Abstract
Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors in China. Arsenic resistance protein 2 (Asr2) was reported to be important for microRNA (miR) biogenesis, and its depletion could reduce the levels of several miRs, including miR-21, which is over-expressed in HCC. We hypothesized that Ars2 is also overexpressed in HCC and may be involved in the biological properties of HCC.
Methods
Ars2 immunolabeling was evaluated in 132 HCCs. Ars2 immunolabeling, Ars2 qRT-PCR and miR-21 were evaluated in 20 HCCs and in paired normal tissues. Ars2 shRNA was transfected into SMCC-7721 and HepG2 HCC cells. The cell proliferation and expression of Ars2 and miR-21 were subsequently evaluated.
Results
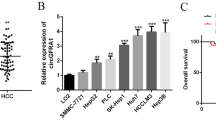
Ars2 was expressed primarily in the nucleus of HCC cells. The expression of Ars2 was statistically correlated with the loss of HCC differentiation and pathological stage. The survival rates of patients with low Ars2 expression in HCC were statistically higher than patients with overexpressed Ars2 in HCC. Ars2 and miR-21 were more highly expressed in HCC specimens than normal tissues, and they were also correlated. The knockdown of Ars2 in HCC cells inhibited miR-21 expression and cell proliferation.
Conclusions
Ars2 is overexpressed in HCC and may have prognostic value; it might play an important role in HCC proliferation and miR-21 expression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fares N, Peron JM (2013) Epidemiology, natural history, and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma. La Revue du praticien 63:216–217, 220–212
Tang ZY (2001) Hepatocellular carcinoma: cause, treatment and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol 7:445–454
Deshmukh M, Hoshida Y (2013) Genomic profiling of cell lines for personalized targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. doi:10.1002/hep.26407
Gruber JJ, Zatechka DS, Sabin LR et al (2009) Ars2 links the nuclear cap-binding complex to RNA interference and cell proliferation. Cell 138:328–339
Sabin LR, Zhou R, Gruber JJ et al (2009) Ars2 regulates both miRNA- and siRNA- dependent silencing and suppresses RNA virus infection in Drosophila. Cell 138:340–351
Beezhold KJ, Castranova V, Chen F (2010) Microprocessor of microRNAs: regulation and potential for therapeutic intervention. Mol Cancer 9:134
Gramantieri L, Fornari F, Callegari E et al (2008) MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 12:2189–2204
You N, Liu W, Wang T et al (2012) Swainsonine inhibits growth and potentiates the cytotoxic effect of paclitaxel in hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep 28:2091–2100
Matuo MC, de Oliveira Takamoto RT, Kikuchi IS et al (2013) Effect of bixin and norbixin on the expression of cytochrome P450 in HepG2 cell line. Cell Biol Int 37:843–848
He Q, Cai L, Shuai L et al (2013) Ars2 is overexpressed in human cholangiocarcinomas and its depletion increases PTEN and PDCD4 by decreasing microRNA-21. Mol Carcinog 52:286–296
Soman G, Yang X, Jiang H et al (2009) MTS dye based colorimetric CTLL-2 cell proliferation assay for product release and stability monitoring of interleukin-15: assay qualification, standardization and statistical analysis. J Immunol Methods 348:83–94
Andreu-Agullo C, Maurin T (2012) Ars2, an essential player in neural stem cell identity. Med Sci 28:459–462
Wilson MD, Wang D, Wagner R et al (2008) ARS2 is a conserved eukaryotic gene essential for early mammalian development. Mol Cell Biol 28:1503–1514
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y et al (2005) Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet 37:766–770
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB et al (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105
Lim LP, Lau NC, Weinstein EG et al (2003) The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev 17:991–1008
Morrisey EE (2010) The magic and mystery of miR-21. J Clin Invest 120:3817–3819
Bhatti I, Lee A, James V et al (2011) Knockdown of microRNA-21 inhibits proliferation and increases cell death by targeting programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg 15:199–208
Selaru FM, Olaru AV, Kan T et al (2009) MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in human cholangiocarcinoma and regulates programmed cell death 4 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3. Hepatology 49:1595–1601
Pezzolesi MG, Platzer P, Waite KA et al (2008) Differential expression of PTEN-targeting microRNAs miR-19a and miR-21 in Cowden syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 82:1141–1149
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) grants 81201948/H1617.
Conflict of interest
No author has any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Q. He and Y. Huang contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
He, Q., Huang, Y., Cai, L. et al. Expression and prognostic value of Ars2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol 19, 880–888 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-013-0642-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-013-0642-6