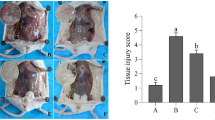
Abstract
Mastitis, a disease that affects both dairy herds and humans, is recognized as the most common source of losses in the dairy industry. Antibiotics have been used for years as the primary treatment for mastitis. However, abuse of antibiotics has led to the emergence of resistant strains and the presence of drug residues and has increased the difficulty of curing this disease. In addition, antibiotics kill most of the microbes that are present in the digestive tract, leading to imbalances in the gut microbiome and destruction of the ecosystem that is normally present in the gut. Gut microbiota play an important role in the host’s health and could be considered the “second brain” of the body. In recent years, the gut microbiota and their metabolites, including lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), have been shown to participate in the development of mastitis. LPS is the main component of the cell walls of gram-negative bacteria. Overproduction of rumen-derived LPS injures the rumen epithelium, resulting in the entry of LPS into the blood and damaged liver function; once in the blood, it circulates into the mammary gland, increasing blood-barrier permeability and leading to mammary gland inflammation. SCFAs, which are produced by gut microbiota as fermentation products, have a protective effect on mammary gland inflammatory responses and help maintain the function of the blood-milk barrier. Recently, increasing attention has been focused on the use of probiotics as a promising alternative for the treatment of mastitis. This review summarizes the effects of the gut microbiome and its metabolites on mastitis as well as the current of probiotics in mastitis. This work may provide a valuable theoretical foundation for the development of fresh ideas for the prevention and treatment of mastitis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar C, Vanegas C, Klotz B (2011) Antagonistic effect of Lactobacillus strains against Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes in milk. J Dairy Res 78:136–143
Al-Asmakh M, Hedin L (2015) Microbiota and the control of blood-tissue barriers. Tissue Barriers 3:e1039691
Al-Asmakh M, Stukenborg JB, Reda A, Anuar F, Strand ML, Hedin L, Pettersson S, Soder O (2014a) The gut microbiota and developmental programming of the testis in mice. PLoS One 9:e103809
Alva-Murillo N, Ochoa-Zarzosa A, Lopez-Meza JE (2012) Short chain fatty acids (propionic and hexanoic) decrease Staphylococcus aureus internalization into bovine mammary epithelial cells and modulate antimicrobial peptide expression. Vet Microbiol 155:324–331
Amir LH, Griffin L, Cullinane M, Garland SM (2016) Probiotics and mastitis: evidence-based marketing? Int Breastfeed J 11:19
Aoyama M, Kotani J, Usami M (2010) Butyrate and propionate induced activated or non-activated neutrophil apoptosis via HDAC inhibitor activity but without activating GPR-41/GPR-43 pathways. Nutrition 26:653–661
Arroyo R, Martin V, Maldonado A, Jimenez E, Fernandez L, Rodriguez JM (2010) Treatment of infectious mastitis during lactation: antibiotics versus oral administration of Lactobacilli isolated from breast milk. Clin Infect Dis 50:1551–1558
Barcenilla A, Pryde SE, Martin JC, Duncan SH, Stewart CS, Henderson C, Flint HJ (2000) Phylogenetic relationships of butyrate-producing bacteria from the human gut. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1654–1661
Beecher C, Daly M, Berry DP, Klostermann K, Flynn J, Meaney W, Hill C, McCarthy TV, Ross RP, Giblin L (2009) Administration of a live culture of Lactococcus lactis DPC 3147 into the bovine mammary gland stimulates the local host immune response, particularly IL-1beta and IL-8 gene expression. J Dairy Res 76:340–348
Beharka AA, Nagaraja TG, Morrill JL, Kennedy GA, Klemm RD (1998) Effects of form of the diet on anatomical, microbial, and fermentative development of the rumen of neonatal calves. J Dairy Sci 81:1946–1955
Ben Shabat SK, Sasson G, Doron-Faigenboim A, Durman T, Yaacoby S, Miller MEB, White BA, Shterzer N, Mizrahi I (2016) Specific microbiome-dependent mechanisms underlie the energy harvest efficiency of ruminants. ISME J 10:2958–2972
Bhutia YD, Ganapathy V (2015) Short, but smart: SCFAs train T cells in the gut to fight autoimmunity in the brain. Immunity 43:629–631
Bouchard DS, Rault L, Berkova N, Le Loir Y, Even S (2013) Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus invasion into bovine mammary epithelial cells by contact with live Lactobacillus casei. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:877–885
Bouchard DS, Seridan B, Saraoui T, Rault L, Germon P, Gonzalez-Moreno C, Nader-Macias FM, Baud D, Francois P, Chuat V, Chain F, Langella P, Nicoli J, Le Loir Y, Even S (2015) Lactic acid bacteria isolated from bovine mammary microbiota: potential allies against bovine mastitis. PLoS One 10:e0144831
Braniste V, Al-Asmakh M, Kowal C, Anuar F, Abbaspour A, Toth M, Korecka A, Bakocevic N, Guan NL, Kundu P, Gulyas B, Halldin C, Hultenby K, Nilsson H, Hebert H, Volpe BT, Diamond B, Pettersson S (2014a) The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Sci Transl Med 6:263ra158
Brown AJ, Goldsworthy SM, Barnes AA, Eilert MM, Tcheang L, Daniels D, Muir AI, Wigglesworth MJ, Kinghorn I, Fraser NJ, Pike NB, Strum JC, Steplewski KM, Murdock PR, Holder JC, Marshall FH, Szekeres PG, Wilson S, Ignar DM, Foord SM, Wise A, Dowell SJ (2003) The orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short chain carboxylic acids. J Biol Chem 278:11312–11319
Chang G, Zhang K, Xu T, Jin D, Seyfert HM, Shen X, Zhuang S (2015a) Feeding a high-grain diet reduces the percentage of LPS clearance and enhances immune gene expression in goat liver. BMC Vet Res 11:67
Chang GJ, Zhuang S, Seyfert HM, Zhang K, Xu TL, Jin D, Guo JF, Shen XZ (2015b) Hepatic TLR4 signaling is activated by LPS from digestive tract during SARA, and epigenetic mechanisms contribute to enforced TLR4 expression. Oncotarget 6:38578–38590
Chang G, Yan J, Ma N, Liu X, Dai H, Bilal MS, Shen X (2018) Dietary sodium butyrate supplementation reduces high-concentrate diet feeding-induced apoptosis in mammary cells in dairy goats. J Agric Food Chem 66:2101–2107
Charrier C, Duncan GJ, Reid MD, Rucklidge GJ, Henderson D, Young P, Russell VJ, Aminov RI, Flint HJ, Louis P (2006) A novel class of CoA-transferase involved in short-chain fatty acid metabolism in butyrate-producing human colonic bacteria. Microbiology 152:179–185
Chen YH, Xu X, Sheng MJ, Zheng Z, Gu Q (2011) Effects of asymmetric dimethylarginine on bovine retinal capillary endothelial cell proliferation, reactive oxygen species production, permeability, intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and occludin expression. Mol Vis 17:332–340
Crispie F, Alonso-Gomez M, O'Loughlin C, Klostermann K, Flynn J, Arkins S, Meaney W, Ross RP, Hill C (2008) Intramammary infusion of a live culture for treatment of bovine mastitis: effect of live lactococci on the mammary immune response. J Dairy Res 75:374–384
Dai H, Liu X, Yan J, Aabdin ZU, Bilal MS, Shen X (2017) Sodium butyrate ameliorates high-concentrate diet-induced inflammation in the rumen epithelium of dairy goats. J Agric Food Chem 65:596–604
Debarry J, Garn H, Hanuszkiewicz A, Dickgreber N, Blumer N, von Mutius E, Bufe A, Gatermann S, Renz H, Holst O, Heine H (2007) Acinetobacter lwoffii and Lactococcus lactis strains isolated from farm cowsheds possess strong allergy-protective properties. J Allergy Clin Immunol 119:1514–1521
Donnet-Hughes A, Perez PF, Dore J, Leclerc M, Levenez F, Benyacoub J, Serrant P, Segura-Roggero I, Schiffrin EJ (2010) Potential role of the intestinal microbiota of the mother in neonatal immune education. Proc Nutr Soc 69:407–415
Dufour S, Frechette A, Barkema HW, Mussell A, Scholl DT (2011) Invited review: effect of udder health management practices on herd somatic cell count. J Dairy Sci 94:563–579
Duncan SH, Holtrop G, Lobley GE, Calder AG, Stewart CS, Flint HJ (2004) Contribution of acetate to butyrate formation by human faecal bacteria. Br J Nutr 91:915–923
Eberle JAM, Widmayer P, Breer H (2014) Receptors for short-chain fatty acids in brush cells at the “gastric groove”. Front Physiol 5:152
Elin RJ, Wolff SM (1976) Biology of endotoxin. Annu Rev Med 27:127–141
Fernandez L, Cardenas N, Arroyo R, Manzano S, Jimenez E, Martin V, Rodriguez JM (2016) Prevention of infectious mastitis by oral administration of Lactobacillus salivarius PS2 during late pregnancy. Clin Infect Dis 62:568–573
Findeisen HM, Kahles FK, Bruemmer D (2013) Epigenetic regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell function in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep 15:319
Gigliucci F, von Meijenfeldt FAB, Knijn A, Michelacci V, Scavia G, Minelli F, Dutilh BE, Ahmad HM, Raangs GC, Friedrich AW, Rossen JWA, Morabito S (2018) Metagenomic characterization of the human intestinal microbiota in fecal samples from STEC-infected patients. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 8:25
Gozho GN, Plaizier JC, Krause DO, Kennedy AD, Wittenberg KM (2005) Subacute ruminal acidosis induces ruminal lipopolysaccharide endotoxin release and triggers an inflammatory response. J Dairy Sci 88:1399–1403
Graham C, Simmons NL (2005) Functional organization of the bovine rumen epithelium. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 288:R173–R181
Guo J, Chang G, Zhang K, Xu L, Jin D, Bilal MS, Shen X (2017) Rumen-derived lipopolysaccharide provoked inflammatory injury in the liver of dairy cows fed a high-concentrate diet. Oncotarget 8:46769–46780
Halestrap AP, Wang X, Poole RC, Jackson VN, Price NT (1997) Lactate transport in heart in relation to myocardial ischemia. Am J Cardiol 80:17A–25A
Halnes I, Baines KJ, Berthon BS, MacDonald-Wicks LK, Gibson PG, Wood LG (2017) Soluble fibre meal challenge reduces airway inflammation and expression of GPR43 and GPR41 in asthma. Nutrients 9(1)
Harrington M (2015) For lack of gut microbes, the blood-brain barrier ‘leaks’. Lab Anim 44:14–14
He CX, Shan YJ, Song W (2015) Targeting gut microbiota as a possible therapy for diabetes. Nutr Res 35:361–367
Hertl JA, Grohn YT, Leach JD, Bar D, Bennett GJ, Gonzalez RN, Rauch BJ, Welcome FL, Tauer LW, Schukken YH (2010) Effects of clinical mastitis caused by gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and other organisms on the probability of conception in New York State Holstein dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 93:1551–1560
Hooper LV, Gordon JI (2001) Commensal host-bacterial relationships in the gut. Science 292:1115–1118
Itavo LCV, dos Santos GT, Jobim CC, Voltolini TV, Ferreira CCB (2000) Evaluation of orange peel silage with different additives by rumen fermentation parameters and energy contribution from volatile fatty acids. Rev Bras Zootec 29:1491–1497
Jami E, Israel A, Kotser A, Mizrahi I (2013a) Exploring the bovine rumen bacterial community from birth to adulthood. ISME J 7:1069–1079
Jeon SJ, Cunha F, Vieira-Neto A, Bicalho RC, Lima S, Bicalho ML, Galvao KN (2017) Blood as a route of transmission of uterine pathogens from the gut to the uterus in cows. Microbiome 5(1):109
Jeurink PV, van Bergenhenegouwen J, Jimenez E, Knippels LMJ, Fernandez L, Garssen J, Knol J, Rodriguez JM, Martin R (2013) Human milk: a source of more life than we imagine. Benefic Microbes 4:17–30
Jewell KA, McCormick CA, Odt CL, Weimer PJ, Suen G (2015) Ruminal bacterial community composition in dairy cows is dynamic over the course of two lactations and correlates with feed efficiency. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:4697–4710
Jimenez E, Fernandez L, Marin ML, Martin R, Odriozola JM, Nueno-Palop C, Narbad A, Olivares M, Xaus J, Rodriguez JM (2005) Isolation of commensal bacteria from umbilical cord blood of healthy neonates born by cesarean section. Curr Microbiol 51:270–274
Jin D, Chang G, Zhang K, Guo J, Xu T, Shen X (2016a) Rumen-derived lipopolysaccharide enhances the expression of lingual antimicrobial peptide in mammary glands of dairy cows fed a high-concentrate diet. BMC Vet Res 12:128
Kelly CJ, Zheng L, Campbell EL, Saeedi B, Scholz CC, Bayless AJ, Wilson KE, Glover LE, Kominsky DJ, Magnuson A, Weir TL, Ehrentraut SF, Pickel C, Kuhn KA, Lanis JM, Nguyen V, Taylor CT, Colgan SP (2015) Crosstalk between microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and intestinal epithelial HIF augments tissue barrier function. Cell Host Microbe 17:662–671
Khafipour E, Krause DO, Plaizier JC (2009a) A grain-based subacute ruminal acidosis challenge causes translocation of lipopolysaccharide and triggers inflammation. J Dairy Sci 92:1060–1070
Kim CH, Park J, Kim M (2014) Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids, T cells, and inflammation. Immune Netw 14:277–288
Klasvogt S, Zuschratter W, Schmidt A, Krober A, Vorwerk S, Wolter R, Isermann B, Wimmers K, Rothkotter HJ, Nossol C (2017) Air-liquid interface enhances oxidative phosphorylation in intestinal epithelial cell line IPEC-J2. Cell Death Discov 3:17001
Klein RD, Kincaid RL, Hodgson AS, Harrison JH, Hillers JK, Cronrath JD (1987) Dietary fiber and early weaning on growth and rumen development of calves. J Dairy Sci 70:2095–2104
Klevenhusen F, Hollmann M, Podstatzky-Lichtenstein L, Krametter-Frotscher R, Aschenbach JR, Zebeli Q (2013) Feeding barley grain-rich diets altered electrophysiological properties and permeability of the ruminal wall in a goat model. J Dairy Sci 96:2293–2302
Klostermann K, Crispie F, Flynn J, Ross RP, Hill C, Meaney W (2008a) Intramammary infusion of a live culture of Lactococcus lactis for treatment of bovine mastitis: comparison with antibiotic treatment in field trials. J Dairy Res 75:365–373
Kobayashi K, Oyama S, Numata A, Rahman MM, Kumura H (2013a) Lipopolysaccharide disrupts the milk-blood barrier by modulating claudins in mammary alveolar tight junctions. PLoS One 8:e62187
Koukias N, Buzzetti E, Tsochatzis EA (2017) Intestinal hormones, gut microbiota and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Minerva Endocrinol 42:184–194
Krause KM, Oetzel GR (2006) Understanding and preventing subacute ruminal acidosis in dairy herds: a review. Anim Feed Sci Technol 126:215–236
Kuznetsova TA, Makarenkova ID, Koneva EL, Aminina NM, Yakush EV (2015) Effect of probiotic product containing bifidobacteria and biogel from brown algae on the intestinal microflora and parameters of innate immunity in mice with experimental drug dysbacteriosis. Vopr Pitan 84:73–79
LeBlanc JG, Chain F, Martin R, Bermudez-Humaran LG, Courau S, Langella P (2017) Beneficial effects on host energy metabolism of short-chain fatty acids and vitamins produced by commensal and probiotic bacteria. Microb Cell Fact: 16(1):79
Lee JF, Zeng Q, Ozaki H, Wang LC, Hand AR, Hla T, Wang E, Lee MJ (2006) Dual roles of tight junction-associated protein, zonula occludens-1, in sphingosine 1-phosphate-mediated endothelial chemotaxis and barrier integrity. J Biol Chem 281:29190–29200
Li H, Myeroff L, Smiraglia D, Romero MF, Pretlow TP, Kasturi L, Lutterbaugh J, Rerko RM, Casey G, Issa JP, Willis J, Willson JKV, Plass C, Markowitz SD (2003) SLC5A8, a sodium transporter, is a tumor suppressor gene silenced by methylation in human colon aberrant crypt foci and cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:8412–8417
Li RW, Connor EE, Li CJ, Baldwin RL, Sparks ME (2012) Characterization of the rumen microbiota of pre-ruminant calves using metagenomic tools. Environ Microbiol 14:129–139
Liu JH, Xu TT, Liu YJ, Zhu WY, Mao SY (2013) A high-grain diet causes massive disruption of ruminal epithelial tight junctions in goats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 305:R232–R241
Louis P, Hold GL, Flint HJ (2014) The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:661–672
Macfarlane S, Macfarlane GT (2003) Regulation of short-chain fatty acid production. Proc Nutr Soc 62:67–72
Macpherson AJ, Uhr T (2004) Induction of protective IgA by intestinal dendritic cells carrying commensal bacteria. Science 303:1662–1665
Marino E, Richards JL, McLeod KH, Stanley D, Yap YA, Knight J, McKenzie C, Kranich J, Oliveira AC, Rossello FJ, Krishnamurthy B, Nefzger CM, Macia L, Thorburn A, Baxter AG, Morahan G, Wong LH, Polo JM, Moore RJ, Lockett TJ, Clarke JM, Topping DL, Harrison LC, Mackay CR (2017) Erratum: gut microbial metabolites limit the frequency of autoimmune T cells and protect against type 1 diabetes. Nat Immunol 18:1271
Marungruang N, Arevalo Sureda E, Lefrancoise A, Westrom B, Nyman M, Prykhodko O, Fak Hallenius F (2018) Impact of dietary induced precocious gut maturation on cecal microbiota and its relation to the blood-brain barrier during the postnatal period in rats. Neurogastroenterol Motil 30:e13285
Masoud W, Takamiya M, Vogensen FK, Lillevang S, Abu Al-Soud W, Sorensen SJ, Jakobsen M (2011) Characterization of bacterial populations in Danish raw milk cheeses made with different starter cultures by denaturating gradient gel electrophoresis and pyrosequencing. Int Dairy J 21:142–148
Masoud W, Vogensen FK, Lillevang S, Abu Al-Soud W, Sorensen SJ, Jakobsen M (2012) The fate of indigenous microbiota, starter cultures, Escherichia coli, Listeria innocua and Staphylococcus aureus in Danish raw milk and cheeses determined by pyrosequencing and quantitative real time (qRT)-PCR. Int J Food Microbiol 153:192–202
Masui R, Sasaki M, Funaki Y, Ogasawara N, Mizuno M, Iida A, Izawa S, Kondo Y, Ito Y, Tamura Y, Yanamoto K, Noda H, Tanabe A, Okaniwa N, Yamaguchi Y, Iwamoto T, Kasugai K (2013) G protein-coupled receptor 43 moderates gut inflammation through cytokine regulation from mononuclear cells. Inflamm Bowel Dis 19:2848–2856
Medrano-Galarza C, Gibbons J, Wagner S, de Passille AM, Rushen J (2012) Behavioral changes in dairy cows with mastitis. J Dairy Sci 95:6994–7002
Michel L, Prat A (2016) One more role for the gut: microbiota and blood brain barrier. Ann Transl Med 4:15
Miller TL, Wolin MJ (1996) Pathways of acetate, propionate, and butyrate formation by the human fecal microbial flora. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1589–1592
Miller RH, Bitman J, Bright SA, Wood DL, Capuco AV (1992) Effect of clinical and subclinical mastitis on lipid composition of teat canal keratin. J Dairy Sci 75:1436–1442
Miyauchi S, Gopal E, Fei YJ, Ganapathy V (2004) Functional identification of SLC5A8, a tumor suppressor down-regulated in colon cancer, as a Na+−coupled transporter for short-chain fatty acids. J Biol Chem 279:13293–13296
Moreira AP, Texeira TF, Ferreira AB, Peluzio Mdo C, Alfenas Rde C (2012) Influence of a high-fat diet on gut microbiota, intestinal permeability and metabolic endotoxaemia. Br J Nutr 108:801–809
Ochoa-Zarzosa A, Villarreal-Fernandez E, Cano-Camacho H, Lopez-Meza JE (2009) Sodium butyrate inhibits Staphylococcus aureus internalization in bovine mammary epithelial cells and induces the expression of antimicrobial peptide genes. Microb Pathog 47:1–7
Ohira H, Fujioka Y, Katagiri C, Mamoto R, Aoyama-Ishikawa M, Amako K, Izumi Y, Nishiumi S, Yoshida M, Usami M, Ikeda M (2013) Butyrate attenuates inflammation and lipolysis generated by the interaction of adipocytes and macrophages. J Atheroscler Thromb 20:425–442
Oikonomou G, Machado VS, Santisteban C, Schukken YH, Bicalho RC (2012) Microbial diversity of bovine mastitic milk as described by pyrosequencing of metagenomic 16s rDNA. Plos One 7(10):e47671
Ouwehand AC, Saxelin M, Salminen S (2004) Phenotypic differences between commercial Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and L-rhamnosus strains recovered from blood. Clin Infect Dis 39:1858–1860
Oviedo-Boyso J, Valdez-Alarcon JJ, Cajero-Juarez M, Ochoa-Zarzosa A, Lopez-Meza JE, Bravo-Patino A, Baizabal-Aguirre VM (2007) Innate immune response of bovine mammary gland to pathogenic bacteria responsible for mastitis. J Inf Secur 54:399–409
Paricio-Talayero JM, Baeza C (2018) Re: “Oral administration to nursing women of lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 prevents lactational mastitis development: a randomized controlled trial” by Hurtado et al. (Breastfeed Med 2017;12:202-209). Breastfeed Med 13(6):453-454
Penner GB, Steele MA, Aschenbach JR, McBride BW (2011) Ruminant nutrition symposium: molecular adaptation of ruminal epithelia to highly fermentable diets. J Anim Sci 89:1108–1119
Perez PF, Dore J, Leclerc M, Levenez F, Benyacoub J, Serrant P, Segura-Roggero I, Schiffrin EJ, Donnet-Hughes A (2007) Bacterial imprinting of the neonatal immune system: lessons from maternal cells? Pediatrics 119:e724–e732
Plaizier JC, Khafipour E, Li S, Gozho GN, Krause DO (2012) Subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA), endotoxins and health consequences. Anim Feed Sci Technol 172:9–21
Reichardt N, Duncan SH, Young P, Belenguer A, Leitch CM, Scott KP, Flint HJ, Louis P (2014) Phylogenetic distribution of three pathways for propionate production within the human gut microbiota. ISME J 8:1323–1335
Rescigno M, Urbano M, Valzasina B, Francolini M, Rotta G, Bonasio R, Granucci F, Kraehenbuhl JP, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P (2001a) Dendritic cells express tight junction proteins and penetrate gut epithelial monolayers to sample bacteria. Nat Immunol 2:361–367
Richards JL, Yap YA, McLeod KH, Mackay CR, Marino E (2016) Dietary metabolites and the gut microbiota: an alternative approach to control inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Clin Transl Immunol 5:e82
Rinkinen M, Jalava K, Westermarck E, Salminen S, Ouwehand AC (2003) Interaction between probiotic lactic acid bacteria and canine enteric pathogens: a risk factor for intestinal Enterococcus faecium colonization? Vet Microbiol 92:111–119
Rodriguez JM (2014) The origin of human milk bacteria: is there a bacterial entero-mammary pathway during late pregnancy and lactation? Adv Nutr 5:779–784
Ryan MP, Flynn J, Hill C, Ross RP, Meaney WJ (1999a) The natural food grade inhibitor, lacticin 3147, reduced the incidence of mastitis after experimental challenge with Streptococcus dysgalactiae in nonlactating dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 82:2625–2631
Sadet-Bourgeteau S, Martin C, Morgavi DP (2010) Bacterial diversity dynamics in rumen epithelium of wethers fed forage and mixed concentrate forage diets. Vet Microbiol 146:98–104
Schaub A, Futterer A, Pfeffer K (2001) PUMA-G, an IFN-gamma-inducible gene in macrophages is a novel member of the seven transmembrane spanning receptor superfamily. Eur J Immunol 31:3714–3725
Schlingmann B, Molina SA, Koval M (2015) Claudins: gatekeepers of lung epithelial function. Semin Cell Dev Biol 42:47–57
Schuijt TJ, Lankelma JM, Scicluna BP, de Sousa e Melo F, Roelofs JJTH, de Boer JD, Hoogendijk AJ, de Beer R, de Vos A, Belzer C, de Vos WM, van der Poll T, Wiersinga WJ (2016) The gut microbiota plays a protective role in the host defence against pneumococcal pneumonia. Gut 65:575–583
Schukken YH, Hertl J, Bar D, Bennett GJ, Gonzalez RN, Rauch BJ, Santisteban C, Schulte HF, Tauer L, Welcome FL, Grohn YT (2009) Effects of repeated gram-positive and gram-negative clinical mastitis episodes on milk yield loss in Holstein dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 92:3091–3105
Shimozono M, Scofield MA, Wangemann P (1997) Functional evidence for a monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) in strial marginal cells and molecular evidence for MCT1 and MCT2 in stria vascularis. Hear Res 114:213–222
Singh N, Gurav A, Sivaprakasam S, Brady E, Padia R, Shi HD, Thangaraju M, Prasad PD, Manicassamy S, Munn DH, Lee JR, Offermanns S, Ganapathy V (2014) Activation of Gpr109a, receptor for niacin and the commensal metabolite butyrate, suppresses colonic inflammation and carcinogenesis. Immunity 40:128–139
Souza RFS, Jardin J, Cauty C, Rault L, Bouchard DS, Bermudez-Humaran LG, Langella P, Monedero V, Seyffert N, Azevedo V, Le Loir Y, Even S (2017) Contribution of sortase SrtA2 to Lactobacillus casei BL23 inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus internalization into bovine mammary epithelial cells. PLoS One 12(3):e0174060
Spiljar M, Merkler D, Trajkovski M (2017) The immune system bridges the gut microbiota with systemic energy homeostasis: focus on TLRs, mucosal barrier, and SCFAs. Front Immunol 8:1353
Stecher B, Chaffron S, Kappeli R, Hapfelmeier S, Freedrich S, Weber TC, Kirundi J, Suar M, McCoy KD, von Mering C, Macpherson AJ, Hardt WD (2010) Like will to like: abundances of closely related species can predict susceptibility to intestinal colonization by pathogenic and commensal bacteria. PLoS Pathog 6(1):e10000711
Subbaramaiah K, Howe LR, Bhardwaj P, Du BH, Gravaghi C, Yantiss RK, Zhou XK, Blaho VA, Hla T, Yang PY, Kopelovich L, Hudis CA, Dannenberg AJ (2011) Obesity is associated with inflammation and elevated aromatase expression in the mouse mammary gland. Cancer Prev Res 4:329–346
Taggart AK, Kero J, Gan X, Cai TQ, Cheng K, Ippolito M, Ren N, Kaplan R, Wu K, Wu TJ, Jin L, Liaw C, Chen R, Richman J, Connolly D, Offermanns S, Wright SD, Waters MG (2005) (D)-beta-Hydroxybutyrate inhibits adipocyte lipolysis via the nicotinic acid receptor PUMA-G. J Biol Chem 280:26649–26652
Thangaraju M, Cresci GA, Liu K, Ananth S, Gnanaprakasam JP, Browning DD, Mellinger JD, Smith SB, Digby GJ, Lambert NA, Prasad PD, Ganapathy V (2009a) GPR109A is a G-protein-coupled receptor for the bacterial fermentation product butyrate and functions as a tumor suppressor in colon. Cancer Res 69:2826–2832
Topping DL, Clifton PM (2001) Short-chain fatty acids and human colonic function: roles of resistant starch and nonstarch polysaccharides. Physiol Rev 81:1031–1064
Tremaroli V, Backhed F (2012) Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 489:242–249
Trompette A, Gollwitzer ES, Yadava K, Sichelstiel AK, Sprenger N, Ngom-Bru C, Blanchard C, Junt T, Nicod LP, Harris NL, Marsland BJ (2014) Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat Med 20:159–166
Twomey DP, Wheelock AI, Flynn J, Meaney WJ, Hill C, Ross RP (2000) Protection against Staphylococcus aureus mastitis in dairy cows using a bismuth-based teat seal containing the bacteriocin, lacticin 3147. J Dairy Sci 83:1981–1988
Usami M, Kishimoto K, Ohata A, Miyoshi M, Aoyama M, Fueda Y, Kotani J (2008) Butyrate and trichostatin A attenuate nuclear factor kappaB activation and tumor necrosis factor alpha secretion and increase prostaglandin E2 secretion in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Nutr Res 28:321–328
Vacheyrou M, Normand AC, Guyot P, Cassagne C, Piarroux R, Bouton Y (2011) Cultivable microbial communities in raw cow milk and potential transfers from stables of sixteen French farms. Int J Food Microbiol 146:253–262
Vazquez-Torres A, Jones-Carson J, Baumler AJ, Falkow S, Valdivia R, Brown W, Le M, Berggren R, Parks WT, Fang FC (1999) Extraintestinal dissemination of Salmonella by CD18-expressing phagocytes. Nature 401:804–808
Verdier-Metz I, Gagne G, Bornes S, Monsallier F, Veisseire P, Delbes-Paus C, Montel MC (2012) Cow teat skin, a potential source of diverse microbial populations for cheese production. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:326–333
Vinolo MA, Rodrigues HG, Hatanaka E, Sato FT, Sampaio SC, Curi R (2011) Suppressive effect of short-chain fatty acids on production of proinflammatory mediators by neutrophils. J Nutr Biochem 22:849–855
Walker WA, Iyengar RS (2015) Breast milk, microbiota, and intestinal immune homeostasis. Pediatr Res 77:220–228
Wang J, Wei Z, Zhang X, Wang Y, Yang Z, Fu Y (2017a) Propionate protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis in mice by restoring blood-milk barrier disruption and suppressing inflammatory response. Front Immunol 8:1108
Wang JJ, Wei ZK, Zhang X, Wang YN, Fu YH, Yang ZT (2017b) Butyrate protects against disruption of the blood-milk barrier and moderates inflammatory responses in a model of mastitis induced by lipopolysaccharide. Br J Pharmacol 174:3811–3822
Wei ZK, Xiao C, Guo CM, Zhang X, Wang YN, Wang JJ, Yang ZT, Fu YH (2017) Sodium acetate inhibits Staphylococcus aureus internalization into bovine mammary epithelial cells by inhibiting NF-kappa B activation. Microb Pathog 107:116–121
Wellnitz O, Wall SK, Saudenova M, Bruckmaier RM (2014) Effect of intramammary administration of prednisolone on the blood-milk barrier during the immune response of the mammary gland to lipopolysaccharide. Am J Vet Res 75:595–601
Wellnitz O, Zbinden C, Huang X, Bruckmaier RM (2016) Short communication: differential loss of bovine mammary epithelial barrier integrity in response to lipopolysaccharide and lipoteichoic acid. J Dairy Sci 99:4851–4856
Willemsen LE, Koetsier MA, van Deventer SJ, van Tol EA (2003) Short chain fatty acids stimulate epithelial mucin 2 expression through differential effects on prostaglandin E(1) and E(2) production by intestinal myofibroblasts. Gut 52:1442–1447
Xie YQ, Xiao M, Ni YL, Jiang SF, Feng GZ, Sang SG, Du GK (2018) Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. Extract prevents diabetes in mice by modulating gut microbiota. J Diabetes Res 4;2018:4230590
Xu T, Tao H, Chang G, Zhang K, Xu L, Shen X (2015) Lipopolysaccharide derived from the rumen down-regulates stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 expression and alters fatty acid composition in the liver of dairy cows fed a high-concentrate diet. BMC Vet Res 11:52
Xu CM, Li XM, Qin BZ, Liu B (2016) Effect of tight junction protein of intestinal epithelium and permeability of colonic mucosa in pathogenesis of injured colonic barrier during chronic recovery stage of rats with inflammatory bowel disease. Asian Pac J Trop Med 9:143–147
Xu J, Chen N, Wu Z, Song Y, Zhang YF, Wu N, Zhang F, Ren XH, Liu Y (2018) 5-Aminosalicylic acid alters the gut bacterial microbiota in patients with ulcerative colitis. Front Microbiol 9:1274
Yanase H, Takebe K, Nio-Kobayashi J, Takahashi-Iwanaga H, Iwanaga T (2008) Cellular expression of a sodium-dependent monocarboxylate transporter (Slc5a8) and the MCT family in the mouse kidney. Histochem Cell Biol 130:957–966
Yitbarek A, Weese JS, Alkie TN, Parkinson J, Sharif S (2018) Influenza A virus subtype H9N2 infection disrupts the composition of intestinal microbiota of chickens. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 94(1)
Young W, Hine BC, Wallace OAM, Callaghan M, Bibiloni R (2015) Transfer of intestinal bacterial components to mammary secretions in the cow. PeerJ 3:e888
Yu J, Ren Y, Xi X, Huang W, Zhang H (2017) A novel lactobacilli-based teat disinfectant for improving bacterial communities in the milks of cow teats with subclinical mastitis. Front Microbiol 8:1782
Yurchenko V, Constant S, Bukrinsky M (2006) Dealing with the family: CD147 interactions with cyclophilins. Immunology 117:301–309
Zebeli Q, Ametaj BN (2009) Relationships between rumen lipopolysaccharide and mediators of inflammatory response with milk fat production and efficiency in dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 92:3800–3809
Zhang CK, Zhai SM, Wu L, Bai YH, Jia JB, Zhang Y, Zhang B, Yan B (2015) Induction of size-dependent breakdown of blood-milk barrier in lactating mice by TiO2 nanoparticles. PLoS One 10(4):e0122591
Zhang K, Chang G, Xu T, Xu L, Guo J, Jin D, Shen X (2016a) Lipopolysaccharide derived from the digestive tract activates inflammatory gene expression and inhibits casein synthesis in the mammary glands of lactating dairy cows. Oncotarget 7:9652–9665
Zhang R, Zhu W, Mao S (2016c) High-concentrate feeding upregulates the expression of inflammation-related genes in the ruminal epithelium of dairy cattle. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 7:42
Zhang ZG, Xu DM, Wang L, Hao JJ, Wang JF, Zhou X, Wang WW, Qiu Q, Huang XD, Zhou JW, Long RJ, Zhao FQ, Shi P (2016d) Convergent evolution of rumen microbiomes in high-altitude mammals. Curr Biol 26:1873–1879
Zhao GJ, Li D, Zhao Q, Lian J, Hu TT, Hong GL, Yao YM, Lu ZQ (2016) Prognostic value of plasma tight-junction proteins for Sepsis in emergency department: an observational study. Shock 45:326–332
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 31602122, 31472248).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Li, S., Fu, Y. et al. Targeting gut microbiota as a possible therapy for mastitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 38, 1409–1423 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03549-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03549-4