Abstract
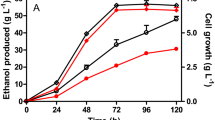
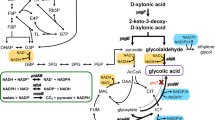
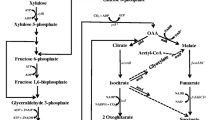
Previously, a native homoethanol pathway was engineered in Escherichia coli B by deletions of competing pathway genes and anaerobic expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH encoded by aceEF-lpd). The resulting ethanol pathway involves glycolysis, PDH, and alcohol dehydrogenase (AdhE). The E. coli B-derived ethanologenic strain SZ420 was then further improved for ethanol tolerance (up to 40 g l−1 ethanol) through adaptive evolution. However, the resulting ethanol tolerant mutant, SZ470, was still unable to complete fermentation of 75 g l−1 xylose, even though the theoretical maximum ethanol titer would have been less than 40 g l−1 should the fermentation have reached completion. In this study, the cra (encoding for a catabolite repressor activator) and the HSR2 region of rng (encoding for RNase G) were deleted from SZ470 in order to improve xylose fermentation. Deletion of the HSR2 domain resulted in significantly increased mRNA levels (47-fold to 409-fold) of multiple glycolytic genes (pgi, tpiA, gapA, eno), as well as the engineered ethanol pathway genes (aceEF-lpd, adhE) and the transcriptional regulator Fnr (fnr). The higher adhE mRNA level resulted in increased AdhE activity (>twofold). Although not measured, the increase of other mRNAs might also enhance expressions of their encoding proteins. The increased enzymes would then enable the resulting strain, RM10, to achieve increased cell growth and complete fermentation of 75 g l−1 xylose with an 84% improved ethanol titer (35 g l−1), compared to that (19 g l−1) obtained by the parent, SZ470. However, deletion of cra resulted in a negative impact on cell growth and xylose fermentation, suggesting that Cra is important for long-term fermentative cell growth.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aristarkhov A, Mikulskis A, Belasco JG, Lin ECC (1996) Translation of the adhE transcript to produce ethanol dehydrogenase requires RNase III cleavage in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 178(14):4327–4332
Buckley M, Wall J (2006) Microbial energy conversion. A report from the American Academy of Microbiology, Washington, DC
Chen K, Iverson AG, Garza EA, Grayburn WS, Zhou S (2010) Metabolic evolution of non-transgenic Escherichia coli SZ420 for enhanced homoethanol fermentation from xylose. Biotechnol Lett 32:87–96
Conway T, Sewell GW, Osman YA, Ingram LO (1987) Cloning and sequencing of the alcohol dehydrogenase II gene from Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 169:2591–2597
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6640–6645
Deana A, Belasco JG (2004) The function of RNase G in Escherichia coli is constrained by its amino and carboxyl termini. Molecular Microbiol 51(4):1205–1217
Dien BS, Cotta MA, Jeffries TW (2003) Bacteria engineered for fuel ethanol production: current status. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63(3):258–266
Garrey SM, Blech M, Riffell JL, Hankins JS, Stickney LM, Diver M, Hsu YR, Kunanithy V, Mackie GA (2009) Substrate binding and active site residues in RNase E and G: role of the 5′-sensor. J Biol Chem 284(46):31843–31850
Hahn-Hagerdal B, Karhumaa K, Fonseca C, Spencer-Martins I, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2007) Towards industrial pentose-fermenting yeast strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:937–953
Ho NMY, Chen Z, Brainard AP (1998) Genetically engineered Saccharomyces yeast capable of effective co-fermentation of glucose and xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1852–1859
Ingram LO, Aldrich HC, Borges AC, Causey TB, Martinez A, Morales F, Saleh A, Yomano LP, York SW, Zaldivar J, Zhou S (1999) Enteric bacterial catalysts for fuel ethanol production. Biotechnol Prog 15:855–866
Jeffries TW (2006) Engineering yeasts for xylose metabolism. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17(3):320–326
Jiang X, Diwa A, Belasco JG (2000) Regions of RNase E important for 5′-end-dependent RNA cleavage and autoregulated synthesis. J Bacteriol 182(9):2468–2475
Jiang X, Belasco JG (2004) Catalytic activation of multimeric RNase E and RNase G by 5′-monophosphorylated RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(25):9211–9216
Jourdan SS, McDowall KJ (2008) Sensing of 5′ monophosphate by Escherichia coli RNase G can significantly enhance association with RNA and stimulate the decay of functional mRNA transcripts in vivo. Molecular Microbiol 67(1):102–115
Jourdan SS, Kime L, Mcdowall KJ (2010) The sequence of sites recognized by a member of the RNase E/G family can control the maximal rate of cleavage, while a 5′-monophosphorylated end appears to function cooperatively in mediating RNA binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391:879–883
Kaga N, Umitsuki G, Clark DP, Nagai K, Wachi M (2002) Extensive overproduction of the AdhE protein by rng mutations depends on mutations in the cra gene or in the Cra-box of the adhE promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 295:92–97
Kaga N, Umitsuki G, Nagai K, Wachi M (2002) RNase G-dependent degradation of the eno mRNA encoding a glycolysis enzyme enolase in Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66(10):2216–2220
Kim Y, Ingram LO, Shanmugam KT (2007) Construction of an Escherichia coli K-12 mutant for homoethanologenic fermentation of glucose and xylose without foreign genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(6):1766–1771
Kim Y, Ingram LO, Shanmugam KT (2008) Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase mutation alters the NADH sensitivity of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 190(11):3851–3858
Kuype M, Hartogg MM, Toirkens MJ, Almering MJ, Winkle AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2005) Metabolic engineering of a xylose-isomerase-expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for rapid anaerobic xylose fermentation. YEMS Yeast Res 5(4–5):399–409
Leonardo MR, Cunningham PR, Clark DP (1993) Anaerobic regulation of the adhE gene, encoding the fermentative alcohol dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 175(3):870–878
Li Z, Pandit S, Deutscher MP (1999) RNase G (CalfA protein) and RNase E are both required for the 5′ maturation of 16S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J 18(10):2878–2885
Lynd LR, Wyman CE, Gerngross TU (1999) Biocommodity engineering. Biotechnol Prog 75:777–793
Membrillo-Hernandez J, Lin ECC (1999) Regulation of expression of the adhE gene, encoding ethanol oxidoreductase in Escherichia coli: transcription from a downstream promoter and regulation by Fnr and RpoS. J Bacteriol 181(24):7571–7579
Mikulskis A, Aristarkhov A, Lin ECC (1997) Regulation of expression of the ethanol dehydrogenase gene (adhE) in Escherichia coli by catabolite repressor activator protein Cra. J Bacteriol 179(22):7129–7134
Miller JH (1992) A short course in bacterial genetics: a laboratory manual and handbook for Escherichia coli and related bacteria. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Neale AD, Scopes RK, Kelley JM, Wettenhall REH (1986) The two alcohol dehydrogenase of Zymomonas mobilis. Eur J Biochem 154:119–124
Nishino K, Inazumi Y, Yamaguchi A (2003) Global analysis of genes regulated by EvgA of the two-component regulatory system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 185:2667–2672
Perrenoud A, Sauer U (2005) Impact of global transcriptional regulation by AraA, ArcB, Cra, Crp, Cya, Fnr, and Mlc on glucose catabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 187(9):3171–3179
Popsai G, Koob MD, Kirkpatrick HA, Blattner FC (1997) Versatile insertion plasmids for targeted genome manipulations in bacteria: isolation, deletion, and rescue of the pathogenicity island LEE of the Escherichia coli O157:H7 genome. J Bacteriol 179:4219–4226
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawets S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods on molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Shin E, Go H, Yeom J, Won M, Bae J, Han SH, Han K, Lee Y, Ha N, Moore CJ, Sohlberg B, Cohen SN, Lee K (2008) Identification of amino acid residues in the catalytic domain of RNase E essential for survival of Escherichia coli: functional analysis of DNase I subdomain. Genetics 179:1871–1879
Tock MR, Walsh AP, Carroll G, McDowall KJ (2000) The CafA protein required for the 5′-maturation of 16S rRNA is a 5′-end-dependent ribonuclease that has context-dependent broad sequence specificity. J Biol Chem 275(2):8726–8732
Trinh CT, Unrean P, Srienc F (2008) Minimal Escherichia coli cell for the most efficient production of ethanol from hexoses and pentoses. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(12):3634–3643
Umitsuki G, Wachi M, Takada A, Hikichi T, Nagai K (2001) Involvement of RNase G in in vivo mRNA metabolism in Escherichia coli. Genes Cells 6:403–410
Wachi M, Umitsuki G, Shimizu N, Takada A, Nagai K (1999) Escherichia coli cafA gene encodes a novel RNase, designated as RNase G, involved in processing of the 5′ end of 16S rRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 259:483–488
Wachi M, Kaga N, Umitsuki G, Clark DP, Nagai K (2001) A novel RNase G mutant that is defective in degradation of adhE mRNA but proficient in the processing of 16S rRNA precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:1301–1306
Wang Y, Manow R, Finan C, Wang J, Garza E, Zhou S (2011) Adaptive evolution of non-transgenic Escherichia coli KC01 for improved ethanol tolerance and homoethanol fermentation from xylose. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38(9):1371–1377
Wang Q, Ou MS, Kim Y, Ingram LO, Shanmugam KT (2010) Metabolic flux control at the pyruvate node in an anaerobic Escherichia coli strain with an active pyruvate dehydrogenase. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(7):2107–2114
Yomano LP, York S, Zhou S, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO (2008) Re-engineering Escherichia coli for ethanol production. Biotechnol Lett 30(12):2097–2103
Zhang M, Eddy C, Deanda K, Finkelstein M, Picataggio S (1995) Metabolic engineering a pentose pathway in ethanologenic Zymomonas mobilis. Science 267:240–243
Zhou S, Iverson AG, Grayburn WS (2008) Engineering a native homoethanol pathway in Escherichia coli B for ethanol production. Biotechnol Lett 30:335–342
Zhou S, Iverson AG, Grayburn WS (2010) Doubling the catabolic reducing power (NADH) output of Escherichia coli fermentation for production of reduced products. Biotechnol Prog 26(1):45–51
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a summer artistry and research grant, biological research incentive fund of Northern Illinois University, a grant from the China National Natural Science Foundation (NSFC31070094), a grant from the Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2011CDA008) and the Chutian Scholar Program, P.R. China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manow, R., Wang, J., Wang, Y. et al. Partial deletion of rng (RNase G)-enhanced homoethanol fermentation of xylose by the non-transgenic Escherichia coli RM10. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 977–985 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1100-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1100-6