Abstract
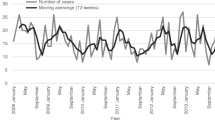
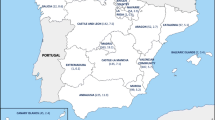
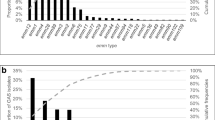
Streptococcus pyogenes or group A streptococcus (GAS) causes mild to severe infections in humans. GAS genotype emm1 is the leading cause of invasive disease worldwide. In the Nordic countries emm28 has been the dominant type since the 1980s. Recently, a resurgence of genotype emm1 was reported from Sweden. Here we present the epidemiology of invasive GAS (iGAS) infections and their association with emm-types in Norway from 2010–2014. We retrospectively collected surveillance data on antimicrobial susceptibility, multilocus sequence type and emm-type, and linked them with demographic and clinical manifestation data to calculate age and sex distributions, major emm- and sequence types and prevalence ratios (PR) on associations between emm-types and clinical manifestations. We analysed 756 iGAS cases and corresponding isolates, with overall incidence of 3.0 per 100000, median age of 59 years (range, 0–102), and male 56 %. Most frequent clinical manifestation was sepsis (49 %) followed by necrotizing fasciitis (9 %). Fifty-two different emm-types and 67 sequence types were identified, distributed into five evolutionary clusters. The most prevalent genotype was emm1 (ST28) in all years (range, 20–33 %) followed by 15 % emm28 in 2014. All isolates were susceptible to penicillin, 15 % resistant to tetracycline and <4 % resistant to erythromycin. A PR of 4.5 (95 % CI, 2.3–8.9) was calculated for emm2 and necrotizing fasciitis. All emm22 isolates were resistant to tetracycline PR 7.5 (95 % CI, 5.8–9.9). This study documented the dominance of emm1, emergence of emm89 and probable import of tetracycline resistant emm112.2 into Norway (2010–2014). Genotype fluctuations between years suggested a mutual exclusive dominance of evolutionary clades.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cunningham MW (2000) Pathogenesis of group A streptococcal infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 13(3):470–511
Beall B, Facklam R, Thompson T (1996) Sequencing emm-specific PCR products for routine and accurate typing of group A streptococci. J Clin Microbiol 34(4):953–958
Steer AC, Law I, Matatolu L, Beall BW, Carapetis JR (2009) Global emm type distribution of group A streptococci: systematic review and implications for vaccine development. Lancet Infect Dis 9(10):611–616. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70178-1
Martin PR, Hoiby EA (1990) Streptococcal serogroup A epidemic in Norway 1987-1988. Scand J Infect Dis 22(4):421–429. doi:10.3109/00365549009027073
Hoiby EA, Hasseltvedt V (1995) Increased incidence of severe Streptococcus group A infections in Noway during the last 10 years. New outbreak 1993-94. Tidsskrift for den Norske laegeforening : tidsskrift for praktisk medicin, ny raekke 115(25):3131–3136
Meisal R, Andreasson IK, Hoiby EA, Aaberge IS, Michaelsen TE, Caugant DA (2010) Streptococcus pyogenes isolates causing severe infections in Norway in 2006 to 2007: emm types, multilocus sequence types, and superantigen profiles. J Clin Microbiol 48(3):842–851. doi:10.1128/JCM.01312-09
Meisal R, Hoiby EA, Aaberge IS, Caugant DA (2008) Sequence type and emm type diversity in Streptococcus pyogenes isolates causing invasive disease in Norway between 1988 and 2003. J Clin Microbiol 46(6):2102–2105. doi:10.1128/JCM.00363-08
Meisal R, Hoiby EA, Caugant DA, Musser JM (2010) Molecular characteristics of pharyngeal and invasive emm3 Streptococcus pyogenes strains from Norway, 1988-2003. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis: Off publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol 29(1):31–43. doi:10.1007/s10096-009-0814-5
Siljander T, Lyytikainen O, Vahakuopus S, Snellman M, Jalava J, Vuopio J (2010) Epidemiology, outcome and emm types of invasive group A streptococcal infections in Finland. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis: Off publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol 29(10):1229–1235. doi:10.1007/s10096-010-0989-9
Luca-Harari B, Ekelund K, van der Linden M, Staum-Kaltoft M, Hammerum AM, Jasir A (2008) Clinical and epidemiological aspects of invasive Streptococcus pyogenes infections in Denmark during 2003 and 2004. J Clin Microbiol 46(1):79–86. doi:10.1128/JCM.01626-07
Eriksson BK, Norgren M, McGregor K, Spratt BG, Normark BH (2003) Group A streptococcal infections in Sweden: a comparative study of invasive and noninvasive infections and analysis of dominant T28 emm28 isolates. Clin Infect Dis: Off Publ InfectDis Soc Am 37(9):1189–1193. doi:10.1086/379013
Luca-Harari B, Darenberg J, Neal S, Siljander T, Strakova L, Tanna A, Creti R, Ekelund K, Koliou M, Tassios PT, van der Linden M, Straut M, Vuopio-Varkila J, Bouvet A, Efstratiou A, Schalen C, Henriques-Normark B, Strep ESG, Jasir A (2009) Clinical and microbiological characteristics of severe Streptococcus pyogenes disease in Europe. J Clin Microbiol 47(4):1155–1165. doi:10.1128/JCM.02155-08
O’Loughlin RE, Roberson A, Cieslak PR, Lynfield R, Gershman K, Craig A, Albanese BA, Farley MM, Barrett NL, Spina NL, Beall B, Harrison LH, Reingold A, Van Beneden C, Active Bacterial Core Surveillance T (2007) The epidemiology of invasive group A streptococcal infection and potential vaccine implications: United States, 2000-2004. Clin Infect Dis: Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am 45(7):853–862. doi:10.1086/521264
Aziz RK, Kotb M (2008) Rise and persistence of global M1T1 clone of Streptococcus pyogenes. Emerg Infect Dis 14(10):1511–1517. doi:10.3201/eid1410.071660
Bessen DE, Lizano S (2010) Tissue tropisms in group A streptococcal infections. Future Microbiol 5(4):623–638. doi:10.2217/fmb.10.28
Nielsen HU, Hammerum AM, Ekelund K, Bang D, Pallesen LV, Frimodt-Moller N (2004) Tetracycline and macrolide co-resistance in Streptococcus pyogenes: co-selection as a reason for increase in macrolide-resistant S. pyogenes? Microb Drug Resist 10(3):231–238. doi:10.1089/mdr.2004.10.231
Darenberg J, Henriques-Normark B, Lepp T, Tegmark-Wisell K, Tegnel A, Widgren K (2013) Increased incidence of invasive group A streptococcal infections in Sweden, January 2012-February 2013. Euro surveillance : bulletin Europeen sur les maladies transmissibles = European communicable disease bulletin 18(14):20443
Smit PW, Lindholm L, Lyytikainen O, Jalava J, Patari-Sampo A, Vuopio J (2015) Epidemiology and emm types of invasive group A streptococcal infections in Finland, 2008-2013. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis: Off publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol 34(10):2131–2136. doi:10.1007/s10096-015-2462-2
Enright MC, Spratt BG, Kalia A, Cross JH, Bessen DE (2001) Multilocus sequence typing of Streptococcus pyogenes and the relationships between emm type and clone. Infect Immun 69(4):2416–2427. doi:10.1128/IAI.69.4.2416-2427.2001
Mentasti M, Fry NK, Afshar B, Palepou-Foxley C, Naik FC, Harrison TG (2012) Application of Legionella pneumophila-specific quantitative real-time PCR combined with direct amplification and sequence-based typing in the diagnosis and epidemiological investigation of Legionnaires’ disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis: Off publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol 31(8):2017–2028. doi:10.1007/s10096-011-1535-0
Turner CE, Abbott J, Lamagni T, Holden MT, David S, Jones MD, Game L, Efstratiou A, Sriskandan S (2015) Emergence of a new highly successful acapsular group A streptococcus clade of genotype emm89 in the United Kingdom. MBio 6(4), e00622. doi:10.1128/mBio.00622-15
Shea PR, Ewbank AL, Gonzalez-Lugo JH, Martagon-Rosado AJ, Martinez-Gutierrez JC, Rehman HA, Serrano-Gonzalez M, Fittipaldi N, Beres SB, Flores AR, Low DE, Willey BM, Musser JM (2011) Group A Streptococcus emm gene types in pharyngeal isolates, Ontario, Canada, 2002-2010. Emerg Infect Dis 17(11):2010–2017. doi:10.3201/eid1711.110159
Darenberg J, Luca-Harari B, Jasir A, Sandgren A, Pettersson H, Schalen C, Norgren M, Romanus V, Norrby-Teglund A, Normark BH (2007) Molecular and clinical characteristics of invasive group A streptococcal infection in Sweden. Clin Infect Dis: Off Publ InfectDis Soc Am 45(4):450–458. doi:10.1086/519936
Imohl M, Reinert RR, Ocklenburg C, van der Linden M (2010) Epidemiology of invasive Streptococcus pyogenes disease in Germany during 2003-2007. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 58(3):389–396. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2010.00652.x
Chen YY, Huang CT, Yao SM, Chang YC, Shen PW, Chou CY, Li SY (2007) Molecular epidemiology of group A streptococcus causing scarlet fever in northern Taiwan, 2001-2002. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 58(3):289–295. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2007.01.013
Areas GP, Schuab RB, Neves FP, Barros RR (2014) Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns, emm type distribution and genetic diversity of Streptococcus pyogenes recovered in Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 109(7):935–939
Syrogiannopoulos GA, Grivea IN, Al-Lahham A, Panagiotou M, Tsantouli AG, Michoula Ralf Rene Reinert AN, van der Linden M (2013) Seven-year surveillance of emm types of pediatric Group A streptococcal pharyngitis isolates in Western Greece. PLoS One 8(8), e71558. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0071558
Tewodros W, Kronvall G (2005) M protein gene (emm type) analysis of group A beta-hemolytic streptococci from Ethiopia reveals unique patterns. J Clin Microbiol 43(9):4369–4376. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.9.4369-4376.2005
Sagar V, Kumar R, Ganguly NK, Chakraborti A (2008) Comparative analysis of emm type pattern of Group A Streptococcus throat and skin isolates from India and their association with closely related SIC, a streptococcal virulence factor. BMC Microbiol 8:150. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-8-150
Thapaliya D, O’Brien AM, Wardyn SE, Smith TC (2015) Epidemiology of necrotizing infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes at an Iowa hospital. J Infect Public Health 8(6):634–641. doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2015.06.003
Acknowledgements
The excellent technical assistance provided by Anne Witsø, Jan Oksnes, Anne Alme Ramstad and Gunnhild Rødal is highly acknowledged. We would also like to thank the staffs at all medical microbiological laboratories providing iGAS isolates to the National Reference Laboratory, and local and international EUPHEM coordinators for guidance and assistance in all stages of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the Norwegian Institute of Public Health.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Ethical approval
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
No identifying information is included.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naseer, U., Steinbakk, M., Blystad, H. et al. Epidemiology of invasive group A streptococcal infections in Norway 2010–2014: A retrospective cohort study. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 35, 1639–1648 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-016-2704-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-016-2704-y