Abstract
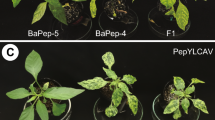
Two recessive resistance genes against Clover yellow vein virus (ClYVV), cyv1 and cyv2, have been previously reported. We recently screened resistant peas from a separate set of pea lines and classified them into two groups according to their distinct modes of resistance. We later revealed that one group carries cyv2, encoding eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E), in linkage group (LG) VI. We explored the possibility that the resistance gene, tentatively designated non-cyv2, that confers resistance to the other group, was actually cyv1. We found that PI 236493, which carries cyv1, had restricted cell-to-cell movement of ClYVV similar to that in non-cyv2 peas including PI 429853. PI 429853 was crossed with susceptible line PI 250438. Mapping of F2 progeny revealed that non-cyv2 was 4 cM from the simple sequence repeat marker AB40, whose loci are close to cyv1, mo, and sbm-2 mapped in LG II, which mediates resistance to other potyviruses. Moreover, PI 429853 crossed with PI 236493 produced F1 progeny resistant to ClYVV, raising the possibility that non-cyv2 is allelic to cyv1. Because mo was previously mapped with eIF(iso)4E in LG II, we examined the possibility that non-cyv2, cyv1, and mo encoded eIF(iso)4E. However, there was no difference in the nucleotide sequence of the eIF(iso)4E-coding region between susceptible and resistant pea lines. The eIF(iso)4E gene was equivalently expressed in both PI 429853 and PI 250438 before and after ClYVV infection. Our results suggest that these resistance genes are unlikely to encode eIF(iso)4E on LG II.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Razzak A, Guiraud T, Peypelut M, Walter J, Houvenaghel MC, Candresse T, Le Gall O, German-Retana S (2009) Involvement of the cylindrical inclusion (CI) protein in the overcoming of an eIF4E-mediated resistance against Lettuce mosaic potyvirus. Mol Plant Pathol 10:109–113
Andrade M, Sato M, Uyeda I (2007) Two resistance modes to Clover yellow vein virus in pea characterized by a green fluorescent protein-tagged virus. Phytopathology 97:544–550
Andrade M, Abe Y, Nakahara KS, Uyeda I (2009) The cyv-2 resistance to Clover yellow vein virus in pea is controlled by the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. J Gen Plant Pathol 75:241–249
Atsumi G, Kagaya U, Kitazawa H, Nakahara KS, Uyeda I (2009) Activation of the salicylic acid signaling pathway enhances Clover yellow vein virus virulence in susceptible pea cultivars. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22:166–175
Aubert G, Morin J, Jacquin F, Loridon K, Quillet MC, Petit A, Rameau C, Lejeune-Hénaut I, Huguet T, Burstin J (2006) Functional mapping in pea, as an aid to the candidate gene selection and for investigating synteny with the model legume Medicago truncatula. Theor Appl Genet 112:1024–1041
Bruun-Rasmussen M, Møller IS, Tulinius G, Hansen JKR, Lund OS, Johansen IE (2007) The same allele of translation initiation factor 4E mediates resistance against two Potyvirus spp. in Pisum sativum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:1075–1082
Diaz-Pendon J, Truniger V, Nieto C, Garcia-Mas J, Bendahmane A, Aranda MA (2004) Advances in understanding recessive resistance to plant viruses. Mol Plant Pathol 5:223–233
Ellis THN, Posyer SJ (2002) An integrated and comparative view of pea genetic and cytogenetic maps. New Phytol 153:17–25
Gao Z, Eyers S, Thomas C, Ellis N, Maule AJ (2004a) Identification of markers tightly linked to sbm recessive genes for resistance to Pea seed-borne mosaic virus. Theor Appl Genet 109:488–494
Gao Z, Johansen E, Eyers S, Thomas CL, Ellis THN, Maule AJ (2004b) The potyvirus recessive resistance gene, sbm1, identifies a novel role for translation initiation factor eIF4E in cell-to-cell trafficking. Plant J 40:376–385
German-Retana S, Walter J, Doublet B, Roudet-Tavert G, Nicaise V, Lecampion C, Houvenaghel MC, Robaglia C, Michon T, Le Gall O (2008) Mutational analysis of plant cap-binding protein eIF4E reveals key amino acids involved in biochemical functions and potyvirus infection. J Virol 82:7601–7612
Harrison CJ, Mould RM, Leech MJ, Johnson SA, Turner L, Schreck SL, Baird KM, Jack PL, Rawsthorne S, Hedley CL, Wang TL (2000) The rug3 locus of pea encodes plastidial phosphoglucomutase. Plant Physiol 122:1187–1192
Hjulsager CK, Olsen BS, Jensen DMK, Cordea MI, Krath BN, Johansen IE, Lund OS (2006) Multiple determinants in the coding region of Pea seed-borne mosaic virus P3 are involved in virulence against sbm-2 resistance. Virology 355:52–61
Hwang J, Li J, Liu WY, An SJ, Cho H, Her NH, Yeam I, Kim D, Kang BC (2009) Double mutations in eIF4E and eIFiso4E confer recessive resistance to Chilli veinal mottle virus in pepper. Mol Cells 27:329–336
Johansen IE, Lund OS, Hjulsager CK, Laursen J (2001) Recessive resistance in Pisum sativum and potyvirus pathotype resolved in a gene-for-cistron correspondence between host and virus. J Virol 75:6609–6614
Kang BC, Yeam I, Frantz JD, Murphy JF, Jahn MM (2005a) The pvr1 locus in Capsicum encodes a translation initiation factor eIF4E that interacts with Tobacco etch virus VPg. Plant J 42:392–405
Kang BC, Yeam I, Jahn MM (2005b) Genetics of plant virus resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43:581–621
Kanyuka K, McGrann G, Alhudaib K, Hariri D, Adams MJ (2004) Biological and sequence analysis of a novel European isolate of Barley mild mosaic virus that overcomes the barley rym5 resistance gene. Arch Virol 149:1469–1480
Loridon K, McPhee K, Morin J, Dubreuil P, Pilet-Nayel ML, Aubert G, Rameau C, Baranger A, Coyne C, Lejeune-Hènaut I, Burstin J (2005) Microsatellite marker polymorphism and mapping in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Theor Appl Genet 111:1022–1031
Manly KF, Cudmore RH Jr, Meer JM (2001) Map manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm Genome 12:930–932
Nakahara KS, Shimada R, Choi SH, Yamamoto H, Shao J, Uyeda I (2010) Involvement of the P1 cistron in overcoming eIF4E-mediated recessive resistance against Clover yellow vein virus in pea. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 23:1460–1469
Nicaise V, German-Retana S, Sanjuán R, Dubrana MP, Mazier M, Maisonneuve B, Candresse T, Caranta C, Le Gall O (2003) The eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E controls lettuce susceptibility to the Potyvirus Lettuce mosaic virus. Plant Physiol 132:1272–1282
Nicaise V, Gallois JL, Chafiai F, Allen LM, Schurdi-Levraud V, Browning KS, Candresse T, Caranta C, Le Gall O, German-Retana S (2007) Coordinated and selective recruitment of eIF4E and eIF4G factors for potyvirus infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 581:1041–1046
Provvidenti R (1987) Inheritance of resistance to clover yellow vein virus in Pisum sativum. J Hered 78:126–128
Provvidenti R, Hampton RO (1991) Chromosomal distribution of genes for resistance to seven potyviruses in Pisum sativum. Pisum Genet 23:26–28
Ravelo G, Kagaya U, Inukai T, Sato M, Uyeda I (2007) Genetic analysis of lethal tip necrosis induced by Clover yellow vein virus infection in pea. J Gen Plant Pathol 73:59–65
Ruffel S, Dussault MH, Palloix A, Moury B, Bendahmane A, Robaglia C, Caranta C (2002) A natural recessive resistance gene against potato virus Y in pepper corresponds to the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E). Plant J 32:1067–1075
Ruffel S, Gallois JL, Moury B, Robaglia C, Palloix A, Caranta C (2006) Simultaneous mutations in translation initiation factors eIF4E and eIF(iso)4E are required to prevent pepper veinal mottle virus infection of pepper. J Gen Virol 87:2089–2098
Sato M, Masuta C, Uyeda I (2003) Natural resistance to Clover yellow vein virus in beans controlled by a single recessive locus. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:994–1002
Sato M, Nakahara KS, Yoshii M, Ishikawa M, Uyeda I (2005) Selective involvement of members of the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E family in the infection of Arabidopsis thaliana by potyviruses. FEBS Lett 579:1167–1171
Stein N, Perovic D, Kumlehn J, Pellio B, Stracke S, Streng S, Ordon F, Graner A (2005) The eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E confers multiallelic recessive Bymovirus resistance in Hordeum vulgare (L.). Plant J 42:912–922
Truniger V, Aranda MA (2009) Recessive resistance to plant viruses. Adv Virus Res 75:119–159
Weeden NF, Provvidenti R, Marx GA (1984) An isozyme marker for resistance to bean yellow mosaic virus in Pisum sativum. J Hered 75:411–412
Weeden NF, Ellis THN, Timmereman-Vaughan GM, Swiecicki WK, Rozov SM, Berdnikov VA (1998) A consensus linkage map for Pisum sativum. Pisum Genet 30:1–4
Acknowledgments
We thank H. Ishii for excellent laboratory assistance. This work was supported by JSPS/MEXT KAKENHI (18108001, 20688002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, S.H., Nakahara, K.S., Andrade, M. et al. Characterization of the recessive resistance gene cyv1 of Pisum sativum against Clover yellow vein virus . J Gen Plant Pathol 78, 269–276 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-012-0383-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-012-0383-9