogyne incognita vis-à-vis perturbed nematode infectivity in eggplant. Front Plant Sci 8:473
Shivakumara TN, Dutta TK, Mandal A, Rao U (2018) Estimation of lipid reserves in different life stages of Meloidogyne incognita using image analysis of Nile Red-stained nematodes. Nematology. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685411-00003212
Sindhu AS, Maier TR, Mitchum MG, Hussey RS, Davis EL, Baum TJ (2009) Effective and specific in planta RNAi in cyst nematodes: expression interference of four parasitism genes reduces parasitic success. J Exp Bot 60:315–324
Tian XX, Pang JC, Zheng J, Chen J, To SST, Ng HK (2002) Antisense epidermal growth factor receptor RNA transfection in human glioblastoma cells down-regulates telomerase activity and telomere length. Br J Cancer 86:1328
Urwin PE, Lilley CJ, Atkinson HJ (2002) Ingestion of double-stranded RNA by preparasitic juvenile cyst nematodes leads to RNA interference. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 15:747–752
Valaperta R, Sansone V, Lombardi F, Verdelli C, Colombo A, Valisi M, Brigonzi E, Costa E, Meola G (2013) Identification and characterization of DM1 patients by a new diagnostic certified assay: neuromuscular and cardiac assessments. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/958510
Wang X, Li H, Hu Y, Fu P, Xu J (2007) Molecular cloning and analysis of a new venom allergen-like protein gene from the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Exp Parasitol 117:133–140
Whitehead AG, Hemming JR (1965) A comparison of some quantitative methods of extracting small vermiform nematodes from soil. Ann Appl Biol 55:25–38
Yamada M, Ishii M, Miura M, Sato S, Kanno A, Ohori H, Toyota T (1993) Three distinct Southern blot hybridization patterns of HBV-DNA in the sera of HBV carriers. Tohoku J Exp Med 170:219–228
Yamamura Y, Shim WB (2008) The coiled-coil protein-binding motif in Fusarium verticillioides Fsr1 is essential for maize stalk rot virulence. Microbiology 154:1637–1645
Yan X, Cheng XY, Wang YS, Luo J, Mao ZC, Ferris VR, Xie BY (2012) Comparative transcriptomics of two pathogenic pinewood nematodes yields insights into parasitic adaptation to life on pine hosts. Gene 505:81–90
Acknowledgements
Ph.D. student SC acknowledges her co-advisor Dr. Vishakha Raina, School of Biotechnology, KIIT, Bhubaneswar, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, S., Dutta, T.K., Shivakumara, T.N. et al. RNAi of esophageal gland-specific gene Mi-msp-1 alters early stage infection behaviour of root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. J Gen Plant Pathol 85, 232–242 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-019-00837-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-019-00837-x