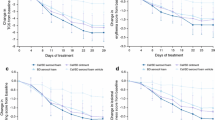
Background: Although betamethasone valerate (BMV) foam, 0.12% (Luxiq, Connectics Corporation, Palo Alto, CA) is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of corticosteroid-responsive scalp dermatoses, no data are available for its use on nonscalp psoriasis. Objective: We evaluated the safety and efficacy of BMV foam in treating psoriatic lesions at nonscalp sites. Methods: We conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, paired-comparison, split-body study of 40 patients with mild to moderate plaque-type psoriasis. Patients applied BMV foam and placebo foam twice daily for 12 weeks. Results: At the end of the treatment period, 70% of patients had greater than 50% improvement of lesions on their active foam-treated side compared with 24% of patients with similar improvement on their placebo foam-treated side. Adverse effects were limited to temporary stinging, burning, or itching in several patients. Three patients (7.5%) withdrew because of stinging or itching. Conclusions: The results indicate that BMV foam is effective against nonscalp psoriasis. Twice-daily applications are well tolerated, compliance exceeds 90%, cosmetic characteristics are acceptable, and the medication may reduce the need for multiple prescriptions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Stein, L., Sherr, A., Solodkina, G. et al. Betamethasone Valerate Foam for Treatment of Nonscalp Psoriasis. JCMS 5, 303–307 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10227-001-0006-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10227-001-0006-0