Abstract
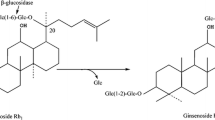
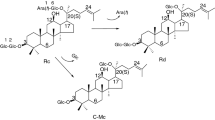
Fourteen phytopathogenic fungi were tested for their ability to transform the major ginsenosides to the active minor ginsenoside Rd. The transformation products were identified by TLC and HPLC, and their structures were assigned by NMR analysis. Cladosporium fulvum, a tomato pathogen, was found to transform major ginsenoside Rb1 to Rd as the sole product. The following optimum conditions for transforming Rd by C. fulvum were determined: the time of substrate addition, 24 h; substrate concentration, 0.25 mg ml−1; temperature, 37°C; pH 5.0; and biotransformation period, 8 days. At these optimum conditions, the maximum yield was 86% (molar ratio). Further, a preparative scale transformation with C. fulvum was performed at a dose of 100 mg of Rb1 by a yield of 80%. This fungus has potential to be applied on the preparation for Rd in pharmaceutical industry.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen LQ, Kim MK, Lee JW, Lee YJ, Yang DC (2006) Conversion of major ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside F2 by Caulobacter leidyia. Biotechnol Lett 28:1121–1127. doi:10.1007/s10529-006-9059-x
Chi H, Ji GE (2005) Transformation of ginsenosides Rb1 and Re from Panax ginseng by food microorganisms. Biotechnol Lett 27:765–771. doi:10.1007/s10529-005-5632-y
Dong A, Ye M, Guo H, Zheng J, Guo D (2003) Microbial transformation of ginsenoside Rb1 by Rhizopus stolonifer and Curvularia lunata. Biotechnol Lett 25:339–344. doi:10.1023/A:1022320824000
Dou DQ, Chen YJ, Liang LH, Pang FG, Shimizu N, Takeda T (2001) Six new dammarane-type triterpene saponins from leaves of Panax ginseng. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 49:442–446. doi:10.1248/cpb.49.442
Kim MK, Lee JW, Lee KY, Yang DC (2005) Microbial conversion of major ginsenoside Rb1 to pharmaceutically active minor ginsenoside Rd. J Microbiol 43:456–462
Lee JK, Choi SS, Lee HK, Han KJ, Han EJ, Suh HW (2003) Effects of ginsenoside Rd and decursinol on the neurotoxic responses induced by kainic acid in mice. Planta Med 69:230–234. doi:10.1055/s-2003-38475
Luan H, Liu X, Qi X, Hu Y, Hao D, Cui Y, Yang L (2006) Purification and characterization of a novel stable ginsenoside Rb1-hydrolyzing β-d-glucosidase from China white jade snail. Process Biochem 41:1974–1980. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2006.04.011
Park JD, Rhee DK, Lee YH (2005) Biological activities and chemistry of saponins from Panax ginseng C. A Meyer Phytochem Rev 4:159–175. doi:10.1007/s11101-005-2835-8
Shi Q, Hao Q, Bouissac J, Lu Y, Tian S, Luu B (2005) Ginsenoside-Rd from Panax notoginseng enhances astrocyte differentiation from neural stem cells. Life Sci 76:983–995. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2004.07.026
Son JW, Kim HJ, Oh DK (2008) Ginsenoside Rd production from the major ginsenoside Rb1 by β-glucosidase from Thermus caldophilus. Biotechnol Lett 30:713–716. doi:10.1007/s10529-007-9590-4
Teng RW, Li HZ, Chen JT, Wang DZ, He YN, Yang CR (2002) Complete assignment of H-1 and C-13 NMR data for nine protopanaxatriol glycosides. Magn Reson Chem 40:483–488. doi:10.1002/mrc.1033
Zeng S, Guan YY, Liu DY, He H, Wang W, Qiu QY, Wang XR, Wang YD (2003) Synthesis of 12-epi-ginsenoside Rd and its effects on contractions of rat aortic rings. Chin Pharmacol Bull 19:282–286
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Universities (NCET-05-0321 to GT), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20070200004 to YZ), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30570417 to YZ), the program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team (PCSIRT) in University (#IRT0519) and the Analysis and Testing Foundation of Northeast Normal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Wang, J., Li, J. et al. Highly selective biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to Rd by the phytopathogenic fungus Cladosporium fulvum (syn. Fulvia fulva). J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 721–726 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-009-0542-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-009-0542-y