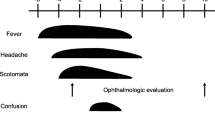
Abstract
We report a 71-year-old man with legionellosis, who presented with abducens nerve palsy, singultus, confusion, memory impairment, ataxia, and hyporeflexia. Legionella pneumonia was diagnosed on the basis of detection of Legionella pneumophila antigen in the urine. The cerebrospinal fluid was negative for the antigen and antibody, but an oligoclonal band was detected, and the IgG index was elevated. It was speculated that an undetermined immune-mediated mechanism had contributed to the development of the neurological manifestations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shetty KR, Cilyo CL, Starr BD, Harter DH (1980) Legionnaires’ disease with profound cerebellar involvement. Arch Neurol 37:379–380
Weir AI, Bone I, Kennedy DH (1982) Neurological involvement in legionellosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45:603–608
Johnson JD, Raff MJ, Van Arsdall JA (1984) Neurologic manifestations of Legionnaires’ disease. Medicine 63:303–310
Pendlebury WW, Perl DP, Winn WC Jr, McQuillen JB (1983) Neuropathologic evaluation of 40 confirmed cases of Legionella pneumonia. Neurology 33:1340–1344
Helbig JH, Uldum SA, Lück PC, Harrison TG (2001) Detection of Legionella pneumophila antigen in urine samples by the BinaxNOW immunochromatographic assay and comparison with both Binax Legionella urinary enzyme immunoassay (EIA) and biotest legionella urine antigen EIA. J Med Microbiol 50:509–516
Gilbert LG, Bastian I (2009) Legionella laboratory case definitions. Public Health Laboratory Network. Communicable Disease Network Australia, 2007. http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/cda-phlncd-legionella.htm. Cited 26 June 2009
Hische EA, van der Helm HJ, van Walbeek HK (1982) The cerebrospinal fluid immunoglobulin G index as a diagnostic aid in multiple sclerosis: a Bayesian approach. Clin Chem 28:354–355
Nakajima I (2003) Oligoclonal band in Japanese Multiple Sclerosis. Animus 38:8 (in Japanese)
Blyth CC, Adams DN, Chen SC (2009) Diagnostic and typing methods for investigating Legionella infection. N S W Public Health Bull 20:157–161
Muñoz JA, Díaz Ortuño A, Rodríguez González T, Rubiés-Prat J (1988) Paralysis of the 3d cranial nerve in legionellosis. Rev Clin Esp 57:182 (in Spanish)
Reynaga E, Pedro-Botet ML, Lozano-Sánchez M, Sopena N, Sabriá M (2001) Third cranial nerve palsy and Legionnaire’s disease. Rev Neurol 32:896 (in Spanish)
Lattimer GL, Rhodes LV 3rd (1978) Legionnaires’disease. Clinical findings and one year follow-up. JAMA 240:1169–1171
Katzenstein TL, Dahl G, Greulich A, Nielsen AL (1992) Legionnaires’ disease—a multifaceted syndrome. Ugeskr Laeger 154:2762–2763 (in Danish)
Morgan DJ, Gawler J (1981) Severe peripheral neuropathy complicating Legionnaires’ disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 283:1577–1578
Davis JN (1970) An experimental study of hiccup. Brain 93:851–872
Shelburne SA, Kielhofner MA, Tiwari PS (2004) Cerebellar involvement in legionellosis. South Med J 97:61–64
Wong KH, Moss CW, Hochstein DH, Arko RJ, Schalla WO (1979) “Endotoxicity” of the Legionnaires’ disease bacterium. Ann Intern Med 90:624–627
Spieker S, Petersen D, Rolfs A, Fehrenbach F, Kuntz R, Seuffer RH, Fetter M, Dichgans J (1988) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis following Pontiac fever. Eur Neurol 40:169–172
Nagamitsu S, Matsuishi T, Ishibashi M, Yamashita Y, Nishimi T, Ichikawa K, Yamanishi K, Kato H (1999) Decreased cerebellar blood flow in postinfectious acute cerebellar ataxia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:109–112
Conrad AJ, Chiang EY, Andeen LE, Avolio C, Walker SM, Baumhefner RW, Mirzayan R, Tourtellotte WW (1994) Quantitation of intrathecal measles virus IgG antibody synthesis rate: subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 54:99–108
Contini C, Fainardi E, Cultrera R, Canipari R, Peyron F, Delia S, Paolino E, Granieri E (1998) Advanced laboratory techniques for diagnosing Toxoplasma gondii encephalitis in AIDS patients: significance of intrathecal production and comparison with PCR and ECL-western blotting. J Neuroimmunol 92:29–37
Rousseau P (1995) Hiccups. South Med J 88:175–181
Netter FH (1989) Thorax. In: Atlas of human anatomy, 1st edn. CIBA-GEIGY Corp, Summit, plate 182
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konno, S., Kono, H., Kitazono, H. et al. Legionellosis presenting as singultus and external ophthalmoplegia. Neurol Sci 33, 1435–1437 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0927-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0927-3