Abstract
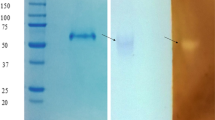
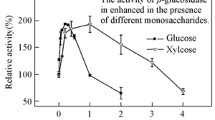
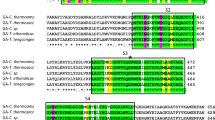
A glucoamylase from Aspergillus niveus was produced by submerged fermentation in Khanna medium, initial pH 6.5 for 72 h, at 40°C. The enzyme was purified by DEAE-Fractogel and Concanavalin A-Sepharose chromatography. The enzyme showed 11% carbohydrate content, an isoelectric point of 3.8 and a molecular mass of 77 and 76 kDa estimated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis or Bio-Sil-Sec-400 gel filtration, respectively. The pH optimum was 5.0–5.5, and the enzyme remained stable for at least 2 h in the pH range of 4.0–9.5. The temperature optimum was 65°C and retained 100% activity after 240 min at 60°C. The glucoamylase remained completely active in the presence of 10% methanol and acetone. After 120 min hydrolysis of starch, glucose was the unique product formed, confirming that the enzyme was a glucoamylase (1,4-alpha-d-glucan glucohydrolase). The K m was calculated as 0.32 mg ml−1. Circular dichroism spectroscopy estimated a secondary structure content of 33% α-helix, 17% β-sheet and 50% random structure, which is similar to that observed in the crystal structures of glucoamylases from other Aspergillus species. The tryptic peptide sequence analysis showed similarity with glucoamylases from A. niger, A. kawachi, A. ficcum, A. terreus, A. awamori and A. shirousami. We conclude that the reported properties, such as solvent, pH and temperature stabilities, make A. niveus glucoamylase a potentially attractive enzyme for biotechnological applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleshin AE, Hoffman C, Firsov LM, Honzatko RB (1994) Refined crystal structures of glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori var. X100. J Mol Biol 238:575–591
Ali S, Hossain Z (1991) Characteristics for glucoamylase from Aspergillus terreus. J Appl Bacteriol 71:144–146
Andrade MA, Chacon P, Merelo JJ, Moran F (1993) Evaluation of secondary structure of proteins from UV circular dichroism spectra using an unsupervised learning neural network. Protein Eng Des Sel 6:383–390
Aquino AC, Jorge AJ, Terenzi HF, Polizeli MLTM (2003) Studies on thermostable α-amylase from thermophilic fungus Scytalidium thermophilum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:323–328
Davis BJ (1964) Disc electrophoresis II. Methods and application to human serum proteins. Ann NY Acad Sci 121:404–427
Deléage G, Geourjon C (1993) An interactive graphic program for calculating the secondary structures content of proteins from circular dichroism spectrum. Comput Appl Biosci 9:197–199
Doukyu N, Aono R (2001) Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of a gene encoding an organic solvent and detergent-tolerant cholesterol oxidase of Burkholderia cepacia strain ST-200. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:146–152
Doukyu N, Aono R, Kuwahara H (2003) Isolation of Paenibacillus illinoisensis that produces cyclodextrin glucanotransferase resistant to organic solvents. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:334–340
Doukyu N, Yamagishi W, Kuwahara H, Ogino H, Furuki N (2007) Purification and characterization of a maltooligosaccharide-forming amylase that improves product selectivity in water-miscible organic solvents, from dimethylsulfoxide-tolerant Brachybacterium sp. strain LB25. Extremophiles 11(6):781–788
Fukushima T, Mizuki T, Echigo A, Inoue A, Usami R (2005) Organic solvent tolerance of halophilic α-amylase from a Haloarchaeon Haloarcula sp. Strain S-1. Extremophiles 9:85–89
Ghosh AB, Chatterjee B, Das A (1991) Purification and characterization of glucoamylases of Aspergillus terreus NA-170 mutant. J Appl Bacteriol 71:162–169
Imai Y, Sukura M, Masamoto M, Nagayasu K (1994) Glucoamylase production of Aspergillus oryzae in fed-batch culture using a statistical regression model. J Ferment Bioeng 78:310–314
Jafari-Aghdam J, Khajeh K, Ranjbar B, Netmat-Gorgani M (2005) Deglycosylation of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger: effect on structure, activity and stability. Biochim Biophys Acta 1750:61–68
Kaur P, Satyanarayana T (2004) Production and saccharification by a thermostable and neutral glucoamylase of a thermophilic mould Thermomucor indicae-seudaticae. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:419–425
Kelly CT, Giblin M, Forgarty WM (1986) Resolution, purification and characterization of two extracellular glucohydrolases, α-glucosidase and maltase of Bacillus licheniformis. Can J Microbiol 32:342–347
Khanna P, Sundari SS, Kumar NJ (1995) Production, isolation and partial purification of xylanase from Aspergillus sp. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:242–243
Klibanov A (1997) Why are enzymes less active in organic solvents than in water? Trends Biotechnol 15:97–101
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lee CK, Le QT, Kim YH, Shim JH, Lee SJ, Park JH, Lee KP, Song SH, Auh JH, Lee SJ, Park KH (2008) Enzymatic synthesis and properties of highly branched rice starch amylose and amylopectin cluster. J Agric Food Chem 56(1):126–131
Leone FA, Baranauskas JA, Ciancaglini P (1995) Enzyplot: a microcomputer assistant program for teaching enzyme kinectis. Biochem Educ 23:35–37
Lowry O, Rosebrough N, Farr A, Randall R (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Meagher MM, Nikolov ZL, Reilly PJ (1989) Subsite mapping of Aspergillus niger glucoamylases I and II with malto- and isomaltooligosaccharides. Biotechnol Bioeng 34:681–688
Michelin M, Ruller R, Ward RJ, Moraes LAB, Jorge JA, Terenzi HF, Polizeli MLTM (2008) Purification and biochemical characterization of a thermostable extracellular glucoamylase produced by the thermotolerant fungus Paecilomyces variotii. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:17–25
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Norouzian D, Azim A, Jeno MS, Murrauy MY (2006) Fungal glucoamylases, review. Biotechnol Adv 44:80–85
Ogino H, Miyamoto K, Ishikawa H (1994) Organic-solvent-tolerant bacterium which secrets organic-solvent-stable lipolytic enzyme. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1929–1932
Ogino H, Yasui K, Shinotani T, Ishihara T, Ishikawa H (1995) Organic-solvent-tolerant bacterium which secrets organic-solvent-stable proteolytic enzyme. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4258–4262
Pandey A, Nigam P, Soccol CR, Soccol VT, Singh D, Mohan R (2000) Advances in microbial amylases. Review. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 31:135–152
Silva TM, Attili-Angelis D, Carvalho AFA, Da Silva R, Gomes E (2005) Production of sacharogenic and dextrinogenic amylases by Rhizomucor pusillus A 13.36. J Microbiol 43:561–568
Soni KS, Gupta KJ (2003) A solid state fermentation based bacterial α-amylase and fungal glucoamylase system and its suitability for the hydrolysis of wheat starch. Process Biochem 39:185–192
Sorimachi K, Jacks AJ, Le Gal-Coëffet MF, Williamson G, Archer DB, Williamson MP (1996) Solution structure of the granular starch binding domain of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol 259:970–987
Spinelli BBL, Polizeli MLTM, Jorge AJ, Terenzi HF (1996) Biochemical characterization of glucoamylase from the hyper producer exo-1 mutant strain of Neurospora crassa. FEMS Microbiol Lett 138:173–177
Sukura E, Doelle HW (1989) A one step process for the production of single cell protein and amyloglucosidase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 30:135–140
Suresh C, Dubey AK, Srikanta S, Kumar US (1999) Characterization of starch hydrolysing of Aspergillus niger. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:673–675
Vihinen M, Mantsala P (1989) Microbial amylolytic enzymes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 24(4):329–418
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) and Conselho de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPQ). J. A. Jorge, H. F. Terenzi and M. L. T. M. Polizeli are Research Fellows of CNPq. T. M. Silva is recipient FAPESP Fellowship and this work was part of a Doctor Thesis submitted by T. M. Silva to FFCLRP-USP. We thank Ricardo F. Alarcon and Mauricio de Oliveira for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, T.M., Maller, A., de Lima Damásio, A.R. et al. Properties of a purified thermostable glucoamylase from Aspergillus niveus . J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 1439–1446 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-009-0630-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-009-0630-z