Abstract
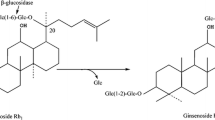
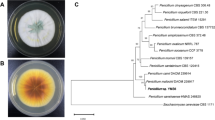
Ginsenoside Rb1 is the main predominant component in Panax species. In this study, an eco-friendly and convenient preparation method for ginsenoside CK has been established, and five strains of β-glucosidase-producing microorganisms were screened out from the soil of a Panax notoginseng planting field using Esculin-R2A agar. Aspergillus niger XD101 showed that it has excellent biocatalytic activity for ginsenosides; one of the isolates can convert ginsenoside Rb1 to CK using extracellular enzyme from the mycelium. Mycelia of A. niger were cultivated in wheat bran media at 30 °C for 11 days. By the removal of mycelia from cultured broth, enzyme salt fractionation by ammonium sulfate (70%, v/v) precipitation, and dialysis, sequentially, crude enzyme preparations from fermentation liquid supernatant were obtained. The enzymatic transformed Rb1 as the following pathways: Rb1→Rd→F2→CK. The optimized reaction conditions are at reaction time of 72 h, in the range of pH 4–5, and temperature of 50–60 °C. Active minor ginsenosides can be obtained by a specific bioconversion via A. niger XD101 producing the ginsenoside-hydrolyzing β-glucosidase. In addition, the crude enzyme can be resulted in producing ginsenoside CK via conversion of ginsenoside Rb1 at high conversion yield (94.4%). FDA generally regarded, A.niger as safe microorganism. Therefore, these results indicate that A. niger XD10 may provide an alternative method to prepare ginsenoside CK without food safety issues in the pharmaceutical industry.










Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
22 April 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03574-0
References
Park, C. S., Yoo, M. H., Noh, K. H., & Oh, D. K. (2010). Biotransformation of ginsenosides by hydrolyzing the sugar moieties of ginsenosides using microbial glycosidases. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 87, 9–19.
Yoo, M. H., Yeom, S. J., Park, C. S., Lee, K. W., & Oh, D. K. (2011). Production of aglycon protopanaxadiol via compound K by a thermostable β-glycosidase from Pyrococcus furiosus. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 89, 1019–1028.
Luan, H., Qi, L. X., Hu, Y., Hao, D., Cui, Y., & Yang, L. (2006). Purification and characterization of a novel stable ginsenoside Rb1-hydrolyzing β-D-glucosidase China white jade snail. Process Biochemistry, 41(9), 1974–1980.
Duan, Z. G., Wei, B., Deng, J. J., Mi, Y., Dong, Y. F., Zhu, C. H., Fu, R. Z., Qu, L. L., & Fan, D. D. (2018). The anti-tumor effect of ginsenoside Rh4 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 499, 482–487.
Lin, F., Guo, X., & Lu, W. (2015). Efficient biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to Rd by isolated Aspergillus versicolor, excreting β-glucosidase in the spore production phase of solid culture. Anton Leeuw, 108(5), 1117–1127.
Upadhyaya, J., Kim, M. J., Kim, Y. H., Ko, S. R., Park, H. W., & Kim, M. K. (2016). Enzymatic formation of compound-K from ginsenoside Rb1 by enzyme preparation from cultured mycelia of Armillaria mellea. Journal of Ginseng Research, 40, 105–112.
Lei, C., Wu, S. Q., Zhao, C. A., & Yin, C. R. (2016). Microbial conversion of major ginsenosides in ginseng total saponins by Platycodon grandiflorumendophytes. Journal of Ginseng Research, 40, 366–374.
Kim, M. J., Upadhyaya, J., Yun, M. S., Ryu, N. S., Song, Y. E., Park, H. W., Kim, Y. H., & Kim, M. K. (2017). Highly regioselective biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb2 into compound Y and compound K by β-glycosidase purified from Armillaria mellea mycelia. Journal of Ginseng Research, 42, 504–511.
Hwang, C. R., Lee, S. H., Jang, G. Y., Hwang, I. G., Kim, H. Y., Woo, K. S., Lee, J., & Jeong, H. S. (2014). Changes in ginsenoside compositions and antioxidant activities of hydroponic-cultured ginseng roots and leaves with heating temperature. Journal of Ginseng Research, 38(3), 180–186.
Sun, C., Gao, W., Zhao, B., & Cheng, L. (2013). Optimization of the selective preparation of 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 catalyzed by d, l-tartaric acid using response surface methodology. Fitoterapia., 84, 213–221.
Quan, L. H., Kim, Y. J., Li, G. H., Choi, K. T., & Yang, D. C. (2013). Microbial transformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to compound K by Lactobacillus paralimentarius. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 29, 1001–1007.
Song, X., Wu, H., Piao, X., Yin, Z., & Yin, C. (2017). Microbial transformation of ginsenosides extracted from Panax ginseng adventitious roots in an airlift bioreactor. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 26, 20–26.
Murthy, H. N., Georgiev, M. I., Kim, Y. S., Jeong, C. S., Kim, S. J., Park, S. Y., & Paek, K. Y. (2014). Ginsenosides: prospective for sustainable biotechnological production. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98(14), 6243–6254.
Eom, S. J., Kim, K. T., & Paik, H. D. (2018). Microbial bioconversion of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng and their improved bioactivities. Food Review International, 34, 698–712.
Ku, S. (2016). Finding and producing probiotic glycosylases for the biocatalysis of ginsenosides: a mini review. Molecules, 21, 645.
Chang, K. H., Jo, M. N., Kim, K. T., & Paik, H. D. (2014). Evaluation of glucosidases of Aspergillus niger strain comparing with other glucosidases in transformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenosides Rg3. Journal of Ginseng Research, 38, 47–51.
Kim, S. H., Min, J. W., Quan, L. H., Lee, S., Yang, D. U., & Yang, D. C. (2012). Enzymatic transformation of ginsenoside Rb1 by Lactobacillus pentosus strain 6105 from kimchi. Journal of Ginseng Research, 36, 291–297.
Cui, L., Wu, S. Q., Zhao, C. A., & Yin, C. R. (2016). Microbial conversion of major ginsenosides in ginseng total saponins by Platycodon grandiflorum endophytes. Journal of Ginseng Research, 40, 366–374.
Yan, Q., Zhou, W., Shi, X., Zhou, P., Ju, D., & Feng, M. (2010). Biotransformation pathways of ginsenoside Rb1 to compound K by β-glucosidases in fungus Paecilomyces Bainier sp. 229. Process Biochemistry, 45(9), 1550–1556.
Quan, L. H., Piao, J. Y., Min, J. W., Kim, H. B., Kim, S. R., Yang, D. U., & Yang, D. C. (2011). Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to prosapogenins, gypenoside XVII, ginsenoside Rd, ginsenoside F2, and compound K by Leuconostoc mesenteroides DC102. Journal of Ginseng Research, 35, 344.
Zhao, Y., Lee, H. G., Kim, S. K., Yu, H., Jin, F., & Im, W. T. (2016). Mucilaginibacter pocheonensis sp. nov. with ginsenoside converting activity isolated from soil of ginseng cultivating field. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66, 2862–2868.
Chi, H., & Ji, G. E. (2005). Transformation of ginsenosides Rb1 and Re from Panax ginseng by food microorganisms. Biotechnology Letters, 27(11), 765–771.
Cheng, L. Q., Kim, M. K., Lee, J. W., Lee, Y. J., & Yang, D. C. (2006). Conversion of major ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside F2 by Caulobacter leidyia. Biotechnology Letters, 28(14), 1121–1127.
Ye, L., Zhou, C. Q., Zhou, W., Zhou, P., Chen, D. F., Liu, X. H., Shi, X. L., & Feng, M. Q. (2010). Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside Rd by highly substrate-tolerant Paecilomyces bainier 229-7. Bioresource Technology, 101, 7872–7876.
Feng, L., Xu, C., Li, Z., Dai, Y., Han, H., Yu, S., & Liu, S. (2016). Microbial conversion of ginsenoside Rd from Rb1 by the fungus mutant Aspergillus niger strain TH-10a. Preparative Biochemistry, 46, 336–341.
Molina, G., Contesini, F. J., & De, R. R. (2016). β-Glucosidase from Aspergillus//GUPTA V K, Ed. New and future developments in microbial biotechnology and bioengineering. Amsterdam, 155–169.
Yang, X. D., Yang, Y. Y., Ouyang, D. S., & Yang, G. P. (2015). A review of biotransformation and pharmacology of ginsenoside compound K. Fitoterapia, 100, 208–220.
Wang, Y., Choi, K. D., Yu, H., Jin, F., & Im, W. (2016). Production of ginsenoside F1 using commercial enzyme Cellulase KN. Journal of Ginseng Research, 40(2), 121–126.
Luan, H., Qi, L. X., Hu, Y., Hao, D., Cui, Y., & Yang, L. (2006). Purification and characterization of a novel stable ginsenoside Rb1-hydrolyzing β-D-glucosidase from China white jade snail. Process Biochemistry, 41, 1974–1980.
Du, J., Cui, C. H., Park, S. C., Kim, J. K., Yu, H. S., Jin, F. X., Sun, C. K., Kim, S. C., & Im, W. T. (2014). Identification and characterization of a ginsenoside-transforming β-glucosidase from Pseudonocardia sp. Gsoil 1536 and its application for enhanced production of minor ginsenoside Rg 2 (S). PLoS One, 9, e96914.
Zhang, S. S., Xie, J. C., Zhao, L. G., Pei, J. J., Su, E. Z., Xiao, W., & Wang, Z. Z. (2018). Cloning, overexpression and characterization of a thermostable β-xylosidase from Thermotoga petrophila and cooperated transformation of ginsenoside extract to ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 with a β-glucosidase. Bioorganic Chemistry, 85, 159–167.
Treebupachatsakul, T., Nakazawa, H., Shinbo, H., Fujikawa, H., Nagaiwa, A., Ochiai, N., Kawaguchi, T., Nikaido, M., Totani, K., Shioya, K., Shida, Y., Morikawa, Y., Ogasawara, W., & Okada, H. (2016). Heterologously expressed Aspergillus aculeatus β-glucosidase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a cost-effective alternative to commercial supplementation of β-glucosidase in industrial ethanol production using Trichoderma reesei cellulases. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 121, 27–35.
Kim, M. J., Upadhyaya, J., Yun, M. S., Ryu, N. S., Song, Y. E., Park, H. W., & Kim, M. K. (2017). Highly regioselective biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb2 into compound Y and compound K by β-glycosidase purified from Armillaria mellea mycelia. Journal of Ginseng Research, S1226845317300118.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21706211, 21576160, 21878246, 21676214), the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFA0905200) and the Educational Commission of Shaanxi Province of China (16JS104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JYY, LWN, and FDD conceived and designed the study. JYY performed the experiments and analyzed the data. JYY wrote the paper. LWN and FDD reviewed and edited the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
The original online version of this article was revised: Changes has been made to the authors affiliation (article note has been added) and funding.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 1449 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Li, W. & Fan, D. Biotransformation of Ginsenoside Rb1 to Ginsenoside CK by Strain XD101: a Safe Bioconversion Strategy. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 193, 2110–2127 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03485-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03485-0