Abstract
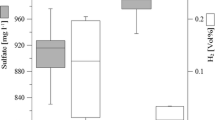
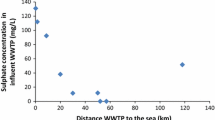
Biogenic production of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) is a problem for the oil industry as it leads to corrosion and reservoir souring. Continuous injection of a low nitrate concentration (0.25–0.33 mM) replaced glutaraldehyde as corrosion and souring control at the Veslefrikk and Gullfaks oil field (North Sea) in 1999. The response to nitrate treatment was a rapid reduction in number and activity of sulphate-reducing bacteria (SRB) in the water injection system biofilm at both fields. The present long-term study shows that SRB activity has remained low at ≤0.3 and ≤0.9 μg H2S/cm2/day at Veslefrikk and Gullfaks respectively, during the 7–8 years with continuous nitrate injection. At Veslefrikk, 16S rRNA gene based community analysis by PCR–DGGE showed that bacteria affiliated to nitrate-reducing sulphide-oxidizing Sulfurimonas (NR–SOB) formed major populations at the injection well head throughout the treatment period. Downstream of deaerator the presence of Sulfurimonas like bacteria was less pronounced, and were no longer observed 40 months into the treatment period. The biofilm community during nitrate treatment was highly diverse and relative stable for long periods of time. At the Gullfaks field, a reduction in corrosion of up to 40% was observed after switch to nitrate treatment. The present study show that nitrate injection may provide a stable long-term inhibition of SRB in sea water injection systems, and that corrosion may be significantly reduced when compared to traditional biocide treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402. doi:10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Beech IB, Gaylarde CC (1999) Recent advances in the study of biocorrosion—an overview. Rev Microbiol 30(3):177–190. doi:10.1590/S0001-37141999000300001
Benson DA, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Wheeler DL (2005) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D34–D38. doi:10.1093/nar/gki063
Bryant RD, Jansen W, Boivin J, Laishley EJ, Costerton JW (1991) Effect of hydrogenase and mixed sulfate-reducing bacterial-populations on the corrosion of steel. Appl Environ Microbiol 57(10):2804–2809
Bryant RD, Kloeke FV, Laishley EJ (1993) Regulation of the periplasmic [Fe] hydrogenase by ferrous iron in Desulfovibrio vulgaris (Hildenborough). Appl Environ Microbiol 59(2):491–495
Cord-Ruwisch R, Kleinitz W, Widdel F (1987) Sulfate-reducing bacteria and their activities in oil production. J Pet Technol 39(1):97–106. doi:10.2118/13554-PA
Crolet JL (2005) Microbial corrosion in the oil industry: a corrosionist`s view. In: Ollivier B, Magot M (eds) Petroleum microbiology. American society for microbiology, Washington DC, pp 143–169
Dalsgaard T, Bak F (1994) Nitrate reduction in a sulfate-reducing bacterium, Desulfovibrio desulfuricans, isolated from rice paddy soil-sulfide inhibition, kinetics, and regulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 60(1):291–297
Dinh HT, Kuever J, Mussmann M, Hassel AW, Stratmann M, Widdel F (2004) Iron corrosion by novel anaerobic microorganisms. Nature 427(6977):829–832. doi:10.1038/nature02321
Dunsmore B, Whitfield TB, Lawson PA, Collins MD (2004) Corrosion by sulfate-reducing bacteria that utilize nitrate. Corrosion 2004 paper 04763. NACE International, Houston
Fjellbirkeland A, Torsvik V, Øvreas L (2001) Methanotrophic diversity in an agricultural soil as evaluated by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles of pmoA, mxaF and 16S rDNA sequences. Anton Leeuw Int J G 79(2):209–217. doi:10.1023/A:1010221409815
Gevertz D, Telang AJ, Voordouw G, Jenneman GE (2000) Isolation and characterization of strains CVO and FWKOB, two novel nitrate-reducing, sulfide-oxidizing bacteria isolated from oil field brine. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(6):2491–2501. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.6.2491-2501.2000
Greene EA, Hubert C, Nemati M, Jenneman GE, Voordouw G (2003) Nitrite reductase activity of sulphate-reducing bacteria prevents their inhibition by nitrate-reducing, sulphide-oxidizing bacteria. Environ Microbiol 5(7):607–617. doi:10.1046/j.1462-2920.2003.00446.x
Herbert BN (1987) Reservoir souring. In: Hill EC, Shennan JL, Watkinson RJ (eds) Microbial problems in the offshore industry. Wiley, London, pp 63–71
Hoff KA (1988) Rapid and simple method for double staining of bacteria with 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole and fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled antibodies. Appl Environ Microbiol 54(12):2949–2952
Jenneman GE, McInerney MJ, Knapp RM (1986) Effect of nitrate on biogenic sulfide production. Appl Environ Microbiol 51(6):1205–1211
Jenneman GE, Moffitt PD, Bala GA, Webb RH (1999) Sulfide removal in reservoir brine by indigenous bacteria. Soc Pet Eng Prod Facil 14(3):219–225
Little B, Lee J, Ray R (2007) A review of ‘green’ strategies to prevent or mitigate microbiologically influenced corrosion. Biofouling 23(2):87–97. doi:10.1080/08927010601151782
Maxwell S, Hamilton WA (1986) Modified radiorespirometric assay for determining the sulfate reduction activity of biofilms on metal-surfaces. J Microbiol Methods 5(2):83–91. doi:10.1016/0167-7012(86)90004-7
Muyzer G, Dewaal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial-populations by denaturing gradient gel-electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes-coding for 16S ribosomal-RNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(3):695–700
Myhr S, Lillebo BLP, Sunde E, Beeder J, Torsvik T (2002) Inhibition of microbial H2S production in an oil reservoir model column by nitrate injection. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58(3):400–408. doi:10.1007/s00253-001-0881-8
Myhr S, Torsvik T (2000) Denitrovibrio acetiphilus, a novel genus and species of dissimilatory nitrate-reducing bacterium isolated from an oil reservoir model column. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1611–1619
Nemati M, Jenneman GE, Voordouw G (2001) Impact of nitrate-mediated microbial control of souring in oil reservoirs on the extent of corrosion. Biotechnol Prog 17(5):852–859. doi:10.1021/bp010084v
Nilsen RK, Beeder J, Thorstenson T, Torsvik T (1996) Distribution of thermophilic marine sulfate reducers in North Sea oil field waters and oil reservoirs. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(5):1793–1798
Page RDM (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12(4):357–358
Poduska RA, Anderson BD (1981) Successful storage lagoon odor control. J Water Pollut Control Fed 53(3):299–310
Rempel CL, Evitts RW, Nemati M (2006) Dynamics of corrosion rates associated with nitrite or nitrate mediated control of souring under biological conditions simulating an oil reservoir. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33(10):878–886. doi:10.1007/s10295-006-0142-z
Schafer H, McDonald IR, Nightingale PD, Murrell JC (2005) Evidence for the presence of a CmuA methyltransferase pathway in novel marine methyl halide-oxidizing bacteria. Environ Microbiol 7(6):839–852. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00757.x
Sekar R, Fuchs BM, Amann R, Pernthaler J (2004) Flow sorting of marine bacterioplankton after fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(10):6210–6219. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.10.6210-6219.2004
Stefess GC, Torremans RAM, de Schrijver R, Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (1996) Quantitative measurement of sulphur formation by steady state and transient state continuous cultures of autotrophic Thiobacillus species. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 45(1–2):169–175. doi:10.1007/s002530050666
Sunde E, Lillebø BLP, Bødtker G, Torsvik T, Thorstenson T (2004) H2S inhibition by nitrate injection on the Gullfaks field. Corrosion 2004 paper 04760. NACE International, Houston
Tatusova TA, Madden TL (1999) BLAST 2 SEQUENCES, a new tool for comparing protein and nucleotide sequences. FEMS Microbiol Lett 174(2):247–250. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13575.x
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25(24):4876–4882. doi:10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Thorstenson T, Bødtker G, Lillebø BLP, Torsvik T, Sunde E, Beeder J (2002) Biocide replacement by nitrate in sea water injection systems. Corrosion 2002 paper 02033. NACE International, Houston
Vance I, Thrasher DR (2005) Reservoir souring: mechanisms and prevention. In: Ollivier B, Magot M (eds) Petroleum microbiology. American society for microbiology, Washington DC, pp 123–142
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16):5261–5267. doi:10.1128/AEM.00062-07
Widdel F (1988) Microbiology and ecology of sulfate- and sulfur-reducing bacteria. In: Zehnder AJB (ed) Biology of anaerobic microorganisms. Wiley, New York, pp 469–585
Øvreas L, Forney L, Daae FL, Torsvik V (1997) Distribution of bacterioplankton in meromictic Lake Saelenvannet, as determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of PCR-amplified gene fragments coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(9):3367–3373
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Kristine Lysnes, Tove Leiknes, Nirmaladevi Sivasambu and Hege Ommedal for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bødtker, G., Thorstenson, T., Lillebø, BL.P. et al. The effect of long-term nitrate treatment on SRB activity, corrosion rate and bacterial community composition in offshore water injection systems. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35, 1625–1636 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-008-0406-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-008-0406-x