Abstract
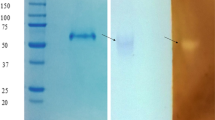
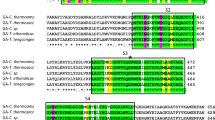
An extracellular glucoamylase produced by Paecilomyces variotii was purified using DEAE-cellulose ion exchange chromatography and Sephadex G-100 gel filtration. The purified protein migrated as a single band in 7% PAGE and 8% SDS-PAGE. The estimated molecular mass was 86.5 kDa (SDS-PAGE). Optima of temperature and pH were 55 °C and 5.0, respectively. In the absence of substrate the purified glucoamylase was stable for 1 h at 50 and 55 °C, with a t 50 of 45 min at 60 °C. The substrate contributed to protect the enzyme against thermal denaturation. The enzyme was mainly activated by manganese metal ions. The glucoamylase produced by P. variotii preferentially hydrolyzed amylopectin, glycogen and starch, and to a lesser extent malto-oligossacarides and amylose. Sucrose, p-nitrophenyl α-d-maltoside, methyl-α-d-glucopyranoside, pullulan, α- and β-cyclodextrin, and trehalose were not hydrolyzed. After 24 h, the products of starch hydrolysis, analyzed by thin layer chromatography, showed only glucose. The circular dichroism spectrum showed a protein rich in α-helix. The sequence of amino acids of the purified enzyme VVTDSFR appears similar to glucoamylases purified from Talaromyces emersonii and with the precursor of the glucoamylase from Aspergillus oryzae. These results suggested the character of the enzyme studied as a glucoamylase (1,4-α-d-glucan glucohydrolase).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
James JA, Lee BH (1997) Glucoamylases: microbial sources, industrial applications and molecular biology—a review. J Food Biochem 21:1–52
Fierobe HP, Clarke AJ, Tull D, Svensson B (1998) Enzymatic properties of ceysteinsulfonic acid derivative of the catalytic base mutant Glu400→Cys of glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori. Biochemistry 37:3753–3759
Thorsen TS, Johnsen AH, Josefsen K, Jensen B (2006) Identification and characterization of glucoamylase from fungus Thermomyces lanuginosus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1764:671–676
Norouzian D, Akbarzadeh A, Scharer JM, Moo Young M (2006) Fungal glucoamylases. Biotechnol Adv 24:80–85
Pandey A (1995) Glucoamylase research and overview. Starch 47(11):439–445
Reilly PJ (1999) Protein engineering of glucoamylase to improve industrial properties: a review. Starch 51:269–274
Rizzatti ACS, Jorge JA, Terenzi HF, Rechia CGV, Polizeli MLTM (2001) Purification and properties of a thermostable extracellular β-d-xylosidase produced by a thermotolerant Aspergillus phoenicis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 26:156–160
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–489
Jones RL, Verner JE (1967) The bioassay of gibberelins. Plant 72:155–161
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:267–275
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Hanes CS (1932) The effect of starch concentration upon the velocity of hydrolysis by the amylase of germinated barley. Biochem J 26:1406–1421
Tipton KF (1993) Principles of enzyme assay and kinetic studies. In: Eisenthal R, Danson MJ (eds) Enzyme assays: a practical approach. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 23–25
Davis BJ (1964) Disc electrophoresis. II. Methods and application to human serum proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci 121:404–427
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Blum H, Beier H, Gross HJ (1987) Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 8:93–99
Aquino ACMM, Jorge JA, Terenzi HF, Polizeli MLTM (2001) Thermostable glucose-tolerant glucoamylase produced by the thermophilic fungus Scytalidium thermophilum. Folia Microbiol 46(1):11–16
O’Farrel PZ, Goodman HM, O’Farrel PH (1977) High resolution two dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell 12:1133–1142
Fontana JD, Gebara M, Blumel M, Schneider H, Mackenzie CR, Johnson KG (1988) α-4-O-methyl-D-glucuronidase component of xylanolytic complexes. Methods Enzymol 160:560–571
Vihinen M, Mäntsälä P (1989) Microbial amylolytic enzymes (Review). Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 24(4):329–419
Pazur JH, Knull HR, Cepure A (1971) Glucoenzymes: structure and properties of the two forms of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger. Carbohyd Res 20:83–96
Yamasaki Y, Suzuki Y, Ozawa J (1977) Three forms of α-glucosidase and glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori. Agric Biol Chem 41:2149–2161
Nguyen QD, Rezessy-Szabó JM, Claeyssens M, Stals I, Hoschke A (2002) Purification and characterisation of amylolytic enzymes from thermophilic fungus Thermomyces lanuginosus strain ATCC 34626. Enzyme Microb Technol 31:345–352
Cereia M, Terenzi HF, Jorge JA, Greene LJ, Rosa JC, Polizeli MLTM (2000) Glucoamylase activity from the thermophilic fungus Scytalidium thermophilum. Biochemical and regulatory properties. J Basic Microbiol 40(2):83–92
Silva WB, Peralta RM (1998) Purification and characterization of a thermostable glucoamylase from Aspergillus fumigatus. Can J Microbiol 44:493–497
MacKenzie DA, Jeenes DJ, Xinghua G, Archer DB (2000) Molecular basis of glucoamylases overproduction by a mutagenised industrial strain of Aspergillus niger. Enz Microbial Technol 26:193–200
Tosi LRO, Terenzi HF, Jorge JA (1993) Purification and characterization of an extracellular glucoamylase from the thermophilic fungus Humicola grisea var. thermoidea. Can J Microbiol 39:846–852
Kanlayakrit W, Ishimatsu K, Nakao M, Hayashida S (1987) Characteristics of raw-starch-digesting glucoamylase from thermophilic Rhizomucor pusillus. J Ferment Technol 65:379–385
Wilson JJ, Ingledew WM (1982) Isolation and characterization of Schwanniomyces alluvius amylolytic enzymes. Appl Environ Microbiol 44(2):301–307
Fagerstrom R, Vanio A, Suorante K, Pakula T, Kalkkinen N, Torkkeli H (1990) Comparation of two glucoamylases from Hormoconis resinae. J Gen Microbiol 136:913–920
Bhumibhamon O (1983) Production of amyloglucosidase by submerged culture. Thai J Agric Sci 16:173
Tsekova K, Georgieva M, Ganchev I (1983) Enzyme preparation glucoamylase from culture liquid of strain Aspergillus niger B77. I. Isolation of crude enzyme preparation and study of some of its properties. Acta Microbiol Bulgaria 13:83
Stoffer B, Frandsen TP, Busk PK, Schneider P, Svendsen I, Svensson B (1993) Production, purification and characterization of the catalytic domain of glucoamylase from Aspergillus niger. Biochem J 292:197–202
Spinelli LBB, Polizeli MLTM, Terenzi HF, Jorge JA (1996) Biochemical characterization of glucoamylase from the hyperproducer exo-1 mutant strain of Neurospora crassa. FEMS Microbiol Lett 138:173–177
Schulz GE, Schirmer RH (1979) Principles of protein structure, chap 3. Springer, Berlin
Sandrim VC, Rizzatti ACS, Terenzi HF, Jorge JA, Milagres AMF, Polizeli MLTM (2005) Purification and biochemical characterization of two xylanases produced by Aspergillus caespitosus and their potential for kraft pulp bleaching. Process Biochem 40:1823–1828
Saha BC, Mitsue T, Ueda S (1979) Glucoamylase produced by submerged culture of Aspergillus oryzae. Starch/Särke 31:307–312
Aleshin AE, Firsov LM, Honzatko RB (1994) Refined structure for the complex of acarbose with glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori var. X100 to 2.4-A resolution. J Biol Chem 269(22):15631–15639
Nielsen BR, Lehmbeck J, Frandsen TP (2002) Cloning, heterologous expression, and enzymatic characterization of a thermostable glucoamylase from Talaromyces emersonii. Protein Expr Purif 26:1–8
Coutinho PM, Reilly PJ (1997) Glucoamylase structural, functional, and evolutionary relationships. Proteins Struct Funct Gen 29:334–347
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) and Conselho de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). J.A.J., H.F.T. and M.L.T.M.P are Research Fellows of CNPq. M.M. was recipient of CAPES Fellowship and this work was part of a Master Dissertation submitted by M.M. to the Departamento de Biologia, FFCLRP, USP. We thank Ricardo Alarcon for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michelin, M., Ruller, R., Ward, R.J. et al. Purification and biochemical characterization of a thermostable extracellular glucoamylase produced by the thermotolerant fungus Paecilomyces variotii . J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35, 17–25 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-007-0261-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-007-0261-1