Abstract
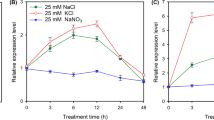
A number of cyclic nucleotide gated channel (CNGC) genes have been identified in plant genomes, but their functions are mainly undefined. In this study, we identified the role of CNGC10 in the response of Arabidopsis thaliana to salt stress. The cngc10 T-DNA insertion mutant showed greater tolerance to salt than wild-type A. thaliana during seed germination and seedling growth. The cngc10 mutant accumulated less Na+ and K+, but not less Ca2+, in shoots in response to salt stress. By contrast, overexpression of CNGC10 resulted in greater sensitivity to salt stress, and complementation of this gene recovered salt sensitivity. In response to salt stress, heterologous expression of CNGC10 in the Na+ sensitive yeast mutant strain B31 inhibited growth due to accumulation of Na+ at a rate greater than that of yeast transformed with an empty vector. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis demonstrated that CNGC10 was expressed mainly in roots and flowers. GUS analysis of a root cross section indicated that CNGC10 was expressed mainly in the endodermis and epidermis. Furthermore, the expression of CNGC10 in roots was dramatically inhibited by exposure to 200 mM NaCl for 6 h. These data suggest that CNGC10 negatively regulates salt tolerance in A. thaliana and may be involved in mediating Na+ transport.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali R, Ma W, Lemtiri-Chlieh F, Tsaltas D, Leng Q, von Bodman S, Berkowitz GA (2007) Death don’t have no mercy and neither does calcium: Arabidopsis cyclic nucleotide gated channel 2 and innate immunity. Plant Cell 19:1081–1095
Apse MP, Blumwald E (2007) Na+ transport in plants. FEBS Lett 581:2247–2254
Bañuelos MA, Sychrová H, Bleykasten-Grosshans C, Souciet JL, Potier S (1998) The Nha1 antiporter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mediates sodium and potassium efflux. Microbiology 144:2749–2758
Borsics T, Webb D, Andeme-Ondzighi C, Staehelin LA, Christopher DA (2007) The cyclic nucleotide-gated calmodulin-binding channel AtCNGC10 localizes to the plasma membrane and influences numerous growth responses and starch accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 225:563–573
Chen YF, Li LQ, Xu Q, Kong YH, Wang H, Wu WH (2009) The WRKY6 transcription factor modulates PHOSPHATE1 expression in response to low Pi stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:3554–3566
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Czechowski T, Stitt M, Altmann T, Udvardi MK, Scheible WR (2005) Genome-wide identification and testing of superior reference genes for transcript normalization in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:5–17
Daniel Gietz R, Woods RA (2002) Transformation of yeast by lithium acetate/single-stranded carrier DNA/polyethylene glycol method. Methods Enzymol 350:87–96
Demidchik V, Tester M (2002) Sodium fluxes through nonselective cationchannels in the plasma membrane of protoplasts from Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol 128:379–387
Dietrich P, Anschutz U, Kugler A, Becker D (2010) Physiology and biophysics of plant ligand-gated ion channels. Plant Biol 12(Suppl. 1):80–93
Essah PA, Davenport R, Tester M (2003) Sodium influx and accumulation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 133:307–318
Finka A, Cuendet AF, Maathuis FJ, Saidi Y, Goloubinoff P (2012) Plasma membrane cyclic nucleotide gated calcium channels control land plant thermal sensing and acquired thermotolerance. Plant Cell 24:3333–3348
Frietsch S, Wang YF, Sladek C, Poulsen LR, Romanowsky SM, Schroeder JI, Harper JF (2007) A cyclic nucleotide-gated channel is essential for polarized tip growth of pollen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:14531–14536
Gobert A, Park G, Amtmann A, Sanders D, Maathuis FJ (2006) Arabidopsis thaliana cyclic nucleotide gated channel 3 forms a non-selective ion transporter involved in germination and cation transport. J Exp Bot 57:791–800
Guo KM, Babourina O, Christopher DA, Borsics T, Rengel Z (2008) The cyclic nucleotide-gated channel, AtCNGC10, influences salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Physiol Plant 134:499–507
Guo KM, Babourina O, Christopher DA, Borsics T, Rengel Z (2010) The cyclic nucleotide-gated channel AtCNGC10 transports Ca2+ and Mg2+ in Arabidopsis. Physiol Plant 139:303–312
Hasegawa PM (2013) Sodium (Na+) homeostasis and salt tolerance of plants. Environ Exp Bot 92:19–31
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Kader MA, Lindberg S (2010) Cytosolic calcium and pH signaling in plants under salinity stress. Plant Signal Behav 5:233–238
Kugler A, Köhler B, Palme K, Wolff P, Dietrich P (2009) Salt-dependent regulation of a CNG channel subfamily in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 9:140
Leng Q, Mercier RW, Yao W, Berkowitz GA (1999) Cloning and first functional characterization of a plant cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel. Plant Physiol 121(3):753–761
Leng Q, Mercier RW, Hua BG, Fromm H, Berkowitz GA (2002) Electrophysiological analysis of cloned cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels. Plant Physiol 128:400–410
Li XL, Borsics T, Harrington HM, Christopher DA (2005) Arabidopsis AtCNGC10 rescues potassium channel mutants of E. coli, yeast and Arabidopsis and is regulated by calcium/calmodulin and cyclic GMP in E. coli. Funct Plant Biol 32:643–653
Ma W, Ali R, Berkowitz GA (2006) Characterization of plant phenotypes associated with loss of function of AtCNGC1, a plant cyclic nucleotide gated cation channel. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:494–505
Maathuis FJM, Filatov V, Herzyk P, Krijger GC, Axelsen BK, Chen S, Green BJ, Li Y, Madagan KL, Sánchez-Fernández R, Forde BG, Palmgren MG, Rea PA, Williams LE, Sanders D, Amtmann A (2003) Transcriptome analysis of root transporters reveals participation of multiple gene families in the response to cation stress. Plant J 35:675–692
Moeder W, Urquhart W, Ung H, Yoshioka K (2011) The role of cyclic nucleotide gated ion channels in plant immunity. Mol Plant 4:442–452
Møller IS, Gilliham M, Jha D, Mayo GM, Roy SJ, Coates JC, Haseloffa J, Tester M (2009) Shoot Na+ exclusion and increased salinity tolerance engineered by cell type-specific alteration of Na+ transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21:2163–2178
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Peng YH, Zhu YF, Mao YQ, Wang SM, Su WA, Tang ZC (2004) Alkali grass resists salt stress through high K+ and an endodermis barrier to Na+. J Exp Bot 55:939–949
Plett DC, Møller IS (2010) Na+ transport in glycophytic plants: what we know and would like to know. Plant Cell Environ 33:612–626
Shi HZ, Ishitani M, Kim C, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6896–6901
Taiz L, Zeiger E (2002) Plant physiology, 3rd edn. Sinauer Associates, Inc., Sunderland, Massachusetts, pp 105–107
Tyerman SD (2002) Nonselective cation channels. Multiple functions, commonalities. Plant Physiol 128:327–328
Wang YF, Munemasa S, Nishimura N, Ren HM, Robert N, Han M, Puzõrjova I, Kollist H, Lee S, Mori I, Schroeder JI (2013) Identification of cyclic GMP-activated nonselective Ca2+-permeable cation channels and associated CNGC5 & CNGC6 genes in Arabidopsis guard cells. Plant Physiol 163:578–590
Ward JM, Hirschi KD, Sze H (2003) Plants pass the salt. Trends Plant Sci 8:200–201
Xl Li, Borsics T, Harrington H, Christopher D (2005) Arabidopsis AtCNGC10 rescues potassium channel mutants of E. coli, yeast and Arabidopsis and is regulated by calcium/calmodulin and cyclic GMP in E. coli. Funct Plant Biol 32:643–653
Yamaguchi T, Hamamoto S, Uozumi N (2013) Sodium transport system in plant cells. Front Plant Sci 4:410
Yokoi S, Quintero FJ, Cubero B, Ruiz MT, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Pardo JM (2002) Differential expression and function of Arabidopsis thaliana NHX Na+/H+ antiporters in the salt stress response. Plant J 30:529–539
Yu IC, Parker J, Bent AF (1998) Gene-for-gene disease resistance without the hypersensitive response in Arabidopsis dnd1 mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7819–7824
Yu L, Nie J, Cao C, Jin Y, Yan M, Wang F, Liu J, Xiao Y, Liang Y, Zhang W (2010) Phosphatidic acid mediates salt stress response by regulation of MPK6 in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 188:762–773
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Alonso Rodríguez-Navarro (at Centro de Biotecnología y Genómica de Plantas, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid) to provide Na+ sensitive yeast mutant strain B31. This work is supported by grants from National Basic Research Program of China (2012CB114200), NSFC grants (31171461 and 91117003), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYTZ201402) to W Zhang, and grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (31100194 and 31470364) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYZ201423) to Q. Zhang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10265_2014_679_MOESM1_ESM.ppt
Supplementary material 1 (PPT 396 kb). Fig. S1 Salt tolerance of seedlings. a Expression of CNGC10 as determined by RT-PCR in shoots (top) and roots (bottom) of cngc10, over-expressing lines (OE-1, OE-3), complemented lines (COM-2, COM-5), and the WT. EF1α was used as the reference gene. b Four-day-old seedlings of cngc10, OE-1, OE-3, COM-2, COM-5, and WT were transferred to 1/2 MS (control) (top) or medium containing 200 mM NaCl (middle) or 400 mM mannitol (bottom). Photographs were taken on day 4 (NaCl treatment) or 14 (mannitol treatment or control). Fig. S2 Growth curves and ion contents of yeasts grown in Na+-free medium. a Growth curves of CNGC10-, HKT1;1-, and pYES2-transformed B31 exhibited no obvious difference in Na+-free AP medium. b Na+ contents in yeasts grown for 8 h in liquid Na+-free AP medium. c K+ contents in yeasts grown for 8 h in liquid Na+-free AP medium. d Ca2+ contents in yeasts after growth for 8 h in liquid Na+-free AP medium. Values are mean ± SE (n = 5)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Y., Jing, W., Zhang, Q. et al. Cyclic nucleotide gated channel 10 negatively regulates salt tolerance by mediating Na+ transport in Arabidopsis . J Plant Res 128, 211–220 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-014-0679-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-014-0679-2