Abstract
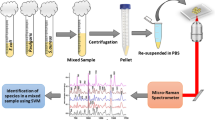
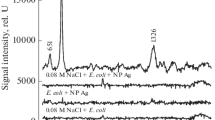
This study aimed to evaluate the differences in the Raman spectra of nine clinical species of bacteria isolated from infections (three Gram-positive and six Gram-negative species), correlating the spectra with the chemical composition of each species and to develop a classification model through discriminant analysis to categorize each bacterial strain using the peaks with the most significant differences. Bacteria were cultured in Mueller Hinton agar and a sample of biomass was harvested and placed in an aluminum sample holder. A total of 475 spectra from 115 different strains were obtained through a dispersive Raman spectrometer (830 nm) with exposure time of 50 s. The intensities of the peaks were evaluated by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the peaks with significant differences were related to the differences in the biochemical composition of the strains. Discriminant analysis based on quadratic distance applied to the peaks with the most significant differences and partial least squares applied to the whole spectrum showed 89.5% and 90.1% of global accuracy, respectively, for classification of the spectra in all the groups. Raman spectroscopy could be a promising technique to identify spectral differences related to the biochemical content of pathogenic microorganisms and to provide a faster diagnosis of infectious diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization (2015) Facts and sheets. Details. Antibiotic resistance. WHO, Geneva http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/antibiotic-resistance/en/. Accessed 10 February 2019
Ibrahim EH, Sherman G, Ward S, Fraser VJ, Kollef MH (2000) The influence of inadequate antimicrobial treatment of bloodstream infections on patient outcomes in the ICU setting. Chest 118(1):146–155. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.118.1.146
Kerremans JJ, Verboom P, Stijnen T, Van Roijen LH, Goessens W, Verbrugh HA, Vos MC (2008) Rapid identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing reduce antibiotic use and accelerate pathogen-directed antibiotic use. J Antimicrob Chemother 61(2):428–435. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkm497
Breed RS, Murray EGD, Smith NR (1957) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. The Williams and Wilkins Company, Baltimore
D’Souza HA, Campbell M, Baron EJ (2004) Practical bench comparison of BBL CHROMagar Orientation and standard two-plate media for urine cultures. J Clin Microbiol 42(1):60–64. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.42.1.60-64.2004
Hill SC, Pinnick RG, Niles S, Pan Y-L, Holler S, Chang RK, Bottiger JR, Chen BT, Orr C-S, Feather GA (1999) Real-time measurement of fluorescence spectra from single airborne biological particles. Field Anal Chem Technol 3:221–239. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1520-6521(1999)3:4/5<221::aid-fact2>3.0.co;2-7
Spector BC, Reinisch L, Smith D, Werkhaven JA (2000) Noninvasive fluorescent identification of bacteria causing acute otitis media in a chinchilla model. Laryngoscope 110(7):1119–1123. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200007000-00009
Giana HE, Silveira L, Zângaro RA, Pacheco MTT (2003) Rapid identification of bacterial species by fluorescence spectroscopy and classification through principal components analysis. J Fluoresc 13(6):489–493. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOFL.0000008059.74052.3c
Maquelin K, Kirschner C, Choo-Smith LP, Ngo-Thi NA, van Vreeswijk T, Stämmler M, Endtz HP, Bruining HA, Naumann D, Puppels GJ (2003) Prospective study of the performance of vibrational spectroscopies for rapid identification of bacterial and fungal pathogens recovered from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol 41(1):324–329. https://doi.org/10.1128/jcm.41.1.324-329.2003
Jaureguiberry M, Madoz LV, Giuliodori MJ, Wagener K, Prunner I, Grunert T et al (2016) Identification of Escherichia coli and Trueperella pyogenes isolated from the uterus of dairy cows using routine bacteriological testing and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Acta Vet Scand 58(1):81. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13028-016-0262-z
Romanolo KF, Gorski L, Wang S, Lauzon CR (2015) Rapid identification and classification of Listeria spp. and serotype assignment of Listeria monocytogenes using Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy and artificial neural network analysis. PLoS One 10(11):e0143425. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143425
Maquelin K, Kirschner C, Choo-Smith LP, Nvan den Braak H, Endtz HP, Naumann D, Puppels GJ (2002) Identification of medically relevant microorganisms by vibrational spectroscopy. J Microbiol Methods 51(3):255–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S01677012(02)001276
Choo-Smith LP, Maquelin K, van Vreeswijk T, Bruining HA, Puppels GJ, Ngo Thi NA, Kirschner C, Naumann D, Ami D, Villa AM, Orsini F, Doglia SM, Lamfarraj H, Sockalingum GD, Manfait M, Allouch P, Endtz HP (2001) Investigating microbial (micro) colony heterogeneity by vibrational spectroscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(4):1461–1469. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.67.4.1461-1469.2001
Rösch P, Schmitt M, Kiefer W, Popp J (2003) The identification of microorganisms by micro-Raman spectroscopy. J Mol Struct 661-662:363–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2003.06.004
Harz M, Rösch P, Peschke KD, Ronneberger O, Burkhardt H, Popp J (2005) Micro-Raman spectroscopic identification of bacterial cells of the genus Staphylococcus and dependence on their cultivation conditions. Analyst 130(11):1543–1550. https://doi.org/10.1039/b507715j
Maquelin K, Dijkshoorn L, van der Reijden TJ, Puppels GJ (2006) Rapid epidemiological analysis of Acinetobacter strains by Raman spectroscopy. J Microbiol Methods 64(1):126–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2005.04.028
Willemse-Erix DFM, Scholtes-Timmerman MJ, Jachtenberg JW, van Leeuwen WB, Horst-Kreft D, Schut TC, Deurenberg RH, Puppels GJ, van Belkum A, Vos MC, Maquelin K (2009) Optical fingerprinting in bacterial epidemiology: Raman spectroscopy as a real-time typing method. J Clin Microbiol 47(3):652–659. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01900-08
Harz M, Rösch P, Popp J (2009) Vibrational spectroscopy - a powerful tool for the rapid identification of microbial cells at the single-cell level. Cytometry A 75(2):104–113. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.20682
Paret ML, Sharma SK, Green LM, Alvarez AM (2010) Biochemical characterization of Gram-positive and Gram-negative plant-associated bacteria with micro-Raman spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc 64(4):433–441. https://doi.org/10.1366/000370210791114293
Oliveira FSS, Giana HE, Silveira L (2012) Discrimination of selected species of pathogenic bacteria using near-infrared Raman spectroscopy and principal components analysis. J Biomed Opt 17(10):107004. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JBO.17.10.107004
Neugebauer U, Rösch P, Popp J (2015) Raman spectroscopy towards clinical application: drug monitoring and pathogen identification. Int J Antimicrob Agents 46(Suppl 1):35–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.10.014
Pahlow S, Stöckel S, Pollok S, Cialla-May D, Rösch P, Weber K, Popp J (2016) Rapid identification of Pseudomonas spp. via Raman spectroscopy using pyoverdine as capture probe. Anal Chem 88(3):1570–1577. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02829
Hanlon EB, Manoharan R, Koo TW, Shafer KE, Motz JT, Fitzmaurice M, Kramer JR, Itzkan I, Dasari RR, Feld MS (2000) Prospects for in vivo Raman spectroscopy. Phys Med Biol 45(2):R51–R59. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/45/2/201
Kirschner C, Maquelin K, Pina P, Ngo Thi NA, Choo-Smith LP, Sockalingum GD, Sandt C, Ami D, Orsini F, Doglia SM, Allouch P, Mainfait M, Puppels GJ, Naumann D (2001) Classification and identification of Enterococci: a comparative phenotypic, genotypic, and vibrational spectroscopic study. J Clin Microbiol 39(5):1763–1770. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.39.5.1763-1770.2001
Jarvis R, Goodacre R (2004) Discrimination of bacteria using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal Chem 76(1):40–47. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac034689c
Hutsebaut D, Vandroemme J, Heyrman J, Dawyndt P, Vandenabeele P, Moens L, de Vos P (2006) Raman microspectroscopy as an identification tool within the phylogenetically homogeneous ‘Bacillus subtilis’ group. Syst Appl Microbiol 29(8):650–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2006.02.001
Jarvis R, Goodacre R (2008) Characterization and identification of bacteria using SERS. Chem Soc Rev 37(5):931–936. https://doi.org/10.1039/b705973f
Maquelin K, Choo-Smith LP, van Vreeswijk T, Endtz HP, Bennett BSR, Bruining HA, Puppels GJ (2000) Raman spectroscopic method for identification of clinically relevant microorganisms growing on solid culture medium. Anal Chem 72(1):12–19. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac991011h
Zeiri L, Bronk BV, Shabtai Y, Eichler J, Efrima S (2004) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy as a tool for probing specific biochemical components in bacteria. Appl Spectrosc 58(1):33–40. https://doi.org/10.1366/000370204322729441
Ciobotă V, Burkhardt EM, Schumacher W, Rösch P, Küsel K, Popp J (2010) The influence of intracellular storage material on bacterial identification by means of Raman spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 397(7):2929–2937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3895-1
Naumann D, Barnickel G, Bradaczek H, Labischinski H, Giesbrecht P (1982) Potentialities of infrared spectroscopy for cell wall analytical studies and rejection of models based on crystalline chitin. Eur J Biochem 125(3):505–515. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06711.x
Lasch P (2012) Spectral pre-processing for biomedical vibrational spectroscopy and microspectroscopic imaging. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 117:100–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2012.03.011
McHugh ML (2011) Multiple comparison analysis testing in ANOVA. Biochemia Medica 21(3):203–209. https://doi.org/10.11613/BM.2011.029
Ripley BD (1998) Pattern classification and neural networks. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Barker M, Rayens W (2003) Partial least squares for discrimination. J Chemometrics 17:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.785
Nunes CA, Freitas MP, Pinheiro ACM, Bastos SC (2012) Chemoface: a novel free user-friendly interface for chemometrics. J Braz Chem Soc 23(11):2003–2010. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0103-50532012005000073
She CY, Dinh ND, Thu AT (1974) Laser Raman scattering of glucosamine, N-acetylglucosamine and glucuronic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta 372(2):345–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4165(74)90196-2
Talari ACS, Movasaghi Z, Rehman S, Rehman IU (2007) Raman spectroscopy of biological tissues. Appl Spectrosc Rev 50(1):46–111. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2014.923902
Huang WE, Li M, Jarvis RM, Goodacre R, Banwart SA (2010) Shining light on the microbial world the application of Raman microspectroscopy. Adv Appl Mycrobiol 70:153–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2164(10)70005-8
Lemma T, Saliniemi A, Hynninen V, Hytönen VP, Toppari JJ (2016) SERS detection of cell surface and intracellular components of microorganisms using nano-aggregated Ag substrate. Vib Spectrosc 83:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2016.01.006
Jehlicka J, Edwards HGM, Oren A (2014) Raman spectroscopy of microbial pigments. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(11):3286–3295. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00699-14
Kusic D, Kampe B, Rösch P, Popp J (2014) Identification of water pathogens by Raman microspectroscopy. Water Res 48:179–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.09.030
Tang M, McEwen GD, Wu Y, Miller CD, Zhou A (2013) Characterization and analysis of mycobacteria and Gram-negative bacteria and co-culture mixtures by Raman microspectroscopy, FTIR, and atomic force microscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(5):1577–1591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6556-8
Hanai K, Kawai S, Kuwae A (1991) Vibrational and NMR spectra of phenylpyruvic acid and its salts in aqueous solution. J Mol Struct 245(1–2):21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2860(91)87003-Z
Islas S, Becerra A, Luisi PL, Lazcano A (2004) Comparative genomics and the gene complement of a minimal cell. Orig Life Evol Biosph 34(1–2):243–256. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ORIG.0000009844.90540.52
Siddiqui SA, Dwivedi A, Singh PK, Hasan T, Jain S, Sundaraganesan N, Saleem H, Misra N (2009) Vibrational dynamics and potential energy distribution of two well-known neurotransmitter receptors: tyramine and dopamine hydrochloride. J Theor Comput Chem 8(3):433–450. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219633609004861
Heidari H, Bethel CR, Papp-Wallace KM, de Boer PAJ, Bonomo RA, Carey PR (2014) Following drug uptake and reactions inside Escherichia coli cells by Raman microspectroscopy. Biochemistry 53(25):4113–4121. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi500529c
Jarvis RM, Brooker A, Goodacre R (2004) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for bacterial discrimination utilizing a scanning electron microscope with a Raman spectroscopy interface. Anal Chem 76(17):5198–5202. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac049663f
Sjoholm I (1975) Protein a from Staphylococcus aureus: spectropolarimetric and spectrophotometric studies. Eur J Biochem 51(1):55–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03906.x
Sundaram J, Park B, Kwon Y, Lawrence KC (2013) Surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) with biopolymer encapsulated silver nanosubstrates for rapid detection of foodborne pathogens. Int J Food Microbiol 167(1):67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.05.013
Strola SA, Baritaux JC, Schultz E, Simon AC, Allier C, Espagnon I, Jary D, Dinten JM (2014) Single bacteria identification by Raman spectroscopy. J Biomed Opt 19(11):111610. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JBO.19.11.111610
Wu X, Chen J, Zhao Y, Zughaier SM (2014) Rapid detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biomarkers in biological fluids using surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Proc SPIE 9107:91070A. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2053156
Premasiri R, Chen Y, Williamson PM, Bandarage DC, Pyles C, Ziegler LD (2017) Rapid urinary tract infection diagnostics by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): identification and antibiotic susceptibilities. Anal Bioanal Chem 409(11):3043–3054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0244-7
Hamasha K, Mohaidat QI, Putnam RA, Woodman RC, Palchaudhuri S, Rehse SJ (2013) Sensitive and specific discrimination of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Escherichia coli using Raman spectroscopy-a comparison of two multivariate analysis techniques. Biomed Opt Express 4(4):481–489. https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.4.000481
Xuan Nguyen NT, Sarter S, Hai Nquyen N, Daniel P (2017) Detection of molecular changes induced by antibiotics in Escherichia coli using vibrational spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 27(183):395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.04.077
Dekter HE, Orelio CC, Morsink MC, Tektas S, Vis B, te Witt R, van Leeuwen WB (2017) Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Gram-positive and -negative bacterial isolates directly from spiked blood culture media with Raman spectroscopy. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 36(1):81–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-016-2773-y
de Boer LL, Spliethoff JW, Sterenborg HJ, Ruers TJ (2017) Review: in vivo optical spectral tissue sensing-how to go from research to routine clinical application? Lasers Med Sci 32(3):711–719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-2119-0
de Lima CJ, Moreira LM, Lyon JP, Villaverde AB, Pacheco MT (2009) Catheters: instrumental advancements in biomedical applications of optical fibers. Lasers Med Sci 24(4):621–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-008-0608-5
Funding
Partial financial support was provided by São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) (Grant no. 2009/01788-5) and National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) (Process no. 307509/2017-6). F. S. S. Oliveira and A. M. da Silva received the doctorate fellowship from Brazilian Ministry of Education, Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES - PROSUP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Siqueira e Oliveira, F.S., da Silva, A.M., Pacheco, M.T.T. et al. Biochemical characterization of pathogenic bacterial species using Raman spectroscopy and discrimination model based on selected spectral features. Lasers Med Sci 36, 289–302 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-020-03028-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-020-03028-9