Abstract
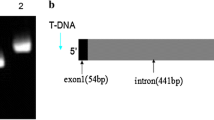
We selected a reduced-pathogenicity mutant of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici, a tomato wilt pathogen, from the transformants generated by restriction enzyme-mediated integration (REMI) transformation. The gene tagged with the plasmid in the mutant was predicted to encode a protein of 321 amino acids and was designated FPD1. Homology search showed its partial similarity to a chloride conductance regulatory protein of Xenopus, suggesting that FPD1 is a transmembrane protein. Although the function of FPD1 has not been identified, it does participate in the pathogenicity of F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici because FPD1-deficient mutants reproduced the reduced pathogenicity on tomato.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence data reported are available in the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases under the accession number AB110097
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawabe, M., Mizutani, K., Yoshida, T. et al. Cloning of the pathogenicity-related gene FPD1 in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici . J Gen Plant Pathol 70, 16–20 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-003-0089-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-003-0089-0