Abstract
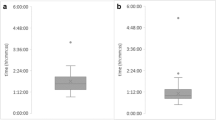
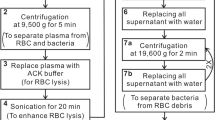
Patients suffering from bacterial bloodstream infections have an increased risk of developing systematic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), which can result in rapid deterioration of the patients’ health. Diagnostic methods for bacterial identification and antimicrobial susceptibility tests are time-consuming. The aim of this study was to investigate whether Raman spectroscopy would be able to rapidly provide an antimicrobial susceptibility profile from bacteria isolated directly from positive blood cultures. First, bacterial strains (n = 133) were inoculated in tryptic soy broth and incubated in the presence or absence of antibiotics for 5 h. Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles were analyzed by Raman spectroscopy. Subsequently, a selection of strains was isolated from blood cultures and analyzed similarly. VITEK®2 technology and broth dilution were used as the reference methods. Raman spectra from 67 antibiotic-susceptible strains showed discriminatory spectra in the absence or at low concentrations of antibiotics as compared to high antibiotic concentrations. For 66 antibiotic-resistant strains, no antimicrobial effect was observed on the bacterial Raman spectra. Full concordance with VITEK®2 data and broth dilution was obtained for the antibiotic-susceptible strains, 68 % and 98 %, respectively, for the resistant strains. Discriminative antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) profiles were obtained for all bacterial strains isolated from blood cultures, resulting in full concordance with the VITEK®2 data. It can be concluded that Raman spectroscopy is able to detect the antimicrobial susceptibility of bacterial species isolated from a positive blood culture bottle within 5 h. Although Raman spectroscopy is cheap and rapid, further optimization is required, to fulfill a great promise for future AST profiling technology development.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balk RA (2000) Severe sepsis and septic shock. Definitions, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations. Crit Care Clin 16:179–192
Caliendo AM, Gilbert DN, Ginocchio CC, Hanson KE, May L, Quinn TC, Tenover FC, Alland D, Blaschke AJ, Bonomo RA, Carroll KC, Ferraro MJ, Hirschhorn LR, Joseph WP, Karchmer T, MacIntyre AT, Reller LB, Jackson AF; Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) (2013) Better tests, better care: improved diagnostics for infectious diseases. Clin Infect Dis 57(Suppl 3):S139–S170. doi:10.1093/cid/cit578
Coelho FR, Martins JO (2012) Diagnostic methods in sepsis: the need of speed. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992) 58:498–504
Gaieski DF, Mikkelsen ME, Band RA, Pines JM, Massone R, Furia FF, Shofer FS, Goyal M (2010) Impact of time to antibiotics on survival in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock in whom early goal-directed therapy was initiated in the emergency department. Crit Care Med 38:1045–1053. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181cc4824
Kumar A, Roberts D, Wood KE, Light B, Parrillo JE, Sharma S, Suppes R, Feinstein D, Zanotti S, Taiberg L, Gurka D, Kumar A, Cheang M (2006) Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit Care Med 34:1589–1596. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000217961.75225.E9
Larché J, Azoulay E, Fieux F, Mesnard L, Moreau D, Thiery G, Darmon M, Le Gall J-R, Schlemmer B (2003) Improved survival of critically ill cancer patients with septic shock. Intensive Care Med 29:1688–1695. doi:10.1007/s00134-003-1957-y
Perez KK, Olsen RJ, Musick WL, Cernoch PL, Davis JR, Peterson LE, Musser JM (2014). Integrating rapid diagnostics and antimicrobial stewardship improves outcomes in patients with antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative bacteremia. J Infect 69:216–225. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2014.05.005
van Belkum A, Durand G, Peyret M, Chatellier S, Zambardi G, Schrenzel J, Shortridge D, Engelhardt A, Dunne WM Jr (2013) Rapid clinical bacteriology and its future Impact. Ann Lab Med 33:14–27. doi:10.3343/alm.2013.33.1.14
Huang AM, Newton D, Kunapuli A, Gandhi TN, Washer LL, Isip J, Collins CD, Nagel JL (2013) Impact of rapid organism identification via matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight combined with antimicrobial stewardship team intervention in adult patients with bacteremia and candidemia. Clin Infect Dis 57:1237–1245. doi:10.1093/cid/cit498
Bork JT, Leekha S, Heil EL, Zhao L, Badamas R, Johnson JK (2015) Rapid testing using the Verigene Gram-negative blood culture nucleic acid test in combination with antimicrobial stewardship intervention against Gram-negative bacteremia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:1588–1595. doi:10.1128/AAC.04259-14
Clerc O, Prod’hom G, Senn L, Jaton K, Zanetti G, Calandra T, Greub G (2014) Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and PCR-based rapid diagnosis of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. Clin Microbiol Infect 20:355–360. doi:10.1111/1469-0691.12329
Ling TKW, Liu ZK, Cheng AFB (2003) Evaluation of the VITEK 2 system for rapid direct identification and susceptibility testing of gram-negative bacilli from positive blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol 41:4705–4707. doi:10.1128/JCM.41.10.4705-4707.2003
La Scola B (2011) Intact cell MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry-based approaches for the diagnosis of bloodstream infections. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 11:287–298. doi:10.1586/erm.11.12
Loonen AJM, Jansz AR, Stalpers J, Wolffs PFG, van den Brule AJC (2012) An evaluation of three processing methods and the effect of reduced culture times for faster direct identification of pathogens from BacT/ALERT blood cultures by MALDI-TOF MS. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 31:1575–1583. doi:10.1007/s10096-011-1480-y
Hamasha K, Mohaidat QI, Putnam RA, Woodman RC, Palchaudhuri S, Rehse SJ (2013) Sensitive and specific discrimination of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Escherichia coli using Raman spectroscopy—a comparison of two multivariate analysis techniques. Biomed Opt Express 4:481–489. doi:10.1364/BOE.4.000481
Jung JS, Popp C, Sparbier K, Lange C, Kostrzewa M, Schubert S (2014) Evaluation of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry for rapid detection of β-lactam resistance in Enterobacteriaceae derived from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol 52:924–930. doi:10.1128/JCM.02691-13
Wimmer JL, Long SW, Cernoch P, Land GA, Davis JR, Musser JM, Olsen RJ (2012) Strategy for rapid identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing of gram-negative bacteria directly recovered from positive blood cultures using the Bruker MALDI Biotyper and the BD Phoenix system. J Clin Microbiol 50:2452–2454. doi:10.1128/JCM.00409-12
Espagnon I, Ostrovskii D, Mathey R, Dupoy M, Joly PL, Novelli-Rousseau A, Pinston F, Gal O, Mallard F, Leroux DF (2014) Direct identification of clinically relevant bacterial and yeast microcolonies and macrocolonies on solid culture media by Raman spectroscopy. J Biomed Opt 19:027004. doi:10.1117/1.JBO.19.2.027004
Maquelin K, Choo-Smith LP, van Vreeswijk T, Endtz HP, Smith B, Bennett R, Bruining HA, Puppels GJ (2000) Raman spectroscopic method for identification of clinically relevant microorganisms growing on solid culture medium. Anal Chem 72:12–19
Huang WE, Li M, Jarvis RM, Goodacre R, Banwart SA (2010) Shining light on the microbial world: the application of Raman microspectroscopy. Adv Appl Microbiol 70:153–186. doi:10.1016/S0065-2164(10)70005-8
Hutsebaut D, Vandenabeele P, Moens L (2005) Evaluation of an accurate calibration and spectral standardization procedure for Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 130:1204–1214. doi:10.1039/b503624k
Loonen AJM, Bos MP, van Meerbergen B, Neerken S, Catsburg A, Dobbelaer I, Penterman R, Maertens G, van de Wiel P, Savelkoul P, van den Brule AJC (2013) Comparison of pathogen DNA isolation methods from large volumes of whole blood to improve molecular diagnosis of bloodstream infections. PLoS One 8, e72349. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072349.t002
Athamneh AIM, Alajlouni RA, Wallace RS, Seleem MN, Senger RS (2014) Phenotypic profiling of antibiotic response signatures in Escherichia coli using Raman spectroscopy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:1302–1314. doi:10.1128/AAC.02098-13
Jung GB, Nam SW, Choi S, Lee G-J, Park H-K (2014) Evaluation of antibiotic effects on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm using Raman spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. Biomed Opt Express 5:3238–3251. doi:10.1364/BOE.5.003238
Liu T-T, Lin Y-H, Hung C-S, Liu T-J, Chen Y, Huang Y-C, Tsai T-H, Wang H-H, Wang D-W, Wang J-K, Wang Y-L, Lin C-H (2009) A high speed detection platform based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering for monitoring antibiotic-induced chemical changes in bacteria cell wall. PLoS One 4, e5470. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005470.g005
Kostrzewa M, Sparbier K, Maier T, Schubert S (2013) MALDI-TOF MS: an upcoming tool for rapid detection of antibiotic resistance in microorganisms. Proteomics Clin Appl 7:767–778. doi:10.1002/prca.201300042
Moritz TJ, Polage CR, Taylor DS, Krol DM, Lane SM, Chan JW (2010) Evaluation of Escherichia coli cell response to antibiotic treatment by use of Raman spectroscopy with laser tweezers. J Clin Microbiol 48:4287–4290. doi:10.1128/JCM.01565-10
Willemse-Erix D, Bakker-Schut T, Slagboom-Bax F, Jachtenberg JW, Lemmens-den Toom N, Papagiannitsis CC, Kuntaman K, Puppels G, van Belkum A, Severin JA, Goessens W, Maquelin K (2012) Rapid typing of extended-spectrum β-lactamase- and carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates by use of SpectraCell RA. J Clin Microbiol 50:1370–1375. doi:10.1128/JCM.05423-11
Bernatová S, Samek O, Pilát Z, Šerý M, Ježek J, Jákl P, Šiler M, Krzyžánek V, Zemánek P, Holá V, Dvořáčková M, Růžička F (2013) Following the mechanisms of bacteriostatic versus bactericidal action using Raman spectroscopy. Molecules 18:13188–13199. doi:10.3390/molecules181113188
Jones RN, Erwin ME, Croco JL (1996) Critical appraisal of E test for the detection of fluoroquinolone resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother 38:21–25
Doern GV, Brueggemann AB, Perla R, Daly J, Halkias D, Jones RN, Saubolle MA (1997) Multicenter laboratory evaluation of the bioMérieux Vitek antimicrobial susceptibility testing system with 11 antimicrobial agents versus members of the family Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol 35(8):2115–2119
Willemse-Erix HFM, Jachtenberg J, Barutçi H, Puppels GJ, van Belkum A, Vos MC, Maquelin K (2010) Proof of principle for successful characterization of methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from skin by use of Raman spectroscopy and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol 48:736–740. doi:10.1128/JCM.01153-09
Gherardi G, Angeletti S, Panitti M, Pompilio A, Di Bonaventura G, Crea F, Avola A, Fico L, Palazzo C, Sapia GF, Visaggio D, Dicuonzo G (2012) Comparative evaluation of the Vitek-2 Compact and Phoenix systems for rapid identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing directly from blood cultures of Gram-negative and Gram-positive isolates. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 72:20–31. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2011.09.015
Orelio CC, Beiboer SHW, Morsink MC, Tektas S, Dekter HE, van Leeuwen WB (2014) Comparison of Raman spectroscopy and two molecular diagnostic methods for Burkholderia cepacia complex species identification. J Microbiol Methods 107:126–132. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2014.10.002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from Stichting Innovatie Alliantie (SIA) RAAK-Pro grant PRO-1 044.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 33 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dekter, H.E., Orelio, C.C., Morsink, M.C. et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Gram-positive and -negative bacterial isolates directly from spiked blood culture media with Raman spectroscopy. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 36, 81–89 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-016-2773-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-016-2773-y