Abstract
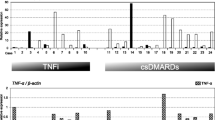
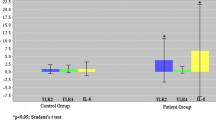
Interleukin-17 is a proinflammatory cytokine. Recent animal studies have shown that IL-17 plays a role in the initiation and progression of arthritis. However, whether IL-17 has a prominent role in human rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or not remains unclear. Here we investigated the role of IL-17 in patients with RA. cDNA was prepared from knee joint synovial tissues of RA (n = 11) and osteoarthritic (OA, n = 10) patients and PBMC of RA (n = 52) and healthy subjects (n = 34). IL-17 gene expression level was measured by real-time PCR, and was compared with various clinical parameters. IL-17 gene expression in synovial tissues of RA was similar to that in OA. IL-17 gene expression level in PBMC of RA patients was significantly higher than in the control. The response (changes in DAS) to two-week treatment with anti-TNF-α blockers (infliximab or etanercept) did not correlate with changes in IL-17 gene expression levels. The IL-17/TNF-α gene expression ratio at baseline (before treatment) tended to be lower in responders to the treatment. Expression of IL-17 gene in PBMC may be associated with the inflammatory process of RA. IL-17/TNF-α expression ratio is a potentially suitable marker of response to anti-TNF-α therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arner EC, Pratta MA. Independent effects of interleukin-1 on proteoglycan breakdown, proteoglycan synthesis, and prostaglandin E2 release from cartilage in organ culture. Arthritis Rheum 1989;32:288–97.
Arend WP, Dayer J-M. Inhibition of the production and effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor α in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38:151–60.
Van de Loo FAJ, Joosten LAB, van Lent PLEM, Arntz OJ, van den Berg WB. Role of interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor α, and interleukin-6 in cartilage proteoglycan metabolism and destruction: effect of in situ blocking in murine antigen- and zymosan-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38:164–72.
Shanahan JC, St Clair W. Tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade: a novel therapy for rheumatic disease. Clin Immunol 2002;103:231–42.
Nishimoto N, Yoshizaki K, Miyasaka N, Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody: a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:1761–9.
Dayer JM, Feige U, Edwards CK 3rd, Burger D. Anti-interleukin-1 therapy in rheumatic diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2001;13:170–6.
Yao Z, Painter SL, Fanslow WC, Ulrich D, Macduff BM, Spriggs MK, et al. Human IL-17: a novel cytokine derived from T cells. J Immunol 1995;155:5483–6.
Fossiez F, Djossou O, Chomarat P, Flores-Romo L, Ait-Yahia S, Maat C, et al. T cell interleukin-17 induces stromal cells to produce proinflammatory and hematopoietic cytokines. J Exp Med 1996;183:2593–603.
Aggarwal S, Gurney AL. IL-17: prototype member of an emerging cytokine family. J Leukoc Biol 2002;71:1.
Nakae S, Nambu A, Sudo K, Iwakura Y. Suppression of immune induction of collagen-induced arthritis in IL-17-deficient mice. J Immunol 2003;171:6173–7.
Nakae S, Saijo S, Horai R, Sudo K, Mori S, Iwakura Y. IL-17 production from activated T cells is required for the spontaneous development of destructive arthritis in mice deficient in IL-1 receptor antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003;100:5986–90.
Lubberts E, Joosten LA, Oppers B, van den Bersselaar L, Coenen-de Roo CJ, Kolls JK, et al. IL-1-independent role of IL-17 in synovial inflammation and joint destruction during collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol 2001;167:1004–13.
Lubberts E, Koenders MI, Oppers-Walgreen B, van den Bersselaar L, Coenen-de Roo CJ, Joosten LA, et al. Treatment with a neutralizing anti-murine interleukin-17 antibody after the onset of collagen-induced arthritis reduces joint inflammation, cartilage destruction, and bone erosion. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:650–9.
Koenders MI, Lubberts E, Oppers-Walgreen B, van den Bersselaar L, Helsen MM, Di Padova FE, et al. Blocking of interleukin-17 during reactivation of experimental arthritis prevents joint inflammation and bone erosion by decreasing RANKL and interleukin-1. Am J Pathol 2005;167:141–9.
Koenders MI, Kolls JK, Oppers-Walgreen B, van den Bersselaar L, Joosten LA, Schurr JR, et al. Interleukin-17 receptor deficiency results in impaired synovial expression of interleukin-1 and matrix metalloproteinases 3, 9, and 13 and prevents cartilage destruction during chronic reactivated streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:3239–47.
Chabaud M, Durand JM, Miossec P. Human interleukin-17: a T cell-derived proinflammatory cytokine produced by the rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum 1999;42:963–70.
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Matsuzaki K, Itoh K, Ishiyama S, et al. IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis. J Clin Invest 1999;103:1345–52.
Ziolkowska M, Koc A, Maslinski W. High levels of IL-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients: IL-15 triggers in vitro IL-17 production via cyclosporin A-sensitive mechanism. J Immunol 2000;164:2832–8.
Chen YF, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Jowett S, Bryan S, Clark W et al. A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimubub, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic exaluation of their cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess 2006;10:1–229.
Katz Y, Nadiv O, Beer Y. Interleukin-17 enhances tumor necrosis factor-α induced synthesis of interleukins 1,6, and 8 in skin and synovial fibroblasts: a possible role as a “fine-tuning cytokine” in inflammation processes. Arthritis Rheum 2001;44:2176–84.
LeGrand A, Fermor B, Fink C, Pisetsky DS, Weinberg JB, Vail TP, et al. Interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin-17 synergistically up-regulate nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production in explants of human osteoarthritic knee menisci. Arthritis Rheum 2001;44:2078–83.
Koenders MI, Lubberts E, van de Loo FA, Oppers-Walgreen B, van den Bersselaar L, Helsen MM, et al. Interleukin-17 acts independently of TNF-alpha under arthritic conditions. J Immunol 2006;176:6262–9.
Koenders MI, Joosten LA, van den Berg WB Potential new targets in arthritis therapy: interleukin (IL)-17 and its relation to tumour necrosis factor and IL-1 in experimental arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2006;65:29–33.
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31:315–24.
Honorati MC, Bovara M, Facchini A. Contribution of interleukin 17 to human cartilage degradation and synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2002;10:799–807.
Wonq PK, Quinn JM, Sims NA, van Nieuwenhuijze A, Campbell IK, Wicks IP, et al. Interleukin-6 modulates production of T lymphocyte-derived cytokines in antigen-induced arthritis and drives inflammation-induced osteoclastogenesis. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:158–68.
Nishimoto N. Clinical benefits of anti-human IL-6 receptor antibody therapy. Clin Calcium 2007;17:562–8.
Mangan PR, Harrington LE, O’Quinn DB, Helms WS, Bullard DC, Elson CO, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta induces development of the T(H)17 lineage. Nature 2006;441:231–4.
Hirota K, Hashimoto M, Yoshitomi H, Tanaka S, Nomura T, Yamaguchi T, et al. T cell self-reactivity forms a cytokine milieu for spontaneous development of IL-17+ Th cells that cause autoimmune arthritis. J Exp Med 2007;204:41–7.
Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 2006;441:235–8.
Murphy CA, Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein W, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA, et al. Divergent pro- and antiinflammatory roles for IL-23 and IL-12 in joint autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med 2003;198:1951–7.
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ, Locksley RM, Stockinger B. TGF beta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17 producing T cells. Immunity 2006;24:179–89.
Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. T(H)-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol 2007;8:345–50.
Hirota K, Hashimoto M, Yoshitomi H, Tanaka S, Nomura T, Yamaguchi T, et al. T cell self-reactivity forms a cytokine milieu for spontaneous development of IL-17+ Th cells that cause autoimmune arthritis. J Exp Med 2007;204:41–7.
Gaffo A, Saag KG, Curtis JR. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2006;63:2451–65.
Mitoma H, Horiuchi T, Hatta N, Tsukamoto H, Harashima S, Kikuchi Y, et al. Infliximab induces potent anti-inflammatory responses by outside-to-inside signals through transmembrane TNF-α. Gastroenterology 2005;128:376–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kohno, M., Tsutsumi, A., Matsui, H. et al. Interleukin-17 gene expression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 18, 15–22 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-007-0015-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-007-0015-y