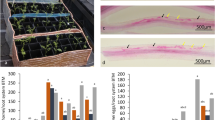
Abstract
Potato cyst nematodes (PCNs) are major pests worldwide that affect potato production. The molecular changes happening in the roots upon PCN infection are still unknown. Identification of transcripts and genes governing PCN resistance will help in the development of resistant varieties. Hence, differential gene expression of compatible (Kufri Jyoti) and incompatible (JEX/A-267) potato genotypes was studied before (0 DAI) and after (10 DAI) inoculation of Globodera rostochiensis J2s through RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq). Total sequencing reads generated ranged between 33 and 37 million per sample, with a read mapping of 48–84% to the potato reference genome. In the infected roots of the resistant genotype JEX/A-267, 516 genes were downregulated, and 566 were upregulated. In comparison, in the susceptible genotype Kufri Jyoti, 316 and 554 genes were downregulated and upregulated, respectively. Genes encoding cell wall proteins, zinc finger protein, WRKY transcription factors, MYB transcription factors, disease resistance proteins, and pathogenesis-related proteins were found to be majorly involved in the incompatible reaction after PCN infection in the resistant genotype, JEX/A-267. Furthermore, RNA-Seq results were validated through quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), and it was observed that ATP, FLAVO, CYTO, and GP genes were upregulated at 5 DAI, which was subsequently downregulated at 10 DAI. The genes encoding ATP, FLAVO, LBR, and GP were present in > 1.5 fold before infection in JEX-A/267 and upregulated 7.9- to 27.6-fold after 5 DAI; subsequently, most of these genes were downregulated to 0.9- to 2.8-fold, except LBR, which was again upregulated to 44.4-fold at 10 DAI.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets analyzed in this study are included in the manuscript. Additional data is available in the supplementary data files.
References
Alkharouf NW, Klink VP, Chouikha IB, Beard HS, MacDonald MH, Meyer S, Knap HT, Khan R, Matthews BF (2006) Timecourse microarray analyses reveal global changes in gene expression of susceptible Glycine max (soybean) roots during infection by Heterodera glycines (soybean cyst nematode). Planta 224:838–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0270-8
Bairwa A, Venkatasalam EP, Priyank HM, Sharma S (2021) Introduction of potato cyst nematodes, life cycle and their management through biobased amendments. In: Kaushal M, Prasad R (eds) Microbial biotechnology in crop protection. Springer, Singapore, pp 79–95
Bairwa A, Venkatasalam EP, Umamaheswari R, Sudha R, Singh BP (2017) Effect of cultural practices on potato cyst nematode population dynamics and potato tuber yield. Indian J Hortic 74:91–96. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-0112.2017.00021.4
Barone A, Ritter E, Schachtschabel U, Debener T, Salamini F, Gebhardt C (1990) Localization by restriction fragment length polymorphism mapping in potato of a major dominant gene conferring resistance to the potato cyst nematode Globodera rostochiensis. Mol Gen Genet 224:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271550
Bendahmane A, Kanyuka K, Baulcombe DC (1999) The Rx gene from potato controls separate virus resistance and cell death responses. Plant Cell 11:781–792. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.11.5.781
Bigeard J, Colcombet J, Hirt H (2015) Signaling mechanisms in pattern triggered immunity (PTI). Mol Plant 8:521–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.022
Bohra A, Rathore A, Gandham P, Saxena RK, Naik SJS, Dutta D, Singh IP, Singh F, Rathore M, Varshney RK, Singh NP (2021) Genome-wide comparative transcriptome analysis of the A4-CMS line ICPA 2043 and its maintainer ICPB 2043 during the floral bud development of pigeonpea. Funct Integr Genomics 21:2510–2263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-021-00775-y
Brosche M, Blomster T, Salojarvi J, Cui F, Sipari N, Leppala J, Lamminmaki A, Tomai G, Narayanasamy S, Reddy RA, Keinanen M, Overmyer K, Kangasjarvi J (2014) Transcriptomics and functional genomics of ROS-induced cell death regulation by radical-induced cell death. PLoS Genet 10:e1004112. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004112
Castelli L, Bryan G, Blok VC, Ramsay G, Phillips MS (2005) Investigation of resistance specificity amongst fifteen wild Solanum species to a range of Globodera pallida and G. rostochiensis populations. Nematology 7:689–699. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854105775143017
Chandrasekar S, Natarajan P, Mhatre PH, Mahajan M, Nivitha S, Palanisamy VE, Reddy UK, Sundararaj P (2022) RNA-seq of cyst nematode infestation of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.): a comparative transcriptome analysis of resistant and susceptible cultivars. Plants 11:1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11081008
Chin S, Behm CA, Mathesius U (2018) Functions of flavonoids in plant-nematode interactions. Plants 7:85. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants7040085
Elashry AM, Habash SS, Vijayapalani P, Brocke-Ahmadinejad N, Blumel R, Seetharam A, Schoof H, Grundler FMW (2020) Transcriptome and parasitome analysis of beet cyst nematode Heterodera schachtii. Sci Rep 10:3315. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60186-0
Eulgem T, Somssich IE (2007) Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:366–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.020
Gebhardt C, Bellin D, Henselewski H, Lehmann W, Schwarzfischer J, Valkonen JPT (2006) Marker-assisted combination of major genes for pathogen resistance in potato. Theor Appl Genet 112:1458–1464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0248-8
Goverse A, Overmars H, Engelbertink J, Schots A, Bakker J, Helder J (2000) Both induction and morphogenesis of cyst nematode feeding cells are mediated by auxin. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:1121–1129. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2000.13.10.1121
Grunewald W, Cannoot B, Friml J, Gheysen G (2009) Parasitic nematodes modulate PIN-mediated auxin transport to facilitate infection. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000266. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000266
Gupta SK, Rai AK, Kanwar SS, Sharma TR (2012) Comparative analysis of zinc finger proteins involved in plant disease resistance. PLoS One 7:e42578. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042578
Han Y, Zhao X, Cao G, Wang Y, Li Y, Liu D, Teng W, Zhang Z, Li D, Qiu L, Zheng H, Li W (2015) Genetic characteristics of soybean resistance to HG type 0 and HG type 1.2.3.5.7 of the cyst nematode analyzed by genome-wide association mapping. BMC Genom 16:598. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1800-1
Hirao T, Fukatsu E, Watanabe A (2012) Characterization of resistance to pine wood nematode infection in Pinus thunbergii using suppression subtractive hybridization. BMC Plant Biol 12:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-13
Hutangura P, Mathesius U, Jones MGK, Rolfe BG (1999) Auxin induction is a trigger for root gall formation caused by root-knot nematodes in white clover and is associated with the activation of the flavonoid pathway. Aust J Plant Physiol 26:221–231. https://doi.org/10.1071/PP98157
Hwang IS, Hwang BK (2010) Role of the pepper cytochrome P450 gene CaCYP450A in defense responses against microbial pathogens. Planta 232:1409–1421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1266-y
Ibrahim HMM, Hosseini P, Alkharouf NW, Hussein EHA, Gamal El-Din AEKY, Aly MAM, Matthews BF (2011) Analysis of gene expression in soybean (Glycine max) roots in response to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita using microarrays and KEGG pathways. BMC Genom 12:220. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-220
Ithal N, Recknor J, Nettleton D, Hearne L, Maier T, Baum TJ, Mitchum MG (2007a) Parallel genome-wide expression profiling of host and pathogen during soybean cyst nematode infection of soybean. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:293–305. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-20-3-0293
Ithal N, Recknor J, Nettleton D, Maier T, Baum TJ, Mitchum MG (2007b) Developmental transcript profiling of cyst nematode feeding cells in soybean roots. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:510–525. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-20-5-0510
Jain S, Chittem K, Brueggeman R, Osorno JM, Richards J, Nelson BD Jr (2016) Comparative transcriptome analysis of resistant and susceptible common bean genotypes in response to soybean cyst nematode infection. PLoS One 11:e0159338. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159338
Jiang J, Ma S, Ye N, Jiang M, Cao J, Zhang J (2017) WRKY transcription factors in plant responses to stresses. J Integr Plant Biol 59:86–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12513
Jones JT, Furlanetto C, Phillips MS (2007) The role of flavonoids produced in response to cyst nematode infection of Arabidopsis thaliana. Nematology 9:671–677. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854107782024875
Kandoth PK, Ithal N, Recknor J, Maier T, Nettleton D, Baum TJ, Mitchum MG (2011) The soybean Rhg1 locus for resistance to the soybean cyst nematode Heterodera glycines regulates the expression of a large number of stress- and defense-related genes in degenerating feeding cells. Plant Physiol 155:1960–1975. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.167536
Karczmarek A, Overmars H, Helder J, Goverse A (2004) Feeding cell development by cyst and root-knot nematodes involves a similar early, local and transient activation of a specific auxin-inducible promoter element. Mol Plant Pathol 5:343–346. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2004.00230.x
Kim JC, Lee SH, Cheong YH, Yoo CM, Lee SI, Chun HJ, Yun DJ, Hong JC, Lee SY, Lim CO, Cho MJ (2002) A novel cold-inducible zinc finger protein from soybean, SCOF-1, enhances cold tolerance in transgenic plants. Plant J 25:247–259. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.00947.x
Klug A, Rhodes D (1987) Zinc fingers: a novel protein motif for nucleic acid recognition. Trends Biochem Sci 12:464–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/0968-0004(87)90231-3
Kochetov AV, Glagoleva AY, Strygina KV, Khlestkina EK, Gerasimova SV, Ibragimova SM, Shatskaya NV, Vasilyev GV, Afonnikov DA, Shmakov NA, Antonova OY, Gavrilenko TA, Alpatyeva NV, Khiutti A, Afanasenko OS (2017) Differential expression of NBS-LRR encoding genes in the root transcriptomes of two Solanum phureja genotypes with contrasting resistance to Globodera rostochiensis. BMC Plant Biol 17:251. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1193-1
Krishna Prasad KS (2006) Potato cyst nematodes and their management in the Nilgiris (India). CPRI Technical Bulletin No. 77. Central Potato Research Institute, Shimla.
Kumar M, Gantasala NP, Roychowdhury T, Thakur PK, Shukla RN BP, MGK J, Rao U (2014) De novo transcriptome sequencing and analysis of the cereal cyst nematode, Heterodera avenae. PLoS ONE 9:e96311. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096311
Kyndt T, Nahar K, Haegeman A, De Vleesschauwer D, Hofte M, Gheysen G (2012) Comparing systemic defence-related gene expression changes upon migratory and sedentary nematode attack in rice. Plant Biol 14:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2011.00524.x
Lamb C, Dixon RA (1997) The oxidative burst in plant disease resistance. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 48:251–275. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.48.1.251
Lambert KN, Ferrie BJ, Nombela G, Brenner ED, Williamson VM (1999) Identification of genes whose transcripts accumulate rapidly in tomato after root-knot nematode infection. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 55:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1006/pmpp.1999.0239
Li J, Todd TC, Trick HN (2010) Rapid in planta evaluation of root expressed transgenes in chimeric soybean plants. Plant Cell Rep 29:113–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-009-0803-2
Li XY, Wang X, Zhang SP, Liu DW, Duan YX, Dong W (2011) Comparative profiling of the transcriptional response to soybean cyst nematode infection of soybean roots by deep sequencing. Chin Sci Bull 56:1904–1911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-011-4510-3
Liu F, Jiang H, Ye S, Chen WP, Liang W, Xu Y, Sun B, Sun J, Wang Q, Cohen JD, Li C (2010) The Arabidopsis P450 protein CYP82C2 modulates jasmonate-induced root growth inhibition, defense gene expression and indole glucosinolate biosynthesis. Cell Res 20:539–552. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2010.36
Liu M, Li X, Liu Y, Cao B (2013) Regulation of flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene involved in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in response to UV-B radiation and drought stress in the desert plant, Reaumuria soongorica. Plant Physiol Biochem 73:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.09.016
Lozano-Torres JL, Wilbers RHP, Gawronski P, Boshoven JC, Finkers-Tomczak A, Cordewener JHG, America AHP, Overmars HA, Van't Klooster JW, Baranowski L, Sobczak M, Ilya M, van der Hoorn RAL, Schots A, de Wit PJGM, Bakker J, Goverse A, Smant G (2012) Dual disease resistance mediated by the immune receptor Cf-2 in tomato requires a common virulence target of a fungus and a nematode. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:10119–10124. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1202867109
Mahajan M, Yadav SK (2014) Overexpression of a tea flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene confers tolerance to salt stress and Alternaria solani in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 85:551–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-014-0203-z
Mangal V, Sood S, Bhardwaj V, Kumar V, Kumar A, Singh B, Dipta B, Dalamu D, Sharma S, Thakur AK, Singh R, Sharma AK, Kumar D (2023) Diagnostic PCR-based markers for biotic stress resistance breeding in potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.). Australas Plant Pathol 52:227–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-023-00915-x
Masoodi KZ, Ahmed N, Mir MA, Bhat B, Shafi A, Mansoor S, Rasool RS, Yaseen M, Dar ZA, Mir JI, Andrabi SM, Ganai NA (2022) Comparative transcriptomics unravels new genes imparting scab resistance in apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.). Funct Integr Genomics 22:315–1330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00889-x
Meng C, Zhang S, Deng YS, Wang GD, Kong FY (2015) Overexpression of a tomato flavanone 3-hydroxylase-like protein gene improves chilling tolerance in tobacco. Plant Physiol Biochem 96:388–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.08.019
Milczarek D, Flis B, Przetakiewicz A (2011) Suitability of molecular markers for selection of potatoes resistant to Globodera spp. Am J Pot Res 88:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-011-9189-0
Moatamedi M, Nasr-Esfahani M, Monazzah M, Faridan VG, Nasr-Esfahani A, Ghadirzadeh E (2023) Transcriptome-proteomic analysis associated with resistance to wheat cyst nematode Heterodera filipjevi. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 125:102024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2023.102024
Molinari S, Fanelli E, Leonetti P (2014) Expression of tomato salicylic acid (SA)-responsive pathogenesis-related genes in Mi-1-mediated and SA-induced resistance to root-knot nematodes. Mol Plant Pathol 15:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12085
Moriya Y, Itoh M, Okuda S, Yoshizawa AC, Kanehisa M (2007) KAAS: an automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W182–W185. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm321
Nahar K, Kyndt T, De Vleesschauwer D, Hofte M, Gheysen G (2011) The jasmonate pathway is a key player in systemically induced defence against root-knot nematodes in rice. Plant Physiol 157:305–316. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.177576
Niebel A, De Almeida EJ, Tire C, Engler G, Van Montagu M, Gheysen G (1993) lnduction patterns of an extensin gene in tobacco upon nematode infection. Plant Cell 5:1697–1710. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.5.12.1697
Onyilo F (2011) Identification of candidate genes for the potato cyst nematode resistance locus Grp1. MSc Thesis,. Ghent University
Paal J, Henselewski H, Muth J, Meksem K, Menendez CM, Salamini F, Ballvora A, Gebhardt C (2004) Molecular cloning of the potato Gro1-4 gene conferring resistance to pathotype Ro1 of the root cyst nematode Globodera rostochiensis, based on a candidate gene approach. Plant J 38:285–297. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02047.x
Pandey SP, Somssich IE (2009) The role of WRKY transcription factors in plant immunity. Plant Physiol 150:1648–1655. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.138990
Park CJ, An JM, Shin YC, Kim KJ, Lee BJ, Paek KH (2004) Molecular characterization of pepper germin-like protein as the novel PR-16 family of pathogenesis-related proteins isolated during the resistance response to viral and bacterial infection. Planta 219:797–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1290-x
Sabeh M, Lord E, Grenier E, St-Arnaud M, Mimee B (2019) What determines host specificity in hyperspecialised plant parasitic nematodes? BMC Genom 20:457. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5853-4
Sanchez-Fernandez R, Davies TGE, Coleman JOD, Rea PA (2001) The Arabidopsis thaliana ABC protein superfamily, a complete inventory. J Biol Chem 276:30231–30244. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M103104200
Sattarzadeh A, Achenbach U, Lubeck J, Strahwald J, Tacke E, Hofferbert HR, Rothsteyn T, Gebhardt C (2006) Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping as basis for developing a PCR-based marker highly diagnostic for potato varieties with high resistance to Globodera pallida pathotype Pa2/3. Mol Breed 18:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9026-1
Sobczak M, Avrova A, Jupowicz J, Phillips MS, Ernst K, Kumar A (2005) Characterization of susceptibility and resistance responses to potato cyst nematode (Globodera spp.) infection of tomato lines in the absence and presence of the broad-spectrum nematode resistance Hero gene. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:58–168. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-18-0158
Song X, Diao J, Ji J, Wang G, Guan C, Jin C, Wang Y (2016) Molecular cloning and identification of a flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene from Lycium chinense, and its overexpression enhances drought stress in tobacco. Plant Physiol Biochem 98:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.11.011
Sun Y, Xia XL, Jiang JF, Chen SM, Chen FD, Lv GS (2016) Salicylic acid-induced changes in physiological parameters and genes of the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in Artemisia vulgaris and Dendranthema nankingense during aphid feeding. Genet Mol Res. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr.15017546
Swiecicka M, Filipecki M, Lont D, Vlient JV, Qin L, Goverse A, Bakker J, Helder J (2009) Dynamics in the tomato root transcriptome on infection with the potato cyst nematode Globodera rostochiensis. Mol Plant Pathol 10:487–500. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00550.x
Szakasits D, Heinen P, Wieczorek K, Hofmann J, Wagner F, Kreil DP, Sykacek P, Grundler FMW, Bohlmann H (2009) The transcriptome of syncytia induced by the cyst nematode Heterodera schachtii in Arabidopsis roots. Plant J 57:771–784. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03727.x
Uehara T, Sugiyama S, Masuta C (2007) Comparative serial analysis of gene expression of transcript profiles of tomato roots infected with cyst nematode. Plant Mol Biol 63:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-006-9081-3
Uehara T, Sugiyama S, Matsuura H, Arie T, Masuta C (2010) Resistant and susceptible responses in tomato to cyst nematode are differentially regulated by salicylic acid. Plant Cell Physio 51:1524–1536. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcq109
Urwin PE, Troth KM, Zubko EI, Atkinson HJ (2001) Effective transgenic resistance to Globodera pallida in potato field trials. Mol Breed 8:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011942003994
van der Voort JR, Lindeman W, Folkertsma R, Hutten R, Overmars H, van der Vossen E, Jacobsen E, Bakker J (1998) A QTL for broad-spectrum resistance to cyst nematode species (Globodera spp.) maps to a resistance gene cluster in potato. Theor Appl Genet 96:654–661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050785
van der Vossen EAG, van der Voort JNAMR, Kanyuka K, Bendahmane A, Sandbrink H, Baulcombe DC, Bakker J, Stiekema WJ, Klein-Lankhorst RM (2000) Homologues of a single resistance-gene cluster in potato confer resistance to distinct pathogens: a virus and a nematode. Plant J 23:567–576. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00814.x
Walter AJ, Willforss J, Lenman M, Alexandersson E, Andreasson E (2018) RNA seq analysis of potato cyst nematode interactions with resistant and susceptible potato roots. Eur J Plant Pathol 152:531–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1474-z
Wasson AP, Pellerone FI, Mathesius U (2006) Silencing the flavonoid pathway in Medicago truncatula inhibits root nodule formation and prevents auxin transport regulation by Rhizobia. Plant Cell 18:1617–1629. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.038232
Watkinson JI, Hendricks L, Sioson AA, Vasquez-Robinet C, Stromberg V, Heath LS, Schuler M, Bohnert HJ, Bonierbale M, Grene R (2006) Accessions of Solanum tuberosum ssp. andigena show differences in photosynthetic recovery after drought stress as reflected in gene expression profiles. Plant Sci 171:745–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2006.07.010
Wei L (2015) Reniform nematode (Rotylenchulus reniformis) manipulation of host root gene expression during syncytium formation in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Thesis, Clemson University, M.Sc
Williamson VM, Kumar A (2006) Nematode resistance in plants: the battle underground. Trends Genet 22:396–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2006.05.003
Wisniewska A, Dabrowska-Bronk J, Szafranski K, Fudali S, Swiecicka M, Czarny M, Wilkowska A, Morgiewicz K, Matusiak J, Sobczak M, Filipecki M (2013) Analysis of tomato gene promoters activated in syncytia induced in tomato and potato hairy roots by Globodera rostochiensis. Transgenic Res 22:557–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-012-9665-4
Wubben MJE II, Su H, Rodermel SR, Baum TJ (2001) Susceptibility to the sugar beet cyst nematode is modulated by ethylene signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14:1206–1212. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2001.14.10.1206
Xing L, Peng K, Xue S, Yuan W, Zhu B, Zhao P, Wu H, Cheng Y, Fang M, Liu Z (2022) Genome-wide analysis of zinc finger-homeodomain (ZF-HD) transcription factors in diploid and tetraploid cotton. Funct Integr Genomics 22:1269–1281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00913-0
Zasada I, Dandurand LM (2018) PCN by the Numbers. Globodera Alliance Newsletter https://www.globodera.org/sites/default/les/newsletters/Issue7. Accessed 14 Oct 2022
Zhang CL, Xu DC, Jiang XC, Zhou Y, Cui J, Zhang CX, Chen DF, Fowler MR, Elliott MC, Scott NW, Dewar AM, Slater A (2008) Genetic approaches to sustainable pest management in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). Ann Appl Biol 152:143–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2008.00228.x
Acknowledgements
We thank the Director, ICAR-CPRI, Shimla, for facilitating the study.
Funding
We acknowledge the financial help from the Centre for Agricultural Bioinformatics CABin project (1006448).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualized and designed the experiments: SS, VB and AB. Performed the experiments: AB, VB, SS, BD, AK, and BS. Phenotyping: EPV, PHM, AKS and SSh. Genotyping: SS, VB, AB, and SuS. Contributed material/facility: SSh, AKS, and VK. Analyzed the data: SS, SR, and TT. Wrote the manuscript: AB and SS. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consented to publish this manuscript in Functional & Integrative Genomics.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Human and animal ethics
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
Table S1. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and their functional annotation in resistant genotype after inoculation (XLSX 2179 kb)
ESM 2
Table S2. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and their functional annotation in susceptible genotype after inoculation (XLSX 2169 kb)
ESM 3
Table S3. Gene Ontology (GO) of upregulated genes in the resistant genotype (XLSX 10 kb)
ESM 4
Table S4. Gene Ontology (GO) of downregulated genes in the resistant genotype (XLSX 10 kb)
ESM 5
Table S5. Gene Ontology (GO) of upregulated genes in the susceptible genotype (XLSX 10 kb)
ESM 6
Table S6. Gene Ontology (GO) of downregulated genes in the susceptible genotype (XLSX 10 kb)
ESM 7
Fig. S1 Heat map of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in control KJC and JC samples (JPG 324 kb)
ESM 8
Fig. S2 Heat map of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in inoculated KJT and JT samples (JPG 400 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bairwa, A., Sood, S., Bhardwaj, V. et al. Identification of genes governing resistance to PCN (Globodera rostochiensis) through transcriptome analysis in Solanum tuberosum. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 242 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01164-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01164-3