Abstract
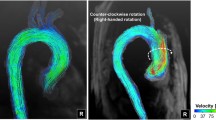
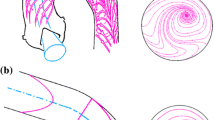
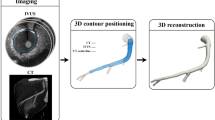
The hemodynamics within the aorta of five healthy humans were investigated to gain insight into the complex helical flow patterns that arise from the existence of asymmetries in the aortic region. The adopted approach is aimed at (1) overcoming the relative paucity of quantitative data regarding helical blood flow dynamics in the human aorta and (2) identifying common characteristics in physiological aortic flow topology, in terms of its helical content. Four-dimensional phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging (4D PC MRI) was combined with algorithms for the calculation of advanced fluid dynamics in this study. These algorithms allowed us to obtain a 4D representation of intra-aortic flow fields and to quantify the aortic helical flow. For our purposes, helicity was used as a measure of the alignment of the velocity and the vorticity. There were two key findings of our study: (1) intra-individual analysis revealed a statistically significant difference in the helical content at different phases of systole and (2) group analysis suggested that aortic helical blood flow dynamics is an emerging behavior that is common to normal individuals. Our results also suggest that helical flow might be caused by natural optimization of fluid transport processes in the cardiovascular system, aimed at obtaining efficient perfusion. The approach here applied to assess in vivo helical blood flow could be the starting point to elucidate the role played by helicity in the generation and decay of rotating flows in the thoracic aorta.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirbekian S, Long RC, Consolini MA, Suo J, Willett NJ, Fielden SW, Giddens DP, Taylor WR, Oshinski JN (2009) In vivo assessment of blood flow patterns in abdominal aorta of mice with MRI: implications for AAA localization. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297: H1290–H1295
Baciewicz FA, Penney DG, Marinelli WA, Marinelli R (1991) Torsional ventricular motion and rotary blood flow. What is the clinical significance. Card Chron 5: 1–8
Bellhouse BJ, Talbot L (1969) The fluid mechanics of the aortic valve. J Fluid Mech 35: 721–736
Bera AK, Jarque CM (1981) Efficient tests for normality, homoscedasticity and serial independence of regression residuals: Monte Carlo evidence. Econ Lett 7(4): 313–318
Bogren HG, Buonocore MH (1999) 4D magnetic resonance velocity mapping of blood flow patterns in the aorta in young vs. elderly normal subjects. J Magn Reson Imaging 10: 861–869
Buonocore MH, Bogren HG (1999) Analysis of flow patterns using MRI. Int J Card Imaging 15: 99–103
Caro CG, Doorly DJ, Tarnawski M, Scott KT, Long Q, Dumoulin CL (1996) Non-planar curvature and branching of arteries and non-planar-type flow. Proc R Soc Lond A 452: 185–197
Chandran KB (1993) Flow dynamics in the human aorta. J Biomech Eng 115: 611–616
Chen Q, Chen S, Eyink GL (2003) The joint cascade of energy and helicity in three-dimensional turbulence. Phys Fluids 15: 361–374
Chen ZS, Fan YB, Deng XY, Xu Z (2009) Swirling flow can suppress flow disturbances in endovascular stents: a numerical study. ASAIO J 55(6): 543–549
Darmofal DL, Haimes R (1996) An analysis of 3D particle path integration algorithms. J Comput Phys 123: 182–195
David L, Esnault A, Calluaud D (2002) Comparison of techniques of interpolation for 2D and 3D velocimetry. In: Proceedings of the eleventh international symposium on applications of laser techniques to fluid mechanics, Lisbon
Fan Y, Xu Z, Jiang W, Deng X, Wang K, Sun A (2008) An S-type bypass can improve the hemodynamics in the bypassed arteries and suppress intimal hyperplasia along the host artery floor. J Biomech 41: 2498–2505
Firmin D, Keegan J (2001) Navigator echoes in cardiac magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 3: 183–193
Frazin LJ, Lanza G, Vonesh M, Khasho F, Spitzzeri C, McGee S, Mehlman D, Chandran KB, Talano J, McPherson D (1990) Functional chiral asymmetry in descending thoracic aorta. Circulation 82: 1985–1994
Frydrychowicz A, Harloff A, Jung B, Zaitsev M, Weigang E, Bley TA, Langer M, Hennig J, Markl M (2007) Time-resolved, 3-dimensional magnetic resonance flow analysis at 3 T: visualization of normal and pathological aortic vascular haemodynamics. J Comput Assist Tomogr 31: 9–15
Frydrychowicz A, Arnold R, Hirtler D, Schlensak C, Stalder AF, Hennig J, Langer M, Markl M (2008a) Multidirectional flow analysis by cardiovascular magnetic resonance in aneurysm development following repair of aortic coarctation. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 10(1): 30
Frydrychowicz A, Arnold R, Harloff A, Schlensak C, Hennig J, Langer M, Markl M (2008b) Images in cardiovascular medicine. In vivo dimensional flow connectivity mapping after extracardiac total cavopulmonary connection. Circulation 118: e16–e17
Gharib M, Rambod E, Kheradvar A, Sahn DJ, Dabiri JO (2006) Optimal vortex formation as an index of cardiac health. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 6305–6308
Grigioni M, Daniele C, Morbiducci U, Del Gaudio C, D’Avenio G, Balducci A, Barbaro V (2005) A mathematical description of blood spiral flow in vessels: application to a numerical study of flow in arterial bending. J Biomech 38: 1375–1386
Hope TA, Markl M, Wigström L, Alley MT, Miller DC, Herfkens RJ (2007) Comparison of flow patterns in ascending aortic aneurysms and volunteers using four-dimensional magnetic resonance velocity mapping. J Magn Reson Imaging 26: 1471–1479
Houston JG, Gandy SJ, Sheppard DG, Dick JB, Belch JJ, Stonebridge PA (2003) Two-dimensional flow quantitative MRI of aortic arch blood flow patterns: Effect of age, sex, and presence of carotid atheromatous disease on prevalence of spiral blood flow. J Magn Reson Imaging 18: 169–174
Kilner PJ, Yang GZ, Mohiaddin RH, Firmin DN, Longmore DB (1993) Helical and retrograde secondary flow patterns in the aortic arch studied by three-directional magnetic resonance velocity mapping. Circulation 88: 2235–2247
Kilner PJ, Yang GZ, Wilkes AJ, Mohiaddin RH, Firmin DN, Yacoub MH (2000) Asymmetric redirection of flow through the heart. Nature 404: 759–761
Kolmogorov AN (1956) Foundations of the theory of probability, 2nd English edn. Chelsea Publishing Company, New York (translation edited by Nathan Morrison)
Ku DN, Giddens DP (1983) Pulsatile flow in a model carotid bifurcation. Arteriosclerosis 3: 31–39
Liu X, Pu F, Fan Y, Deng X, Li D, Li S (2009) A numerical study on the flow of blood and the transport of LDL in the human aorta: the physiological significance of the helical flow in the aortic arch. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297: H163–H170
Malek AM, Alper SL, Izumo S (1999) Hemodynamic shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis. JAMA 282: 2035–2042
Markl M, Draney MT, Hope MD, Levin JM, Chan FP, Alley MT, Pelc NJ, Herfkens RJ (2004) Time-resolved 3-dimensional velocity mapping in the thoracic aorta: visualization of 3-directional blood flow patterns in healthy volunteers and patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr 28: 459–468
Markl M, Harloff A, Föll D, Langer M, Hennig J, Frydrychowicz A (2007) Sclerotic aortic valve: flow-sensitive 4-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging reveals 3 distinct flow-pattern changes. Circulation 116: e336–e337
Marsden AL, Feinstein JA, Taylor CA (2008) A computational framework for derivative-free optimization of cardiovascular geometries. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197: 1890–1905
Mininni PD, Alexakis A, Pouquet A (2006) Large scale flow effects, energy transfer, and self-similarity on turbulence. Phys Rev E 74: 016303
Moffatt HK (1969) The degree of knottedness of tangled vortex lines. J Fluid Mech 36: 17–29
Moffatt HK (1990) The energy spectrum of knots and links. Nature 347: 367–369
Moffatt HK, Tsinober A (1992) Helicity in laminar and turbulent flow. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 24: 281–312
Morbiducci U, Ponzini R, Grigioni M, Redaelli A (2007a) Helical flow as fluid dynamic signature for atherogenesis in aortocoronary bypass. A numeric study. J Biomech 40: 519–534
Morbiducci U, Lemma M, Ponzini R, Boi A, Bondavalli L, Antona C, Montevecchi FM, Redaelli A (2007b) Does flow dynamics of the magnetic vascular coupling for distal anastomosis in coronary artery bypass grafting contribute to the risk of graft failure. Int J Artif Organs 30: 628–639
Morbiducci U, Ponzini R, Rizzo G, Cadioli M, Esposito A, De Cobelli F, Del Maschio A, Montevecchi FM, Redaelli A (2009a) In vivo quantification of helical blood flow in human aorta by time-resolved three-dimensional cine phase contrast MRI. Ann Biomed Eng 37: 516–531
Morbiducci U, Ponzini R, Nobili M, Massai D, Montevecchi FM, Bluestein D, Redaelli A (2009b) Blood damage safety of prosthetic heart valves. Shear induced platelet activation and local flow dynamics: a fluid-structure interaction approach. J Biomech 42(12): 1952–1960
Morbiducci U, Gallo D, Ponzini R, Massai D, Antiga L, Redaelli A, Montevecchi FM (2010) Quantitative analysis of bulk flow in image-based haemodynamic models of the carotid bifurcation: the influence of outflow conditions as test case. Ann Biomed Eng. doi:10.1007/s10439-010-0099-y
Ponzini R, Morbiducci U, Iannaccone F, Rizzo G, Cadioli M, Vismara R, Redaelli A (2009) Synthetic 4D phase contrast MRI datasets: a CFD-based approach for the validation of advanced fluid-dynamics calculations in vivo. In: Tavares JM, Natal Jorge RM (eds) Proceedings of VIPIMAGE 2009, Second Ecomas Thematic Conference on Computational Vision and Medical Image Processing, Porto. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, pp 195–199
Ricca RL (2009) Structural complexity and dynamical systems. In: Ricca RL (eds) Lectures on topological fluid mechanics. Lecture notes in mathematics. Springer, Berlin, pp 167–186
Seed WA, Wood NB (1971) Velocity patterns in the aorta. Cardiovasc Res 5: 319–330
Segadal L, Matre K (1987) Blood velocity distribution in the human ascending aorta. Circulation 76: 90–100
Shadden SC, Taylor CA (2008) Characterization of coherent structures in the cardiovascular system. Ann Biomed Eng 36(7): 1152–1162
Shadden SC, Astorino A, Gerbeau JF (2010) Computational analysis of an aortic valve jet with Lagrangian coherent structures. Chaos 20: 017512
Spilt A, Box FM, van Geest RJ, Reiber JH, Kunz P, Kamper AM, Blauw GJ, van Buchem MA (2002) Reproducibility of total cerebral blood flow measurements using phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 16: 1–5
Steinman DA (2000) Simulated pathline visualization of computed periodic blood flow patterns. J Biomech 33: 623–628
Stonebridge PA, Brophy CM (1991) Spiral laminar flow in arteries. Lancet 338: 1360–1361
Stonebridge PA, Hoskins PR, Allan PL, Belch JF (1996) Spiral laminar flow in vivo. Clin Sci (Lond) 91: 17–21
Sun A, Fan Y, Deng X (2009) Numerical investigation of blood flow in the distal end of an axis-deviated arterial bypass model. Biorheology 46: 83–92
Teitelbaum T, Mininni PD (2009) Effect of helicity and rotation on the free decay of turbulent flows. Phys Rev Lett 103: 014501
Tsinober A, Levich E (1983) On the helical nature of three dimensional coherent structures in turbulent flows. Phys Lett 99: 321–323
Weigang E, Kari FA, Beyersdorf F, Luehr M, Etz CD, Frydrychowicz A, Harloff A, Markl M (2008) Flow-sensitive four-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging: flow patterns in ascending aortic aneurysms. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 34: 11–16
Wigström L, Ebbers T, Fyrenius A, Karlsson M, Engvall J, Wranne B, Bolger AF (1999) Particle trace visualization of intracardiac flow using time-resolved 3D phase contrast MRI. Magn Reson Med 41: 793–799
Yashiro K, Shiratori H, Hamada H (2007) Haemodynamics determined by a genetic programme govern asymmetric development of the aortic arch. Nature 450: 285–288
Yearwood TL, Chandran KB (1982) Physiological pulsatile flow experiments in a model of the human aortic arch. J Biomech 15(9): 683–704
Zhan F, Fan Y, Deng X (2010) Swirling flow created in a glass tube suppressed platelet adhesion to the surface of the tube: its implication in the design of small-caliber arterial grafts. Thromb Res 125(5): 413–418
Zheng T, Fan Y, Xiong Y, Jiang W, Deng X (2009) Hemodynamic performance study on small diameter helical grafts. ASAIO J 55: 192–199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
The Below is the Electronic Supplementary Material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morbiducci, U., Ponzini, R., Rizzo, G. et al. Mechanistic insight into the physiological relevance of helical blood flow in the human aorta: an in vivo study. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 10, 339–355 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-010-0238-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-010-0238-2