Abstract
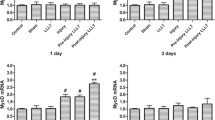
Infrared laser therapy is used for skeletal muscle repair based on its biostimulative effect on satellite cells. However, shortening of telomere length limits regenerative potential in satellite cells, which occurs after each cell division cycle. Also, laser therapy could be more effective on non-physiologic tissues. This study evaluated low-level infrared laser exposure effects on mRNA expression from muscle injury repair and telomere stabilization genes in myoblasts in normal and stressful conditions. Laser fluences were those used in clinical protocols. C2C12 myoblast cultures were exposed to low-level infrared laser (10, 35, and 70 J/cm2) in standard or normal (10 %) and reduced (2 %) fetal bovine serum concentrations; total RNA was extracted for mRNA expression evaluation from muscle injury repair (MyoD and Pax7) and chromosome stabilization (TRF1 and TRF2) genes by real time quantitative polymerization chain reaction. Data show that low-level infrared laser increases the expression of MyoD and Pax7 in 10 J/cm2 fluence, TRF1 expression in all fluences, and TRF2 expression in 70 J/cm2 fluence in both 10 and 2 % fetal bovine serum. Low-level infrared laser increases mRNA expression from genes related to muscle repair and telomere stabilization in myoblasts in standard or normal and stressful conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mesquita-Ferrari RA, Alves AN, de Oliveira CV, Artilheiro PP, Bussadori SK, Rocha LA, Nunes FD, Fernandes KP (2015) Low-level laser irradiation modulates cell viability and creatine kinase activity in C2C12 muscle cells during the differentiation process. Lasers Med Sci 30:2209–2013. doi:10.1007/s10103-015-1715-8
Buono R, Vantaggiato C, Pisa V, Azzoni E, Bassi MT, Brunelli S, Sciorati C, Clementi E (2012) Nitric oxide sustains long-term skeletal muscle regeneration by regulating fate of satellite cells via signaling pathways requiring Vangl2 and cyclic GMP. Stem cells 30:197–209. doi:10.1002/stem.783
Koopman R, Ly CH, Ryall JG (2014) A metabolic link to skeletal muscle wasting and regeneration. Front Physiol 5:32. doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00032, eCollection 2014
Hyatt JP, McCall GE, Kander EM, Zhong H, Roy RR, Huey KA (2008) PAX3/7 expression coincides with MyoD during chronic skeletal muscle overload. Muscle Nerve 38:861–866. doi:10.1002/mus.21006
Shi X, Garry DJ (2006) Muscle stem cells in development, regeneration, and disease. Genes Dev 20:1692–708
Relaix F, Zammit PS (2012) Satellite cells are essential for skeletal muscle regeneration: the cell on the edge returns centre stage. Development 139:2845–2856. doi:10.1242/dev.069088
Duijnisveld BJ, Bigot A, Beenakker KG, Portilho DM, Raz V, van der Heide HJ, Visser CP, Chaouch S, Mamchaoui K, Westendorp RG, Mouly V, Butler-Browne GS, Nelissen RG, Maier AB (2011) Regenerative potential of human muscle stem cells in chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R207. doi:10.1186/ar3540
Mucciardi G, Gali’ A, Barresi V, Mucciardi M, Aguennouz M, Inferrera A, Magno C (2014) Telomere instability in papillary bladder urothelial carcinomas: comparison with grading and risk of recurrence. Indian J Urol 30:245–251. doi:10.4103/0970-1591.134241
Galati A, Micheli E, Alicata C, Ingegnere T, Cicconi A, Pusch MC, Giraud-Panis MJ, Gilson E, Cacchione S (2015) TRF1 and TRF2 binding to telomeres is modulated by nucleosomal organization. Nucleic Acids Res 43:5824–5837. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv507
Ponsot E, Echaniz-Laguna A, Delis AM, Kadi F (2012) Telomere length and regulatory proteins in human skeletal muscle with and without ongoing regenerative cycles. Exp Physiol 97:774–784. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2011.063818
Collins M, Renault V, Grobler LA, St Clair Gibson A, Lambert MI, Wayne Derman E, Butler-Browne GS, Noakes TD, Mouly V (2003) Athletes with exercise-associated fatigue have abnormally short muscle DNA telomeres. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35:1524–1528
Edwards DN, Orren DK, Machwe A (2014) Strand exchange of telomeric DNA catalyzed by the Werner syndrome protein (WRN) is specifically stimulated by TRF2. Nucleic Acids Res 42:7748–7761. doi:10.1093/nar/gku454
Saquilabon Cruz GM, Kong X, Silva BA, Khatibzadeh N, Thai R, Berns MW, Yokomori K (2015) Femtosecond near-infrared laser microirradiation reveals a crucial role for PARP signaling on factor assemblies at DNA damage sites Nucleic. Acids Res
Blanco R, Muñoz P, Flores JM, Klatt P, Blasco MA (2007) Telomerase abrogation dramatically accelerates TRF2-induces epithelial carcinogenesis. Genes Dev 21:206–220
Martínez P, Blasco MA (2010) Role of shelterin in cancer and aging. Aging Cell 9:653–666. doi:10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00596.x
Fernandes KP, Alves AN, Nunes FD, Souza NH, Silva JA Jr, Bussadori SK, Ferrari RA (2013) Effect of photobiomodulation on expression of IL-1β in skeletal muscle following acute injury. Lasers Med Sci 28:1043–1046. doi:10.1007/s10103-012-1233-x
Alves AN, Fernandes KP, Melo CA, Yamaguchi RY, França CM, Teixeira DF, Bussadori SK, Nunes FD, Mesquita-Ferrari RA (2014) Modulating effect of low level-laser therapy on fibrosis in the repair process of the tibialis anterior muscle in rats. Lasers Med Sci 29:813–821. doi:10.1007/s10103-013-1428-9
Assis L, Moretti AI, Abrahão TB, de Souza HP, Hamblin MR, Parizotto NA (2013) Low-level laser therapy (808 nm) contributes to muscle regeneration and prevents fibrosis in rat tibialis anterior muscle after cryolesion. Lasers Med Sci 28:947–955. doi:10.1007/s10103-012-1183-3
Rodrigues NC, Brunelli R, de Araújo HS, Parizotto NA, Renno AC (2013) Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) (660nm) alters gene expression during muscle healing in rats. J Photochem Photobiol B 120:29–35. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2013.01.002
Luo L, Sun Z, Zhang L, Li X, Dong Y, Liu TC (2013) Effects of low-level laser therapy on ROS homeostasis and expression of IGF-1 and TGF- β1 in skeletal muscle during the repair process. Lasers Med Sci 28:725–734. doi:10.1007/s10103-012-1133-0
Burattini S, Ferri P, Battistelli M, Cursi R, Luchetti F, Falcieri E (2004) C2C12 murine myoblasts as a model of skeletal muscle development: morphofunctional characterization. Eur J Histochem 48:223–233
Shefer G, Partridge TA, Heslop L, Gross JG, Oron U, Halevy O (2002) Low-energy laser irradiation promotes the survival and cell cycle entry of skeletal muscle satellite cells. Journal of Cell Science 115:1461–1469
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Method Methods 25:402–408
Alexsandra da Silva Neto Trajano L, da Silva CL, de Carvalho SN, Cortez E, Mencalha AL, De Souza da Fonseca A, Stumbo AC (2016) Cell viability, reactive oxygen species, apoptosis, and necrosis in myoblast cultures exposed to low-level infrared laser. Lasers in Medical Science
Marques MM, Pereira AN, Fujihara NA, Nogueira FN, Eduardo CP (2004) Effect of low-power laser irradiation on protein synthesis and ultrastructure of human gingival fibroblasts. Lasers Surg Med 34:260–265
Walter C, Pabst AM, Ziebart T (2015) Effects of a low-level diode laser on oral keratinocytes, oral fibroblasts, endothelial cells and osteoblasts incubated with bisphosphonates: an in vitro study. Biomed Rep 3:14–18
Wang Y, Zhang RP, Zhao YM, Li QQ, Yan XP, Liu JY, Gou H, Li L (2015) Effects of Pax3 and Pax7 expression on muscle mass in the Pekin duck (Anas platyrhynchos domestica). Genet Mol Res 14:11495–11504. doi:10.4238/2015.September.28.1
Motohashi N, Asakura A (2014) Muscle satellite cell heterogeneity and self-renewal. Front Cell Dev Biol 2:1. doi:10.3389/fcell.2014.00001
Zammit PS, Relaix F, Nagata Y, Ruiz AP, Collins CA, Partridge TA, Beauchamp JR (2006) Pax7 and myogenic progression in skeletal muscle satellite cells. J Cell Sci 119:1824–1832
Rodrigues NC, Assis L, Fernandes KR, Magri A, Ribeiro DA, Brunelli R, Abreu DC, Renno AC (2013) Effects of 660 nm low-level laser therapy on muscle healing process after cryolesion. J Rehabil Res Dev 50:985–996. doi:10.1682/JRRD.2012.08.0147
Brunelli RM, Rodrigues NC, Ribeiro DA, Fernandes K, Magri A, Assis L, Parizotto NA, Cliquet A Jr, Renno AC, Abreu DC (2014) The effects of 780-nm low level laser therapy on muscle healing process after cryolesion. Lasers Med Sci 29:91–96. doi:10.1007/s10103-013-1277-6
Pertille A, Macedo AB, Oliveira CP (2012) Evaluation of muscle regeneration in aged animals after treatment with low-level laser therapy. Rev Bras Fisioter 16:495–501
Silva LH, Silva MT, Gutierrez RM, Conte TC, Toledo CA, Aoki MS, Liebano RE, Miyabara EH (2012) GaAs 904-nm laser irradiation improves myofiber mass recovery during regeneration of skeletal muscle previously damage by crotoxin. Lasers Med Sci 27:993–1000. doi:10.1007/s10103-011-1031-x
Huang YY, Sharma SK, Carroll J, Hamblin MR (2011) Biphasic dose response in low level light therapy - an update. Dose Response 9:602–618. doi:10.2203/dose-response.11-009.Hamblin
Smogorzewska A, van Steensel B, Bianchi A, Oelmann S, Schaefer MR, Schnapp G, de Lange T (2000) Control of human telomere length by TRF1 and TRF2. Mol Cell Biol 20:1659–1668
Decary S, Mouly V, Hamida CB, Sautet A, Barbet JP, Butler-Browne GS (1997) Replicative potential and telomere length in human skeletal muscle: implications for satellite cell-mediated gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther 8:1429–1438
Pitman RT, Wojdyla L, Puri N (2013) Mechanism of DNA damage responses induced by exposure to an oligonucleotide homologous to the telomere overhang in melanoma. Oncotarget 4:761–771
de Lange T (2005) Shelterin: the protein complex that shapes and safeguards human telomeres. Genes Dev 19:2100–2110
Nakanishi K, Kawai T, Kumaki F, Hiroi S, Mukai M, Ikeda E, Koering CE, Gilson E (2003) Expression of mRNAs for telomeric repeat binding factor (TRF)-1 and TRF2 in atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma of the lung. Clin Cancer Res 9:1105–1111
Pal D, Sharma U, Singh SK, Kakkar N, Prasad R (2015) Over-expression of telomere binding factors (TRF1 & TRF2) in renal cell carcinoma and their inhibition by using SiRNA induce apoptosis, reduce cell proliferation and migration in vitro. PLoS One 10:e0115651. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115651
Yamada K, Yagihashi A, Yamada M, Asanuma K, Moriai R, Kobayashi D, Tsuji N, Watanabe N (2002) Decreased gene expression for telomeric-repeat binding factors and TIN2 in malignant hematopoietic cells. Anticancer Res 22:1315–1320
Saito K, Yagihashi A, Nasu S, Izawa Y, Nakamura M, Kobayashi D, Tsuji N, Watanabe N (2002) Gene expression for suppressors of telomerase activity (telomeric-repeat binding factors) in breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res 93:253–258
Muñoz P, Blanco R, de Carcer G, Schoeftner S, Benetti R, Flores JM, Malumbres M, Blasco MA (2009) TRF1 controls telomere length and mitotic fidelity in epithelial homeostasis. Mol Cell Biol 29:1608–1625. doi:10.1128/MCB.01339-08
Laye MJ, Solomon TP, Karstoft K, Pedersen KK, Nielsen SD, Pedersen BK (2012) Increased shelterin mRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and skeletal muscle following an ultra-long-distance running event. J Appl Physiol (1985) 112:773–781. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00997.2011
Ludlow AT, Witkowski S, Marshall MR, Wang J, Lima CJ, Guth LM, Spangenburg EE, Roth SM (2012) Chronic exercise modifies age-related telomere dynamics in a tissue-specific fashion. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 67:911–926. doi:10.1093/gerona/gls002
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ) and Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva Neto Trajano, L.A., Stumbo, A.C., da Silva, C.L. et al. Low-level infrared laser modulates muscle repair and chromosome stabilization genes in myoblasts. Lasers Med Sci 31, 1161–1167 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-1956-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-016-1956-1