Abstract
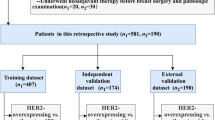
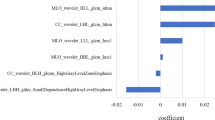
Here, we used pre-treatment CT images to develop and evaluate a radiomic signature that can predict the expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We then verified its predictive performance by cross-referencing its results with clinical characteristics. This two-center retrospective analysis included 125 patients with histologically confirmed NSCLC. A total of 1287 hand-crafted radiomic features were observed from manually determined tumor regions. Valuable features were then selected with a ridge regression-based recursive feature elimination approach. Machine learning–based prediction models were then built from this and compared each other. The final radiomic signature was built using logistic regression in the primary cohort, and then tested in a validation cohort. Finally, we compared the efficacy of the radiomic signature to the clinical model and the radiomic-clinical nomogram. Among the 125 patients, 89 were classified as having PD-L1 positive expression. However, there was no significant difference in PD-L1 expression levels determined by clinical characteristics (P = 0.109–0.955). Upon selecting 9 radiomic features, we found that the logistic regression-based prediction model performed the best (AUC = 0.96, P < 0.001). In the external cohort, our radiomic signature showed an AUC of 0.85, which outperformed both the clinical model (AUC = 0.38, P < 0.001) and the radiomics-nomogram model (AUC = 0.61, P < 0.001). Our CT-based hand-crafted radiomic signature model can effectively predict PD-L1 expression levels, providing a noninvasive means of better understanding PD-L1 expression in patients with NSCLC.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.N. Gettinger, L. Horn, L. Gandhi, D.R. Spigel, S.J. Antonia, N.A. Rizvi, J.D. Powderly, R.S. Heist, R.D. Carvajal, D.M. Jackman, L. V. Sequist, D.C. Smith, P. Leming, D.P. Carbone, M.C. Pinder-Schenck, S.L. Topalian, F.S. Hodi, J.A. Sosman, M. Sznol, D.F. McDermott, D.M. Pardoll, V. Sankar, C.M. Ahlers, M. Salvati, J.M. Wigginton, M.D. Hellmann, G.D. Kollia, A.K. Gupta, J.R. Brahmer: Overall survival and long-term safety of nivolumab (anti-programmed death 1 antibody, BMS-936558, ONO-4538) in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 33(18): 2004-2012, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.58.3708.
R.S. Herbst, P. Baas, D.W. Kim, E. Felip, J.L. Pérez-Gracia, J.Y. Han, J. Molina, J.H. Kim, C.D. Arvis, M.J. Ahn, M. Majem, M.J. Fidler, G. De Castro, M. Garrido, G.M. Lubiniecki, Y. Shentu, E. Im, M. Dolled-Filhart, E.B. Garon: Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387(10027): 1540-1550, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01281-7.
C. Loughran, C. Keeling: Seeding of tumour cells following breast biopsy: a literature review. Br J Radiol 84(1006): 869–874, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/77245199.
N. Girard, C.S. Sima, D.M. Jackman, L. V. Sequist, H. Chen, J.C.H. Yang, H. Ji, B. Waltman, R. Rosell, M. Taron, M.F. Zakowski, M. Ladanyi, G. Riely, W. Pao: Nomogram to predict the presence of EGFR activating mutation in lung adenocarcinoma. Eur Respir J 39(2): 366-372, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00010111.
E. Rios Velazquez, C. Parmar, Y. Liu, T.P. Coroller, G. Cruz, O. Stringfield, Z. Ye, M. Makrigiorgos, F. Fennessy, R.H. Mak, R. Gillies, J. Quackenbush, H.J.W.L. Aerts: Somatic mutations drive distinct imaging phenotypes in lung cancer. Cancer Res 77(14): 3922–3930, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0122.
H. Itakura, A.S. Achrol, L.A. Mitchell, J.J. Loya, T. Liu, E.M. Westbroek, A.H. Feroze, S. Rodriguez, S. Echegaray, T.D. Azad, K.W. Yeom, S. Napel, D.L. Rubin, S.D. Chang, G.R. Harsh, O. Gevaert: Magnetic resonance image features identify glioblastoma phenotypic subtypes with distinct molecular pathway activities. Sci Transl Med 7(303): 303ra138, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa7582.
A.G. Sacher, S.E. Dahlberg, J. Heng, S. Mach, P.A. Jänne, G.R. Oxnard: Association between younger age and targetable genomic alterations and prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol 2(3): 313-320, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.4482.
Y. Li, X. Liu, K. Xu, Z. Qian, K. Wang, X. Fan, S. Li, Y. Wang, T. Jiang: MRI features can predict EGFR expression in lower grade gliomas: a voxel-based radiomic analysis. Eur Radiol 28(1): 356-362, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-4964-z.
SS Yip, HJ Aerts: Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys Med Biol 61(13): R150-66, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/61/13/R150.
M Avanzo, J Stancanello, Naqa IEl: Beyond imaging: the promise of radiomics. Phys Med 38: 122–139, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2017.05.071.
DS Kermany, M Goldbaum, W Cai, CCS Valentim, H Liang, SL Baxter, A McKeown, G Yang, X Wu, F Yan, J Dong, MK Prasadha, J Pei, MYL Ting, J Zhu, C Li, S Hewett, J Dong, I Ziyar, A Shi, R Zhang, L Zheng, R Hou, W Shi, X Fu, Y Duan, V Huu, C Wen, ED Zhang, C L Zhang, O Li, X Wang, Michael A Singer, Xiaodong Sun, Jie Xu, Ali Tafreshi, M Anthony Lewis, Huimin Xia, Kang Zhang: Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning, Cell 172(5): 1122-1131, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.010.
J.R. Brown, M.P. Digiovanna, B. Killelea, D.R. Lannin, D.L. Rimm: Quantitative assessment Ki-67 score for prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Lab Invest 94(1): 98-106, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2013.128.
M. Diehn, C. Nardini, D.S. Wang, S. McGovern, M. Jayaraman, Y. Liang, K. Aldape, S. Cha, M.D. Kuo: Identification of noninvasive imaging surrogates for brain tumor gene-expression modules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(13): 5213-5218, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0801279105.
S. Basu, T.C. Kwee, R. Gatenby, B. Saboury, D.A. Torigian: Evolving role of molecular imaging with PET in detecting and characterizing heterogeneity of cancer tissue at the primary and metastatic sites, a plausible explanation for failed attempts to cure malignant disorders. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38(6): 987-991, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-1787-z.
R.J. Gillies, P.E. Kinahan, H. Hricak: Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278(2): 563-577, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015151169.
P. Lambin, E. Rios-Velazquez, R. Leijenaar, S. Carvalho, R.G.P.M. Van Stiphout, P. Granton, C.M.L. Zegers, R. Gillies, R. Boellard, A. Dekker, H.J.W.L. Aerts: Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur J Cancer 48(4): 441-446, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036.
A.M. Rutman, M.D. Kuo: Radiogenomics: creating a link between molecular diagnostics and diagnostic imaging. Eur J Radiol 70(2): 232-241, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.01.050.
M. Zhou, A. Leung, S. Echegaray, A. Gentles, J.B. Shrager, K.C. Jensen, G.J. Berry, S.K. Plevritis, D.L. Rubin, S. Napel, O. Gevaert: Non-small cell lung cancer radiogenomics map identifies relationships between molecular and imaging phenotypes with prognostic implications. Radiology 286(1): 307-315, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017161845.
YQ Huang, CH Liang, L He, J Tian, CS Liang, X Chen, ZL Ma, ZY Liu: Development and validation of a radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 34(18): 2157-64, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.65.9128.
H.J.W.L. Aerts, E.R. Velazquez, R.T.H. Leijenaar, C. Parmar, P. Grossmann, S. Cavalho, J. Bussink, R. Monshouwer, B. Haibe-Kains, D. Rietveld, F. Hoebers, M.M. Rietbergen, C.R. Leemans, A. Dekker, J. Quackenbush, R.J. Gillies, P. Lambin: Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat Commun 5: 4006, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5006.
M. Vallières, C.R. Freeman, S.R. Skamene, I. El Naqa: A radiomics model from joint FDG-PET and MRI texture features for the prediction of lung metastases in soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities. Phys Med Biol 60(14): 5471-5496, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/60/14/5471.
H.J. Yoon, I. Sohn, J.H. Cho, H.Y. Lee, J.H. Kim, Y. La Choi, H. Kim, G. Lee, K.S. Lee, J. Kim: Decoding tumor phenotypes for ALK, ROS1, and RET fusions in lung adenocarcinoma using a radiomics approach. Medicine (Baltimore) 94(41): e1753, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000001753.
D. Hong, K. Xu, L. Zhang, X. Wan, Y. Guo: Radiomics signature as a predictive factor for EGFR mutations in advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol 10: 28, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00028.
Y. Liu, J. Kim, Y. Balagurunathan, Q. Li, A.L. Garcia, O. Stringfield, Z. Ye, R.J. Gillies: Radiomic features are associated with EGFR mutation status in lung adenocarcinomas. Clin Lung Cancer 17(5): 441-448.e6, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2016.02.001.
J. Song, J. Shi, D. Dong, M. Fang, W. Zhong, K. Wang, N. Wu, Y. Huang, Z. Liu, Y. Cheng, Y. Gan, Y. Zhou, P. Zhou, B. Chen, C. Liang, Z. Liu, W. Li, J. Tian: A new approach to predict progression-free survival in stage IV EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients with EGFR-TKI therapy. Clin Cancer Res 24(15): 3583-3592, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2507.
W. Tu, G. Sun, L. Fan, Y. Wang, Y. Xia, Y. Guan, Q. Li, D. Zhang, S. Liu, Z. Li: Radiomics signature: a potential and incremental predictor for EGFR mutation status in NSCLC patients, comparison with CT morphology. Lung Cancer 132: 28-35, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.03.025.
Z Sun, S Hu, Y Ge, J Wang, S Duan, J Song, C Hu, Y Li: Radiomics study for predicting the expression of PD-L1 in non-small cell lung cancer based on CT images and clinicopathologic features. J Xray Sci Technol 28(3):449–459, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3233/XST-190642.
J. Yoon, Y.J. Suh, K. Han, H. Cho, H.J. Lee, J. Hur, B.W. Choi: Utility of CT radiomics for prediction of PD-L1 expression in advanced lung adenocarcinomas. Thoracic Cancer 11(4): 993-1004, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13352.
Chinese Anti-Cancer Association, Lung Cancer Study Group of Committee of Oncopathology, Chinese Society of Lung Cancer, Expert Group on PD-L1 Testing Consensus: Chinese expert consensus on standards of PD-L1 immunohistochemistry testing for non-small cell lung cancer (in Chinese). Chin J Lung Cancer 23(9): 733-740, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2020.101.43.
A Zwanenburg, M Vallières, MA. Abdalah, HJWL. Aerts, v Andrearczyk, A Apte, S Ashrafinia, S Bakas, RJ. Beukinga, R Boellaard, M Bogowicz, L Boldrini, I Buvat, GJR. Cook, C Davatzikos, A Depeursinge, MC Desseroit, N Dinapoli, CV Dinh, S Echegaray, IE Naqa, AY. Fedorov, R Gatta, RJ. Gillies, V Goh, M Götz, M Guckenberger, SM Ha, M Hatt, F Isensee, P Lambin, S Leger, RTH. Leijenaar, J Lenkowicz, F Lippert, A Losnegård, KH. Maier-Hein, O Morin, H Müller, S Napel, C Nioche, F Orlhac, S Pati, EAG. Pfaehler, A Rahmim, A Rao, J Scherer, MM Siddique, NM. Sijtsema, JS Fernandez, E Spezi, R Steenbakkers, S Tanadini-Lang, D Thorwarth, EGC. Troost, T Upadhaya, V Valentini, LV. Dijk, J Griethuysen, FHP. Velden, P Whybra, C Richter, S Löck: The image biomarker standardization initiative: standardized quantitative radiomics for high-throughput image-based phenotyping, Radiology 295(2): 328–338, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020191145.
J. Wang, C.J. Wu, M.L. Bao, J. Zhang, X.N. Wang, Y.D. Zhang: Machine learning-based analysis of MR radiomics can help to improve the diagnostic performance of PI-RADS v2 in clinically relevant prostate cancer. Eur Radiol 27(10): 4082-4090, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-4800-5.
A. Chalkidou, M.J. O’Doherty, P.K. Marsden: False discovery rates in PET and CT studies with texture features: a systematic review. PLoS One 10(5): e0124165, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124165.
I. Fornacon-Wood, C. Faivre-Finn, J.P.B. O’Connor, G.J. Price: Radiomics as a personalized medicine tool in lung cancer: separating the hope from the hype. Lung Cancer 146: 197-208, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.05.028.
H Borghaei, L Paz-Ares, L Horn, DR. Spigel, M Steins, NE. Ready, LQ. Chow, EE. Vokes, E Felip, E Holgado, F Barlesi, M Kohlhäufl, O Arrieta, MA Burgio, J Fayette, H Lena, E Poddubskaya, DE. Gerber, SN. Gettinger, CM. Rudin, N Rizvi, L Crinò, GR. Blumenschein, SJ. Antonia, C Dorange, CT. Harbison, FG Finckenstein, JR. Brahmer: Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373(17):1627–39, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1507643.
P. Lambin, R.T.H. Leijenaar, T.M. Deist, J. Peerlings, E.E.C. De Jong, J. Van Timmeren, S. Sanduleanu, R.T.H.M. Larue, A.J.G. Even, A. Jochems, Y. Van Wijk, H. Woodruff, J. Van Soest, T. Lustberg, E. Roelofs, W. Van Elmpt, A. Dekker, F.M. Mottaghy, J.E. Wildberger, S. Walsh: Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14(12): 749-762, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.141.
H Kim, JH Chung: PD-L1 testing in non-small cell lung cancer: past, present, and future. J Pathol Transl Med 53(4): 199-206, 2019. https://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2019.04.24.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC61971271, NSFC81701656, NSFC81172133, NSFC81372413), the Taishan Scholars Project of Shandong Province (Tsqn20161023) and the Primary Research and Development Plan of Shandong Province (No. 2018GGX101018, No. 2019QYTPY020), the Special Fund for Scientific Research in the Public Interest (201402011), the Projects of Medical and Health Technology Development Program in Shandong Province (2014WS0058), and the Outstanding Youth Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (JQ201423).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University and Shandong Cancer Hospital. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Z., Dong, Y., Yang, L. et al. CT-Based Hand-crafted Radiomic Signatures Can Predict PD-L1 Expression Levels in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: a Two-Center Study. J Digit Imaging 34, 1073–1085 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-021-00484-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-021-00484-9