Abstract:
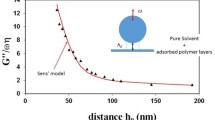
We present an experimental study of the adsorption of hydrophobic highly charged polyelectrolytes on a neutral and hydrophobic surface, the air/water interface. The polymer was a randomly sulphonated polystyrene with charge fractions between 0.3 and 0.9 and the adsorbed layers were characterised by Langmuir through measurements, ellipsometry and X-ray reflectivity. The adsorption rate is always very slow and the resulting layers are very thin (< 3 nm). A maximum of adsorption with the charge fraction is observed which we relate to the conformation of the chains in solution. We show that adsorption is partially irreversible, strongly hysteretic and that the state of an adsorbed layer depends on its history.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 16 June 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Théodoly, O., Ober, R. & Williams, C. Adsorption of hydrophobic polyelectrolytes at the air/water interface: Conformational effect and history dependence. Eur. Phys. J. E 5, 51–58 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s101890170086
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s101890170086