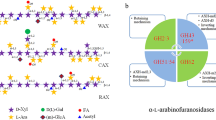
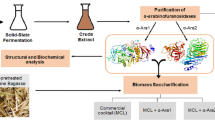
Abstract
Recently, α-l-arabinofuranosidases (EC3.2.1.55) have received increased attention primarily due to their role in the degradation of lignocelluloses as well as their positive effect on the activity of other enzymes acting on lignocelluloses. As a result, these enzymes are used in many biotechnological applications including wine industry, clarification of fruit juices, digestion enhancement of animal feedstuffs and as a natural improver for bread. Moreover, these enzymes could be used to improve existing technologies and to develop new technologies. The production, mechanisms of action, classification, synergistic role, biochemical properties, substrate specificities, molecular biology and biotechnological applications of these enzymes have been reviewed in this article.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Moromi is a fermenting mixture or mash of rice, water, koji (malted soybeans) and A. oryzae, which is produced during the traditional fermentation of soy sauce and in the production of sake, the traditional alcoholic beverage in Japan.
as cited by [108].
References
Adams EL, Kroon PA, Williamson G, Gilbert HJ, Morrisa VJ (2004) Inactivated enzymes as probes of the structure of arabinoxylans as observed by atomic force microscopy. Carbohydr Res 339:579–590
AkaoT, Kida H, Kanaoka M, Hattori M, Kobashi K (1998) Intestinal bacterial hydrolysis is required for the appearance of compound K in rat plasma after oral administration of ginsenoside Rb1 from panax ginseng. J Pharm Pharmacol 50:1155–1160
Aryon AP, Wilson B, Strauss CR, Williams PJ (1987) The properties of glycosidases of Vitis vinifera and a comparison of their β-glucosidase activity with that of exogenous enzymes. An assessment of possible applications in enology. Am J Enol Viticult 38:182–188
Bachmann SL, McCarthy AJ (1991) Purification and cooperative activity of enzymes constituting the xylan-degrading system of Thermomonospora fusca. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:2121–2130
Bacic A, Stone BA (1980) A (1→3)- and (1→4)-linked β-d-glucan in the endosperm cell-walls of wheat. Carbohydr Res 82:372–377
Bae E-A, Choo M-K, Park S-Y, Shin H-Y, Kim D-H (2002) Metabolism of ginsenoside Rc by human intestinal bacteria and its related antiallergic activity. Biol Pharm Bull 25:743–747
Bae E-A, Park S-Y, Kim D-H (2000) Constitutive β-glucosidase hydrolyzing ginsenoside Rb1 and Rb2 from human intestinal bacteria. Biol Pharm Bull 23:1481–1485
Beldman G, Schols HA, Pitson SM, Searl-van Leeuwen MJF, Voragen AGJ (1997) Arabinans and arabinan degrading enzymes. Adv Macromol Carbohydr Res 1:1–64
Beylot M-H, Mckie VA, Voragen AGJ, Doeswijk-Voragen CHL, Gilbert HJ (2001) The Pseudomonas cellulosa glycoside hydrolase family 51 arabinofuranosidase exhibits wide substrate specificity. Biochem J 358:607–614
Bezalel L, Shoham Y, Rosenberg E (1993) Characterization and delignification activity of a thermostable α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:57–62
Birgisson H, Fridjonsson O, Bahrani-Mougeot FK, Hreggvidsson GO, Kristjansson JK, Mattiasson BA (2004) New thermostable α-l-arabinofuranosidase from a novel thermophilic bacterium. Biotechnol Lett 26:1347–1351
Biskup SE, Intert F, Holthnujzen JH, Stengele M, Schultz G (1993) Glycosically bound volatiles-A review 1986–1991. Flav Fragr J 8:61–80
Bolam DN, Xie H, Pell G, Hogg D, Galbraith G, Henrissat B,Gilbert HJ (2004) X4 Modules represent a new family of carbohydrate-binding modules that display novel properties. J Biol Chem 279:22953–22963
Campbell GL, Bedford MR (1992) Enzyme applications for monogastric feeds: a review. Can J Anim Sci 72:449–466
Carvallo M, de Ioannes P, Navarro C, Chavez R, Peirano A, Bull P, Eyzaguirre J (2003) Characterization of an α-l-arabinofuranosidase gene (abf1) from Penicillium purpurogenum and its expression. Mycol Res 107:388–394
Casier JPJ, De Paepe G, Brummer JM (1973) Effect of water-soluble wheat and rye pentosans on the baking properties derived from wheat flours and other raw materials. Getreide Mehl und Brot 27:36–43
Catoire L, Goldenberg R, Pierron M, Morvan C, Hervé du Penhoat C (1998) An efficient procedure for studying pectin structure which combines limited depolymerization and C13 NMR. Eur Biophys J 27:127–136
Chacòn-Martènez CA, Anzola JM, Rojasa A, Hernández F, Junca H, Ocampo W, Del Portillo P (2004) Identification and characterization of the α-l-arabinofuranosidase B of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Dianthi (Fod). Phys Mol Plant Pathol 64:201–208
Chesson A (1987) Supplementary enzymes to improve the utilization of pig and poultary diets. In: Haresigin W, Cole DJA (eds) Recent advances in animal nutrition, Butterworths, London, pp 71–89
Churms SC, Merrifield EH, Stephen AM, Walvyn DR, Polson A, Merwe van den KJ, Spies HSC, Costa N (1983) An L-arabinan from apple-juice concentrates. Carbohydr Res 113:339–344
Coen JA, Dehority BA (1970) Degradation and utilization of hemicellulose from intact forages by pure cultures of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol 20:362–368
Cotta MA (1993) Utilization of Xylooligosaccharides by Selected Ruminal Bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3557–3563
Coutinho PM, Henrissat B (1999) Carbohydrate-active enzymes server at http://www.afmb.cnrs-mrs.fr/_/cazy/CAZY/index.html
Dahlberg L, Holst O, Kristjansson JK (1993) Thermostable xylanolytic enzymes from Rhodothermus marinus grown on xylan. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:63–68
Davies G, Henrissat B (1995) Structures and mechanisms of glycosyl hydrolases. Structure 3:853–859
de Grootet LMJ, van de Vondervoort PJI, de Vries RP, vanKuyk PA, Ruijter IJG, Visser J (2003) Isolation and characterization of two specific regulatory Aspergillus niger mutants shows antagonistic regulation of arabinan and xylan metabolism. Microbiology 149:1183–1191
De Ioannes P, Peirano A, Steiner J, Eyzaguirre J (2000) An α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Penicillium purpurogenum: production, purification and properties. J Biotechnol 7:253–258
De Vries JA, Rombouts FM, Voragen AGJ, Pilnik W (1982) Enzymic degradation of apple pectins. Carbohydr Polym 2:25–33
De Vries RP, Kester HCM, Poulsen CH, Benen JAE, Visser J (2000) Synergy between enzymes from Aspergillus involved in the degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Carbohydr Res 327:401–410
De Vries RP, Visser J (2001) Aspergillus enzymes involved in degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:497–522
Debeche T, Cummings N, Connerton I, Debeire P, O’Donohue MJ (2000) Genetic and biochemical characterization of a highly thermostable α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Thermobacillus xylanilyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol 6:1734–1736
Degrassi G, Vindigni A, Venturi VA (2003) Thermostable α-arabinofuranosidase from xylanolytic Bacillus pumilus: purification and characterization. J Biotechnol 101:69–79
Dehority BA (1965) Degradation and utilization of isolated hemicellulose by pure cultures of cellulolytic rumen bacteria. J Bacteriol 89:1515–1520
Dehority BA (1967) Rate of isolated hemicellulose degradation and utilization by pure cultures of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol 15:987–993
Dehority BA, Scott HW (1967) Extent of cellulose and hemicellulose digestion in various forages by pure cultures of rumen bacteria. J Dairy Sci 50:1136–1141
Ferchichi M, Rèmond C, Simo R, O’Donohue MJ (2003) Investigation of the functional relevance of the catalytically important Glu28 in family 51 arabinosidases. FEBS Lett 553:381–386
Fernández-Espinar MT, Pena JL, Pinaga F, Valles S (1994) Alpha ararbinofuranosidase production by Aspergillus nidulans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 115:107–112
Ferré H, Broberg A, Duus JØ, Thomsen KK (2000) A novel type of arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase isolated from germinated barley. Analysis of substrate preference and specificity by nano-probe NMR. Eur J Biochem 267:6633–6641
Fessas D, Schiraldi A (1998) Texture and staling of wheat bread crumb: effects of water extractable proteins and pentosans. Thermochim Acta 323:17–26
Filho EFE, Puls J, Coughlan MP (1996) Purification and characterization of two arabinofuranosidases from solid-state cultures of the fungus Penicillium capsulatum. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:168–173
Gasparic A, Romana M-L, Martin J, Wallace RJ, Nekrep FV, Flint HJ (1995) Isolation of genes encoding β-d-xylanase, β-d-xylosidase and α-l-arabinofuranosidase activities from the rumen bacterium Prevotella ruminicola B14. FEMS Microbiol Lett 125:135–142
Giinata Z, Bitteur S, Brillouet JM, Bayanove C, Cordonnier R (1988) Sequential enzymic hydrolysis of potentially aromatic glycosides from grape. Carbohydr Res 184:139–149
Giinata Z, Dugelay I, Sapis JC, Baumes R, Baya-nove C (1990) Action des glycosidases exogknes au tours de la vinification: liberation de I’arome a partir de prcurseurs glycosidiques. J Int Sci Vigne Vin 24:133–144
Gobbetti M, De Angelis M, Arnaut P, Tossut P, Corsetti A, Lavermicocca P (1999) Added pentosans in breadmaking: fermentations of derived pentoses by sourdough lactic acid bacteria. Food Microbiol 16:409–418
Gobbetti M, Lavermicocca P, Minervini F, De Angelis M, Corsetti A (2000) Arabinose fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum in sourdough with added pentosans and α-l-arabinofuranosidase: a tool to increase the production of acetic acid. J Appl Microbiol 88:317–324
Gomes J, Gomes I, Terler K, Gubala N, Ditzelmüller G, Steinera W (2000) Optimisation of culture medium and conditions for α-l-rabinofuranosidase production by the extreme thermophilic eubacterium Rhodothermus marinus. Enzyme Microb Technol 27:414–422
Greve LC, Labavitch JM, Hungate RE (1984) α-l-Arabinofuranosidase from Ruminococcus albus 8: purification and possible roles in hydrolysis of alfalfa cell wall. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:1135–1140
Gübitz GM, Haltrich D, Latal B, Steiner W (1997) Mode of depolymerisation of hemicellulose by various mannanases and xylanases in relation to their ability to bleach softwood pulp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47:658–621
Habibi Y, Heyraud A, Mahrouz M, Vignon MR (2004) Structural features of pectic polysaccharides from the skin of Opuntia ficus-indica prickly pear fruits. Carbohydr Res 339:1119–1127
Hasegawa H, Sung JH, Benno Y (1997) Role of human intestinal Prevotella oris in hydrolyzing ginseng saponins. Planta Med 63:436–440
Hashimoto T, Nakata Y (2003) Synergistic degradation of arabinoxylan with α-l-arabinofuranosidase, xylanase and β-xylosidase from soy sauce koji mold, Aspergillus oryzae, in high salt condition. J Biosci Bioeng 95:164–169
Henrissat B, Davies GJ (2000) Glycoside hydrolases and glycosyltransferases families, modules and implications for genomics. Plant Physiol 124:1515–1519
Hespell RB, Cotta MA (1995) Degradation and utilization by Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens H17c of xylans with different chemical and physical properties. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3042–3050
Hespell RB, O`Bryan P (1992) Purification and characterization of an α-L-arabinofuranosidase from Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens GS113. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1082–1088
Hood EE, Jilka JM (1999) Plant-based production of xenogenic proteins. Curr Open Biotechnol 10:382–386
Hövel K, Shallom D, Niefind K, Belakhov V, Shoham G, Baasov T, Shoham Y, Schomburg D (2003) Crystal structure and snapshots along the reaction pathway of a family 51 α-l-arabinofuranosidase. EMBO J 22:4922–4932
Huerta-Ochoa S, Nicolàs-Santiago MS, Acosta-Hernàndez WD, Prado-Barragàn LA, Gutiérrez-López GF, Garcia-Almendàrez BE, Regaldo-González C (2003) Production and partial purification of glycosidases obtained by solid-state fermentation of grape Pomace using Aspergillus niger 10. In: Nathan VE, Gutierrez-Lopez GF, Barbosa G (eds) Food science and food biotechnology. CRS Press, Florida, pp 119–137
Jankiewicz M, Michniewicz J (1987) The effect of soluble pentosans isolated from rye grain on staling of bread. Food Chem 25:241–246
Jiménez T, Martinez-Anaya MA (eds) (1999) Enzymes, a key to improve bread and dough quality: degradation by products and relationship with quality. In: Abstracts of the 17th ICC Conference of the Cereal Across the Continents, Instituto de Agroquimica Tecnologia de Alimentos, Valencia, p 168
Kaji A (1984) L-arabinosidases. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 42:382–394
Kaji A, Tagawa K (1970) Purification, crystallisation, and amino acid composition of α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Aspergillus niger. Biochim Biophys Acta 207:456–464
Kaneko S, Arimoto M, Ohba M, Kobayashi H, Ishii T, Kusakabe I (1998) Purification and substrate specificities of two α-L-arabinofuranosidases from Aspergillus awamori IFO 4033. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4021–4027
Kellet LE, Poole DM, Ferreira LMA, Durrant AJ, Hazlewood GP, Gilbert HJ (1990) Xylanase B and an arabinofuranosidase from Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. cellulosa contain identical cellulose-binding domains and are encoded by adjacent genes. Biochem J 272:369–376
Kim SK, D’Appolonia BL (1977) Bread staling studies. III. Effect of pentosans on dough, bread, and bread staling rate. Cereal Chem 54:225–229
Kimura I, Yoshioka N, Kimura Y, Tajima S (2000) Cloning, sequencing and expression of an α-L-arabinofuranosidase from Aspergillus sojae. J Biosci Bioeng 89:262–266s
Komae K, Kaji A, Sato M (1982) An α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Streptomyces purpuascens IFO 3389. Agric Bio Chem 46:1899–1905
Kormelink FMJ, Voragen AGJ (1993) Degradation of different [(glucurono)arabino] xylans by combination of purified xylan degrading enzymes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:688–695
Koseki T, Okuda M, Sudah S, Kizaki Y, Iwano K, Aramaki I, Matsuzawa H (2003) Role of two α-l-arabinofuranosidases in arabinoxylan degradation and characteristics of the encoding genes from shochu koji molds, Aspergillus kawachii and Aspergillus awamori. J Biosce Bioeng 96:232–241
Kosugi A, Murashima K, Doi RH (2002) Characterization of two noncellulosomal subunits, ArfA and BgaA, from Clostridium cellulovorans that cooperate with the cellulosome in plant cell wall degradation. J Bacteriol 184:6859–6865
Kroon PA, Williamson G (1996) Release of ferulic acid from sugar-beet pulp by using arabinanase, arabinofuranosidase and an esterase from Aspergillus niger. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 23:263–267s
Kuno A, Sbimizu D, Kaneko S, Koyama Y, Yoshida S, Kohayashi H, Hayashi K, Taira K, Kusakabe I (1998) PCR cloning and expression of the F/10 family xylanase gene from Streptomyces olivaceoviridis E-86. J Ferment Bioeng 86:434–439
Leathers TD (2003) Bioconversions of maize residues to value-added co-products using yeast-like fungi. FEMS Yeast Res 3:133–140
Lee RC, Hrmova M, Burton RA, Lahnstein J, Fincher GB (2003) Bifunctional family 3 glycoside hydrolases from barley with α-l-arabinofuranosidase and β-d-Xylosidase activity: characterization, primary structures, and COOH-terminal. J Biol Chem 278:5377–5387
Mai V, Wiegel J, Lorenz W (2000) Cloning, sequencing, and characterization of the bifunctional xylosidase–arabinosidase from the anaerobic thermophile Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus. Gene 247:137–143
Manelius A, Dahlberg L, Holst O (1994) Some properties of a thermostable β-xylosidase from Rhodothermus marinus. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 44:39–48
Margolles A, de los Reyes-Gavilán CG (2003) Purification and functional characterization of a novel α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Bifidobacterium longum B667. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5096–5103
Margolles-Clark E, Tenkanen M, Nakari-Setala T, Penttila M (1996) Cloning of genes encoding α-l-arabinofuranosidase and β-xylosidase from Trichoderma reesei by expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3840–3846
Marlatt C, Ho C-T, Chien M (1992) Studies of aroma constituents bound as glycosides in tomato. J Agric Food Chem 40:249–252
Martinez-Anaya MA, Devesa A (eds) (1999) Enzymes and sourdough starters govern bread and dough quality: influence on dough-bread pentosans. In: Abstracts of the 17th ICC Conference of the Cereal Across the Continents, Instituto de Agroquimica Tecnologia de Alimentos, Valencia p 168
Mateo JJ, Jimènez M (2000) Monoterpenes in grape juice and wines. J Chromatogr A 881:557–567
Mathlouthi N, Saulnier L, Quemener B, Araier L (2002) Xylanase and β-glucanase and other side enzymatic activities have greater effects on the viscosity of several feedstuffs than xylanase and β-glucanase used alone or in combination. J Agric Food Chem 50:5121–5127
Matsumura K, Obata H, Hata Y, Kawato A, Abe Y, Akita O (2004) Isolation and characterization of a novel gene encoding α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Aspergillus oryzae. J Biosci Bioeng 98:77–84
Matte A, Forsberg CW (1992) Purification, characterization, and mode of action of endoxylanases 1 and 2 from Fibrobacter succinogenes S85. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:157–168
Matuso N, Kaneko S, Kuno A, Kobayashi H, Kusakabes I (2000) Purification, characterization and gene cloning of two α-l-arabinofuranosidases from Streptomyces chartreusis GS901. Biochem J 346:9–15
Mc Cleary BV, Harrington J, Allen H (1988) Enzymic solutions to polysaccharide related industrial problems. In: Phillips GO, Williams PA, Wedlock DJ (eds) Gums and stabilizers for the industry. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 51–62
Miyanaga A, Koseki T, Matsuzawa H, Wakagi T, Shoun H, Fushinobu S (2004) Crystal structure of a family 54 α-l-arabinofuranosidase reveals a novel carbohydrate binding module that can bind arabinose. J Biol Chem 279:44907–44914
Miyazaki K (2005) Hyperthermophilic α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Thermotoga maritima MSB8: molecular cloning, gene expression, and characterization of the recombinant protein. Extremophiles 9:399–406
Morales P, Sendra JM, Pèrez-González JA (1995) Purification and characterization of an arabinofuranosidase from Bacillus polymyxa expressed in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 44:112–117
Morrison IM (1982). The degradation of isolated hemicellulose and lignin-hemicellulose complexes by cell free, rumen hemicellulase. Carbohydr Res 101:93–100
Patterson JA (1989) Prospects for establishment of genetically engineered microorganisms in the rumen. Enzyme Microb Technol 11:187–189
Pilnik W (1982) Enzymes in the beverage industry. In: Dupuy P(ed) Use of enzymes in food technology, Lavoisier, Paris, pp 425–449
Piston SM, Voragen AG, Beldman G (1996) Stereochemical course of hydrolysis catalyzed by arabinofuranohydrolases. FEBS Lett 398:7–11
Rahman SAKM, Kato K, Kawai S, Takamizawa K (2003) Substrate specificity of the α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Rhizomucor pusillus HHT-1. Carbohydr Res 338:1469–1476
Rémond C, Ferchichi M, Aubry N, Plantier-Royon R, Portella C, O’Donohue MJ (2002) Enzymatic synthesis of alkyl arabinofuranosides using a thermostable α-l-arabinofuranosidase. Tetrahedron Lett 43:9653–9655
Rémond C, Plantier-Royon R, Aubry N, Maes E, Bliardc C, O’Donohue MJ (2004) Synthesis of pentose-containing disaccharides using a thermostable α-l-arabinofuranosidase. Carbohydr Res 339:2019–2025
Roche N, Berna P, Desgranges C, Durand A (1995) Substrate use and production of α-l-arabinofuranosidase during solid-state culture of Trichoderma reesei on sugar beet pulp. Enzyme Microb Technol 17:935–941
Romboust FM, Voragen AGJ, Searle-van Leenwen MF, Geraeds CCJM, Schols HA, Pilnik W (1988) The arabinanases of Asperigillus niger—purification and characterization of two α-L- arabinofuranosidase and an endo-1,5-α-l-arabinanase. Carbohydr Polym 9:25–47
Rye CS, Withers SG (2000) Glycosidase mechanisms. Curr Opin Chem Biol 4:573–580
Saha BC (2000) α-l-Arabinofuranosidases: biochemistry, molecular biology and application in biotechnology. Biotech Adv 18:403–423
Saha BC (2003) Hemicellulose bioconversion. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:279–291
Saha BC, Bothast RJ (1998) Purification and characterization of a novel thermostable α-l-arabinofuranosidase from a color–variant strain of a Aureobasidium pullulans. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:216–220
Sakamoto T, Kawasaki H (2003) Purification and properties of two type-B α-l-arabinofuranosidases produced by Penicillium chrysogenum. Bioch et Biophy Acta 1621:204–210
Sakamoto T, Thibault J-F (2001) Exo-Arabinanase of Penicillium chrysogenum able to release arabinobiose from α-1,5-l-Arabinan. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3319–3321
Sanai K, Seri K, Inoue S (1997) Inhibition of sucrose digestion and absorption by l-arabinose in rats. Nihon Eiyou Syokuryougaku Kaishi (in Japanese) 50:133–137
Schwab W, Scheller G, Schreier P (1990) Glycosidically bound aroma components from sour cherry. Phytochemistry 29:607–612
Seri K, Sanai K, Matsuo N, Kawakubo K, Xue C, Inoue S (1996) l-arabinose selectively inhibits intestinal sucrase in uncompetitive manner and reduces glycemic response after sucrose ingestion in animals. Metabolism 45:1368–1374
Shallom D, Belakhov V, Solomon D, Gilead-Gropper S, Baasov T, Shoham G, Shohama Y (2002) The identification of the acid-base catalyst of α-arabinofuranosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus T-6, a family 51 glycoside hydrolase. FEBS Lett 514:163–167
Shin H-Y, Park S-Y, Sung JH, Kim D-H (2003) Purification and characterization of α-l-arabinopyranosidase and α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Bifidobacterium breve K-110, a human intestinal anaerobic bacterium metabolizing ginsenoside Rb2 and Rc. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:7116–7123
Skjat M, Kuppinen S, Kofod LV, Fulsang C, Pauly M, Dalofe H, Anderson LN (2001) Functional cloning of an endo-arabinanase from Aspergillus aculeatus and its heterologous exptression in A. oryzae and tobacco. Mol Genet Genomics 265:913–921
Sknchez-Torres P, GonzBlez-Candelas L, Ramón D (1996) Expression in a wine yeast strain of the Aspergillus niger abfB gene. FEMS Microbiol Lett 145:189–194
Sørensen HR, Pedersen S, Viksø-Nielsen A, Meyer AS (2005) Efficiencies of designed enzyme combinations in releasing arabinose and xylose from wheat arabinoxylan in an industrial ethanol fermentation residue. Enzyme Microb Technol 36:773–784
Sozzi GO, Greve LC, Prody GA, Labavitch JM (2002) Gibberellic acid, synthetic auxins, and ethylene differentially modulate α-l-arabinofuranosidase activities in antisense 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase Tomato Pericarp Discs. Plant Physiol 129:1330–1340
Spagna G, Andreani F, Salatelli E, Romagnoli D, Casarini D, Pifferi PG (1998) Immobilization of the glycosidases: α-l-arabinofuranosidase and β-d-glucopyranosidase from Aspergillus niger on a chitosan derivative to increase the aroma of wine. Part II. Enzyme Microb Technol 23:413–421
Spagna G, Barbagalloa RN, Grecob E, Manentib I, Pifferi PG (2002) A mixture of purified glycosidases from Aspergillus niger for oenological application immobilised by inclusion in chitosan gels. Enzyme Microb Technol 30:80–89
Takao M, Akiyama K, Sakai T (2002) Purification and characterization of thermostable endo-1,5-α-l-Arabinase from a strain of Bacillus thermodenitrificans. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1639–1646
Tsujibo H, Takada C, Wakamatsu Y, Kosaka M, Tsuji A, Miamuto K, Inamori Y (2002) Cloning and expression of an arabinofuranosidase (STX- IV) Streptomyces thermoviolaceus OPC-520, and characterization of the enzyme. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:434–438
Tuncer M, Ball AS, Robb A, Wilson MT (1999) Optimization of extracellular lignocellulolytic enzyme production by a thermophilic actinomycete Thermomonospora fusca BD2. Enzyme Microb Technol 25:38–47
Tuncer M (2000) Characterization of β-xylosidase and α-l-arabinofuranosidase activities from Thermomonospora Fusca BD25. Turk J Biol 24:753–767
Tuncer M, Ball AS (2003) Purification and partial characterization of α-l-arabinofuranosidase produced by Thermomonospora fusca. Folia Microbiol 48:168–172
Tuncer M, Ball AS (2003) Co-operative actions and degradation analysis of purified xylan-degrading enzymes from Thermomonospora fusca BD25 on oat-spelt xylan. J Appl Microbiol 94:1030–1035
Utt EA, Eddy CK, Keshav KF, Ingram LO (1991) Sequencing and expression of the Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens xylB gene encoding a novel bifunctional protein with β-d-xylosidase and α-l-arabinofuranosidase activities. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1227–1234
Van laere KMJ, Beldman G, Voragen GJ (1997) A new arabinofuranohydrolase from Bifidobacterium adolescentis able to remove arabinosyl residue from double substituated xylose units in arabinoxylan. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47:231–235
Van Laere KMJ, Voragen CHL, Kroef T, Van den Broek LAM, Beldman G, Voragen AGJ (1999) Purification and mode of action of two different arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolases from Bifidobacterium adolescentis DSM 20083. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:606–613
Viikari L, Kantelinen A, Sundquist J, Linko M (1994) Xylanases in bleaching-from an idea to the industry. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:335–350
Vincent P, Shareck F, Dupont C, Morosoli R, Kluepfel D (1997) New α-l-arabinofuranosidase produced by Streptomyces lividans: cloning and DNA sequence of the abfB gene and characterization of the enzyme. Biochem J 322:845–852
Voragen AGJ, Rombouts FM, Searle-van leeuwen MF, Schols HA, Pilnik W (1988) The degradation of arabinans by endoarabinanase and arabinofuranosidases purified from Aspergillus niger. Food Hydrocolloids 1:423–437
Vorin SG, Baumes RL, Bitteur SM, Gunata ZY, Bayonove CL (1990) Novel monoterpene disaccharide glycosides of Vitis vinifera grapes. J Agric Food Chem 38:1373–1378
Wakabayashi C, Hasegawa H, Murata J, Saiki I (1997) In vivo antimetastatic action of ginseng protopanaxadiol saponins is based on their intestinal bacterial metabolites after oral administration. Oncol Res 9:411–417
Ward OP, Moo-Young M (1989) Degradation of cell wall and related plant polysaccharides. Crit Rev Biotechnol 8:237–274
Weaver J, Whitehead TR, Cotta MA Valentine PC, Salyers AA (1992) Genetic analysis of a locus on the Bacteroides ovatus chromosome which contains xylan utilization genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2764–2770
Whitaker JR (1984) Pectic substances, pectic enzymes and haze formation in fruit juices. Enzyme Microb Technol 6:341–349
Winterhalter P (1990) Bound terpenoids in the juice of the purple passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims). J Agric Food Chem 38:452–455
Wu P, Kuo M-C, Hartman TG, Rosen RT, Ho C-T (1991) Free glycosidically bound aroma compounds in pineapple (Ananas comosus L. Merr.). J Agric Food Chem 39:170–172
Yannai T, Sato M (2000) Purification and characterization of novel α-l-arabinofuranosidase form Pichia capsulata X91. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:1181–1188
Zaldivar J, Nielsen J, Olsson L (2001) Fuel ethanol production from lignocellulose:a challenge for metabolic engineering and process integration. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:17–34
Zechel DL, Withers SG (2000) Glycosidase mechanisms: anatomy of a finely tuned catalyst. Acc Chem Res 33:11–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Numan, M.T., Bhosle, N.B. α-l-Arabinofuranosidases: the potential applications in biotechnology. J IND MICROBIOL BIOTECHNOL 33, 247–260 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-005-0072-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-005-0072-1