Abstract
Introduction
Autoimmune encephalitis (AE) is caused by the antibodies that target receptors and intracellular or surface proteins. To achieve the appropriate therapeutic results, early and proper diagnosis is still the most important issue. In this review, we provide an overview of FDG-PET imaging findings in AE patients and possible relation to different subtypes and clinical features.
Methods
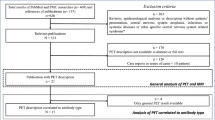
PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus were searched in August 2021 using a predefined search strategy.
Results
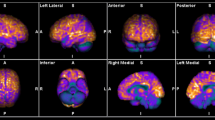
After two-step reviewing, 22 studies with a total of 332 participants were entered into our qualitative synthesis. In anti-NMDAR encephalitis, decreased activity in the occipital lobe was present, in addition, to an increase in frontal, parietal, and specifically medial temporal activity. Anti-VGKC patients showed altered metabolism in cortical and subcortical regions such as striata and cerebellum. Abnormal metabolism in patients with anti-LGI1 has been reported in diverse areas of the brain including medial temporal, hippocampus, cerebellum, and basal ganglia all of which had hypermetabolism. Hypometabolism in parietal, frontal, occipital lobes, temporal, frontal, and hippocampus was observed in AE patients with anti-GAD antibodies.
Conclusion
Our results indicate huge diversity in metabolic patterns among different AE subtypes and it is hard to draw a firm conclusion. Moreover, the timing of imaging, seizures, and acute treatments can alter the PET patterns strongly. Further prospective investigations with specific inclusion and exclusion criteria should be carried out to identify the metabolic defect in different AE subtypes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armangue T, Petit-Pedrol M, Dalmau J (2012) Autoimmune encephalitis in children. J Child Neurol 27(11):1460–1469. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073812448838
Kelley BP, Patel SC, Marin HL, Corrigan JJ, Mitsias PD, Griffith B (2017) Autoimmune encephalitis: pathophysiology and imaging review of an overlooked diagnosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 38(6):1070–1078. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5086
Dinoto A, Cheli M, Ajčević M, Dore F, Crisafulli C, Ukmar M, Sartori A, Manganotti P (2021) ASL MRI and 18F-FDG-PET in autoimmune limbic encephalitis: clues from two paradigmatic cases. Neurol Sci 42(8):3423–3425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-021-05207-0
Dalmau J (2016) NMDA receptor encephalitis and other antibody-mediated disorders of the synapse: the 2016 Cotzias lecture. Neurology 87(23):2471–2482. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000003414
Daif A, Lukas RV, Issa NP, Javed A, VanHaerents S, Reder AT, Tao JX, Warnke P, Rose S, Towle VL, Wu S (2018) Antiglutamic acid decarboxylase 65 (GAD65) antibody-associated epilepsy. Epilepsy & behavior : E&B 80:331–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.01.021
Vallabhaneni D, Naveed MA, Mangla R, Zidan A, Mehta RI (2018) Perfusion imaging in autoimmune encephalitis. Case reports in radiology 2018:3538645. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3538645
Lancaster E (2016) The diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune encephalitis. J Clin Neurol 12(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2016.12.1.1
Venkatesan A, Jagdish B (2019) Imaging in encephalitis. Semin neurol 39(3):312–321. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1687838
Lameka K, Farwell MD, Ichise M (2016) Positron emission tomography. Handb Clin Neurol 135:209–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-53485-9.00011-8
Wei YC, Tseng JR, Wu CL, Su FC, Weng WC, Hsu CC, Chang KH, Wu CF, Hsiao IT, Lin CP (2020) Different FDG-PET metabolic patterns of anti-AMPAR and anti-NMDAR encephalitis: case report and literature review. Brain and behavior 10(3):e01540. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.1540
Steiner I, Budka H, Chaudhuri A, Koskiniemi M, Sainio K, Salonen O, Kennedy PG (2005) Viral encephalitis: a review of diagnostic methods and guidelines for management. Eur J Neurol 12(5):331–343. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2005.01126.x
Heine J, Prüss H, Bartsch T, Ploner CJ, Paul F, Finke C (2015) Imaging of autoimmune encephalitis—relevance for clinical practice and hippocampal function. Neuroscience 309:68–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.05.037
Tobin WO, Pittock SJ (2017) Autoimmune neurology of the central nervous system. Continuum (Minneapolis, Minn) 23 (3, Neurology of Systemic Disease):627–653. https://doi.org/10.1212/con.0000000000000487
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339:b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700
Jang Y, Lee S-T, Bae J-Y, Kim T-J, Jun J-S, Moon J, Jung K-H, Park K-I, Irani SR, Chu K, Lee SK (2018) LGI1 expression and human brain asymmetry: insights from patients with LGI1-antibody encephalitis. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):279. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1314-2
Deuschl C, Rüber T, Ernst L, Fendler WP, Kirchner J, Mönninghoff C, Herrmann K, Quesada CM, Forsting M, Elger CE, Umutlu L (2020) 18F-FDG-PET/MRI in the diagnostic work-up of limbic encephalitis. PLoS ONE 15(1):e0227906–e0227906. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0227906
Chen Y, Xing XW, Zhang JT, Wang RX, Zhao W, Tan QC, Liu RZ, Wang XQ, Huang XS, Yu SY (2016) Autoimmune encephalitis mimicking sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a retrospective study. J Neuroimmunol 295–296:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2016.03.012
Celicanin M, Blaabjerg M, Maersk-Moller C, Beniczky S, Marner L, Thomsen C, Bach FW, Kondziella D, Andersen H, Somnier F, Illes Z, Pinborg LH (2017) Autoimmune encephalitis associated with voltage-gated potassium channels-complex and leucine-rich glioma-inactivated 1 antibodies - a national cohort study. Eur J Neurol 24(8):999–1005. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13324
Wegner F, Wilke F, Raab P, Tayeb SB, Boeck AL, Haense C, Trebst C, Voss E, Schrader C, Logemann F, Ahrens J, Leffler A, Rodriguez-Raecke R, Dengler R, Geworski L, Bengel FM, Berding G, Stangel M, Nabavi E (2014) Anti-leucine rich glioma inactivated 1 protein and anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis show distinct patterns of brain glucose metabolism in 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography. BMC Neurol 14:136. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-14-136
Moreno-Ajona D, Prieto E, Grisanti F, Esparragosa I, Sánchez Orduz L, Gállego Pérez-Larraya J, Arbizu J, Riverol M (2020) (18)F-FDG-PET imaging patterns in autoimmune encephalitis: impact of image analysis on the results. Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland) 10 (6). https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060356
Tripathi M, Tripathi M, Roy SG, Parida GK, Ihtisham K, Dash D, Damle N, Shamim SA, Bal C (2018) Metabolic topography of autoimmune non-paraneoplastic encephalitis. Neuroradiology 60(2):189–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1956-2
Liu X, Shan W, Zhao X, Ren J, Ren G, Chen C, Shi W, Lv R, Li Z, Liu Y, Ai L, Wang Q (2020) The clinical value of (18) F-FDG-PET in autoimmune encephalitis associated with LGI1 antibody. Front Neurol 11:418–418. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00418
Li T-R, Zhang Y-D, Wang Q, Shao X-Q, Lv R-J. Recognition of seizure semiology and semiquantitative FDG-PET analysis of anti-LGI1 encephalitis. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics n/a (n/a). https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13707
Chen C, Wang X, Zhang C, Cui T, Shi WX, Guan HZ, Ren HT, Shao XQ (2017) Seizure semiology in leucine-rich glioma-inactivated protein 1 antibody-associated limbic encephalitis. Epilepsy & behavior : E&B 77:90–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2017.08.011
Fisher RE, Patel NR, Lai EC, Schulz PE (2012) Two different 18F-FDG brain PET metabolic patterns in autoimmune limbic encephalitis. Clin Nucl Med 37(9):e213-218. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0b013e31824852c7
Solnes LB, Jones KM, Rowe SP, Pattanayak P, Nalluri A, Venkatesan A, Probasco JC, Javadi MS (2017) Diagnostic value of (18)F-FDG PET/CT versus MRI in the setting of antibody-specific autoimmune encephalitis. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine 58(8):1307–1313. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.116.184333
Leypoldt F, Buchert R, Kleiter I, Marienhagen J, Gelderblom M, Magnus T, Dalmau J, Gerloff C, Lewerenz J (2012) Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis: distinct pattern of disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83(7):681–686. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2011-301969
Ge J, Deng B, Guan Y, Bao W, Wu P, Chen X, Zuo C (2021) Distinct cerebral (18)F-FDG PET metabolic patterns in anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis patients with different trigger factors. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 14:1756286421995635. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756286421995635
Kerik-Rotenberg N, Diaz-Meneses I, Hernandez-Ramirez R, Muñoz-Casillas R, Reynoso-Mejia CA, Flores-Rivera J, Espinola-Nadurille M, Ramirez-Bermudez J, Aguilar-Palomeque C (2020) A metabolic brain pattern associated with anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. Psychosomatics 61(1):39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psym.2019.08.007
Lagarde S, Lepine A, Caietta E, Pelletier F, Boucraut J, Chabrol B, Milh M, Guedj E (2016) Cerebral (18)fluorodeoxy-glucose positron emission tomography in paediatric anti N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis: a case series. Brain Develop 38(5):461–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.braindev.2015.10.013
Zhu F, Shan W, Lv R, Li Z, Wang Q (2020) Clinical characteristics of GAD 65-associated autoimmune encephalitis. Acta Neurol Scand 142(3):281–293. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.13281
Baumgartner A, Rauer S, Mader I, Meyer PT (2013) Cerebral FDG-PET and MRI findings in autoimmune limbic encephalitis: correlation with autoantibody types. J Neurol 260(11):2744–2753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-7048-2
Masangkay N, Basu S, Moghbel M, Kwee T, Alavi A (2014) Brain 18F-FDG-PET characteristics in patients with paraneoplastic neurological syndrome and its correlation with clinical and MRI findings. Nucl Med Commun 35(10):1038–1046. https://doi.org/10.1097/mnm.0000000000000163
Newey CR, Sarwal A, Hantus S (2016) [(18)F]-Fluoro-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography scan should be obtained early in cases of autoimmune encephalitis. Autoimmune diseases 2016:9450452. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9450452
Probasco JC, Solnes L, Nalluri A, Cohen J, Jones KM, Zan E, Javadi MS, Venkatesan A (2018) Decreased occipital lobe metabolism by FDG-PET/CT: an anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis biomarker. Neurology(R) neuroimmunology & neuroinflammation 5(1):e413. https://doi.org/10.1212/nxi.0000000000000413
Siddiqui SV, Chatterjee U, Kumar D, Siddiqui A, Goyal N (2008) Neuropsychology of prefrontal cortex. Indian J Psychiatry 50(3):202–208. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5545.43634
Gibson LL, McKeever A, Coutinho E, Finke C, Pollak TA (2020) Cognitive impact of neuronal antibodies: encephalitis and beyond. Transl Psychiatry 10(1):304. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-020-00989-x
Li F, Tsien JZ (2009) Memory and the NMDA receptors. N Engl J Med 361(3):302–303. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcibr0902052
Irani SR, Vincent A (2011) NMDA receptor antibody encephalitis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 11(3):298–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-011-0186-y
Shin YW, Lee ST, Shin JW, Moon J, Lim JA, Byun JI, Kim TJ, Lee KJ, Kim YS, Park KI, Jung KH, Lee SK, Chu K (2013) VGKC-complex/LGI1-antibody encephalitis: clinical manifestations and response to immunotherapy. J Neuroimmunol 265(1–2):75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2013.10.005
Irani SR, Alexander S, Waters P, Kleopa KA, Pettingill P, Zuliani L, Peles E, Buckley C, Lang B, Vincent A (2010) Antibodies to Kv1 potassium channel-complex proteins leucine-rich, glioma inactivated 1 protein and contactin-associated protein-2 in limbic encephalitis, Morvan’s syndrome and acquired neuromyotonia. Brain : a journal of neurology 133(9):2734–2748. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq213
Lancaster E, Martinez-Hernandez E, Dalmau J (2011) Encephalitis and antibodies to synaptic and neuronal cell surface proteins. Neurology 77(2):179–189. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e318224afde
Lancaster E, Dalmau J (2012) Neuronal autoantigens—pathogenesis, associated disorders and antibody testing. Nat Rev Neurol 8(7):380–390. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2012.99
Saiz A, Blanco Y, Sabater L, González F, Bataller L, Casamitjana R, Ramió-Torrentà L, Graus F (2008) Spectrum of neurological syndromes associated with glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies: diagnostic clues for this association. Brain : a journal of neurology 131(10):2553–2563. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awn183
Turpin S, Martineau P, Levasseur MA, Meijer I, Décarie JC, Barsalou J, Renaud C, Decaluwe H, Haddad E, Lambert R (2019) 18F-Flurodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography with computed tomography (FDG PET/CT) findings in children with encephalitis and comparison to conventional imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46(6):1309–1324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04302-x
Morbelli S, Arbizu J, Booij J, Chen MK, Chetelat G, Cross DJ, Djekidel M, Drzezga A, Ekmekcioglu O, Garibotto V, Hesse S, Ishii K, Jafari L, Lammertsma AA, Law I, Mathews D, Minoshima S, Mosci K, Pagani M, Pappata S, Silverman DH, Signore A, Van De Giessen E, Villemagne V, Barthel H (2017) Erratum to: the need of standardization and of large clinical studies in an emerging indication of [18 F]FDG PET: the autoimmune encephalitis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 44(3):559–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3598-8
Saif MW, Tzannou I, Makrilia N, Syrigos K (2010) Role and cost effectiveness of PET/CT in management of patients with cancer. Yale J Biol Med 83(2):53–65
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This systematic review has been done in accordance with the rules of the ethical committee of Tehran University of medical sciences.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nabizadeh, F., Ramezannezhad, E., Sardaripour, A. et al. [18F]FDG brain PET and clinical symptoms in different autoantibodies of autoimmune encephalitis: a systematic review. Neurol Sci 43, 4701–4718 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-022-06094-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-022-06094-9