Abstract
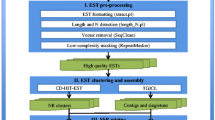
EST-derived microsatellites or simple sequence repeats (eSSR) occur in expressed sequence tags (EST). Here we report characteristics of eSSRs in the wheat genome, construction of consensus chromosome bin maps of SSR-containing ESTs (SSRESTs), and development of eSSR markers for the 21 wheat chromosomes. A Perl script known as MISA was used to identify eSSRs in wheat ESTs available in the database http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/cgi-bin/ace/search/wEST). Among 492,832 ESTs from the database, 36,520 (7.41%) contained 43,598 eSSRs. This is equivalent to 1 eSSR per 5.46 kb EST sequence. About 60% of the eSSRs were trinucleotides, 19.7% were mononucleotide, 16.7% were dinucleotides, and the remaining ∼3% consisted of tetra-, penta-, and hexanucleotides. Among the identified eSSRs, (CCG/CGG)n is the most frequent (20.5%) followed by (A/T)n at 13.6%, (AAC/GTT)n at 11.7%, and (AG/CT)n at 8.7%. Among ESTs previously mapped to wheat chromosome bins, a total of 1,010 eSSR loci were derived from 341 SSRESTs. Consensus chromosome bin maps showing the chromosome locations of SSRESTs, SSR sequence motif, and cDNA library were constructed. A χ 2 test indicated that the distribution pattern of eSSR loci was generally similar to that of the original mapped ESTs in the wheat genome. Forty-eight SSRESTs were converted into PCR-based eSSR markers, and 266 eSSR loci were mapped to specific chromosome arms using wheat cytogenetic stocks. The average polymorphism information content (0.45±0.16) of eSSR markers was lower than that reported for genomic SSRs (0.54±0.19), but higher than RFLPs (0.30±0.27). The eSSR markers were transferable among related Triticeae species, Triticum aestivum, T. durum, T. dicoccoides, Hordeum spontaneum, H. vulgare, and Secale cereale. The results confirm the presence of SSRs in expressed genes of wheat and demonstrate another application of ESTs in genomics research. eSSRs will be useful for gene tagging, gene cloning, and comparative genomics studies of cereal crops.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MD, Kelley JM, Gocayne JD, Dubnick M, Polymeropoulos MH et al (1991) Complementary DNA sequencing: expressed sequence tags and human genome project. Science 252:1651–1656
Anderson JA, Churchill GA, Autrique JE, Tanksley SD, Sorrells ME (1993) Optimizing parental selection for genetic linkage maps. Genome 36:181–186
Awadalla P, Ritland K (1997) Microsatellite variation and evolution in the Mimulus guttatus species complex with contrasting mating systems. Mol Biol Evol 14:1023–1034
Ayres NM, McClung AM, Larkin PD, Bligh HFJ, Jones CA et al (1997) Microsatellites and single-nucleotide polymorphism differentiate apparent amylase classes in an extended pedigree of US rice germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 94:773–781
Bao JS, Corke H, Sun M (2002) Microsatellites in starch-synthesizing genes in relation to starch physiochemical properties in waxy rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 105:898–905
Brown SW, AK Szewc-McFadden, S Kresovichi (1996) Development and application of simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci for plant genome analysis. In: Jauhar PP (ed) Methods of genome analysis in plants. CRC, Boca Raton, Fla., pp 147–159
Chin ECL, Senior ML, Shu H, Smith JSC (1996) Maize simple repetitive DNA sequences: abundance and allele variation. Genome 39:866–873
Conley E, Nduati V, Gonzalez-Hernande JL, Mesfin A, Trudeau-Spanjers M et al (2004) A 2,600-locus chromosome bin map of wheat group 2 reveals interstitial gene-rich islands and colinearity with rice. Genetics 168:625–637
Endo TR, Gill BS (1984) Somatic karyotype, heterochromatin distribution, and nature of chromosome differentiation in common wheat, Triticum aestivum L. em Thell. Chromosoma 89:361–369
Endo TR, Gill BS (1996) The deletion stocks of common wheat. J Hered 87:295–307
Eujayl I, Sorrells ME, Baum M, Wolters P, Powell W (2002) Isolation of EST-derived microsatellite markers for genotyping the A and B genomes of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:399–407
Gao L, Tang J, Li H, Jia J (2003) Analysis of microsatellites in major crops assessed by computational and experimental approaches. Mol Breed 12:245–261
Gill BS, Friebe B, Endo TR (1991) Standard karyotype and nomenclature system for description of chromosome bands and structural aberrations in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Genome 34:830–839
Hackauf B, Wehling P (2002) Identification of microsatellite polymorphisms in an expressed portion of the rye genome. Plant Breed 121:17–25
Holton TA, Christopher JT, McClure L, Harker N, Henry RJ (2002) Identification and mapping of polymorphic SSR markers from expressed gene sequences of barley and wheat. Mol Breed 9:63–71
Hossain KG, Kalavacharla V, Lazo GR, Hegstad J, Wentz MJ et al (2004) A chromosome bin map of 2,148 EST loci of wheat homoeologous group 7. Genetics 168:687–699
Huntington’s Disease Collaborative Research Group (1993) A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington’s disease chromosomes. Cell 72:971–983
Kantety RV, La Rota M, Matthews DE, Sorrells ME (2002) Data mining for simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags from barley, maize, rice, sorghum and wheat. Plant Mol Biol 48:501–510
Lazo GR, Chao S, Hummel DH, Edwards H, Crossman CC et al (2004) Development of an expressed sequence tag (EST) resource for wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): EST generation, unigene analysis, probe selection, and bioinformatics for a 16,000-locus bin-delineated map. Genetics 168:585–593
Li YC, Korol AB, Fahima T, Beiles A, Nevo E (2002) Microsatellites: genomic distribution, putative functions and mutational mechanisms: a review. Mol Ecol 11:2453–2465
Li YC, Korol AB, Fahima T, Nevo E (2004) Microsatellites within genes: structure, function and evolution. Mol Biol Evol 21:991–1007
Linkiewicz AM, Qi LL, Gill BS, Echalier B, Chao S et al (2004) A 2,500-locus bin map of wheat homoeologous group 5 provides new insights on gene distribution and colinearity with rice. Genetics 168:665–676
Litt M, Luty JA (1989) A hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiac muscle actin gene. Am J Hum Genet 44:397–401
Liu YG, Tsunewaki K (1991) Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of wheat. II. Linkage maps of the RFLP sites in common wheat. Jpn J Genet 66:617–633
Metzgar D, Bytof J, Wills C (2000) Selection against frameshift mutations limits microsatellite expansion in coding DNA. Genome Res 10:72–80
Mickelson-Young L, Endo TR, Gill BS (1995) A cytogenetic ladder-map of the wheat homoeologous group-4 chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 90:1007–1011
Miftahudin, Ross K, Ma XF, Mahmoud A, Layton J et al (2004) Analysis of EST loci on wheat chromosome group 4. Genetics 168:651–663
Morgante M, Hanafey M, Powell W (2002) Microsatellites are preferentially associated with nonrepetitive DNA in plant genomes. Nat Genet 30:194–200
Munkvold JD, Greene RA, Bermudez-Kandianis CE, La Rota CM, Edwards H et al (2004) Group 3 chromosome bin maps of wheat and their relationship to rice chromosome 1. Genetics 168:639–650
Nicot N, Chiquet V, Gandon B, Amilhat L, Legeai F et al (2004) Study of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers from wheat expressed sequence tags (ESTs). Theor Appl Genet 109:800–805
Peng JH (2000) Genomics of wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicoccoides: genetic maps, mapping of stripe rust resistance genes and QTLs for agronomic traits. PhD thesis, University of Haifa, Israel
Peng JH, Fahima T, Röder MS, Li YC, Dahan A et al (1999) Microsatellite tagging of stripe-rust resistance gene YrH52 derived from wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicoccoides, and suggestive negative crossover interference on chromosome 1B. Theor Appl Genet 98:862–872
Peng JH, Fahima T, Röder MS, Huang QY, Dahan A et al (2000a) High-density molecular map of chromosome region harboring stripe-rust resistance gene YrH52 and Yr15 derived from wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicccoides. Genetica 109:199–210
Peng JH, Fahima T, Röder MS, Li YC, Grama A et al (2000b) Microsatellite high-density mapping of stripe-rust resistance gene YrH52 region on chromosome 1B and evaluation of its marker-assisted selection in F2 generation in wild emmer wheat. New Phytol 146:141–154
Peng JH, Korol AB, Fahima T, Röder MS, Ronin YI et al (2000c) Molecular genetic maps in wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicoccoides: genome-wide coverage, massive negative interference, and putative quasi-linkage. Genome Res 10:509–1531
Peng JH, Ronin YI, Fahima T, Röder MS, Li YC et al (2003) Domestication quantitative trait loci in Triticum dicoccoides, the progenitor of wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2489–2494
Peng JH, Zadeh H, Lazo GR, Gustafson JP, Chao S et al (2004) Chromosome bin map of expressed sequence tags in homoeologous group 1 of hexaploid wheat and homoeology with rice and Arabidopsis. Genetics 168:609–623
Qi LL, B Echalier, Chao S, Lazo GR, Butler GE et al (2004) A chromosome bin map of 16,000 EST loci and distribution of genes among the three genomes of polyploid wheat. Genetics 168:701–712
Randhawa HS, Dilbirligi M, Sidhu D, Erayman M, Sandhu D et al (2004) Deletion mapping of homoeologous group 6-specific wheat ESTs. Genetics 168:677–686
Röder MS, Plaschke J, König SU, Börner A, Sorrells ME et al (1995) Abundance, variability and chromosomal location of microsatellites in wheat. Mol Gen Genet 246:327–333
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH et al (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Saha MC, Rouf Mian MA, Eujayl I, Zwonitzer JC, Wang L et al (2004) Tall fescue EST-SSR markers with transferability across several grass species. Theor Appl Genet 109:783–791
Schlötterer C (2000) Evolutionary dynamics of microsatellite DNA. Chromosoma 109:365–371
Schlötterer C, Wiehe T (1999) Microsatellite, a neutral marker to infer selective sweeps. In: Goldstein DB, Schlötterer C (eds) Microsatellites: evolution and applications. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 238–247
Schloss SJ, Mitchell SE, White GM, Kukatla R, Bowers JE et al (2002) Characterization of RFLP probe sequences for gene discovery and SSR development in Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Theor Appl Genet 105:912–920
Schug MD, Wetterstrand KA, Gaudette MS, Lim RH, Hutter CM et al (1998) The distribution and frequency of microsatellite loci in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Ecol 7:57–70
Sears ER (1969) Wheat cytogenetics. Annu Rev Genet 3:451–468
Somers DJ, Isaac P, Edwards K (2004) A high density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1105–1114
Sourdille P, Tavaud M, Charmet G, Bernard M (2001) Transferability of wheat microsatellites to diploid Triticeae species carrying the A, B, and D genome. Theor Appl Genet 103:346–352
Sourdille P, Singh S, Cadalen T, Brown-Guedira GL, Gay G et al (2004) Microsatellite-based deletion bin system for the establishment of genetic–physical map relationships in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Funct Integr Genomics 4:12–25
StatSoft (1996) STATISTICA for Windows [computer program manual]. Tulsa, OK 74104
Tachida H, Iizuka M (1992) Persistence of repeated sequences that evolve by replication slippage. Genetics 131:471–478
Tautz D, Trick M, Dover GA (1986) Cryptic simplicity in DNA is a major source of genetic variation. Nature 322:652–656
Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney RK, Graner A (2003) Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 106:411–422
Varshney RK, Thiel T, Stein N, Langridge P, Graner A (2002) In silico analysis on frequency and distribution of microsatellites in ESTs of some cereal species. Cell Mol Biol Lett 7:537–546
Wang Z, Weber JL, Zhong G, Tanksley (1994) Survey of plant short tandem DNA repeats. Theor Appl Genet 88:1–6
Acknowledgements
The EST data is based upon work supported by a grant from the National Science Foundation, USA under Cooperative Agreement No. DBI-9975989. This study was also partially supported by the US Department of Agriculture under Cooperative Agreements USDA Contract No. 2001-52100-11293, USDA Contract No. 2003-34205-13636, and Hatch Funds. We sincerely thank Dr. M. Tahir for his help in SSR analysis, H. Zadeh-Gardel, H. Wang and K. J. Morey for their technical support, and all the group members of US wheat EST project (http://wheat.pw.usda.gov/NSF/project/participants.html) for their contributions to the mapping data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, J.H., Lapitan, N.L.V. Characterization of EST-derived microsatellites in the wheat genome and development of eSSR markers. Funct Integr Genomics 5, 80–96 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-004-0128-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-004-0128-8