Abstract
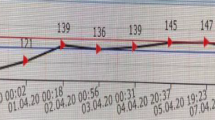
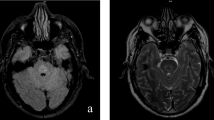
Central pontine myelinolysis and extrapontine myelinolysis are rare demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system. These diseases are related frequently to rapid correction of hyponatremia. They have also been described in association with other underlying conditions such as alcoholism and malnutrition. In the present study, we report a case of central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis with acute hepatic dysfunction. The patient had no apparent evidence of hyponatremia and no history of alcohol abuse. On admission, the patient was lethargic; dysphagia, dysarthria, and quadriplegia were noted. Laboratory examination showed significantly increased transaminase without hyponatremia. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed abnormal signal intensities in the pons and thalamus. Consciousness level and clinical symptoms improved gradually within a week. We suggest that acute hepatic dysfunction may play an important role in the development of central pontine myelinolysis and extrapontine myelinolysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RD, Victor M, Mancall EL (1959) Central pontine myelinolysis: a hitherto undescribed disease occurring in alcoholic and malnourished patients. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 81:778–780
Lampl C, Yazdi K (2002) Central pontine myelinolysis. Eur Neurol 47:3–10
Wight DG, Laureno R, Victor M (1979) Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Brain 102:361–385
Sterns RH, Riggs JE, Schochet SS Jr (1986) Osmotic demyelination syndrome following correction of hyponatremia. New Engl J Med 314:1535–1542
Laureno R, Karp BI (1988) Pontine and extrapontine myelinoysis following rapid correction of hyponatremia. Lancet 1:1439–1441
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Rojiani AM, Christopher MF (2006) Central and extrapontine myelinolysis: then and now. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:1–11
Wirth S (1995) “Accompanying hepatitis” in viral infections. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 120:461
Chan PK (2002) Outbreak of avian influenza A (H5N1) virus infection in Hong Kong in 1997. Clin Infect Dis 34(Suppl 2):S58–S64
Polakos NK, Cornejo JC, Murray DA et al (2006) Kupffer cell-dependent hepatitis occurs during influenza infection. Am J Pathol 168(4):1169–1178
Fraser CL, Arieff AI (1985) Hepatic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 313:865–873
Hiroo I, Hidetomo M, Hirotaka K et al (2008) Central pontine lesions observed with MRI in four diabetic patients. Inter Med 47:1425–1430
Norenberg MD (2010) Central pontine myelinolysis: historical and mechanistic considerations. Metab Brain Dis 25(1):97–106
Powers JM, McKeever PE (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. An ultrastructural and elemental study. J Neurol Sci 29:65–81
Shurtliff LF, Ajax ET, Englert E Jr, D’Agostino AN (1966) Central pontine myelinolysis and cirrhosis of the liver. A report of four cases. Am J Clin Pathol 46:239–244
Neuwelt EA, Barnett PA, Bigner DD et al (1982) Effects of adrenal cortical steroids and osmotic blood-brain barrier opening on methotrexate delivery to gliomas in the rodent: the factor of the blood-brain barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:4420–4423
Sugimura Y, Murase T, Takefuji S et al (2005) Protective effect of dexamethasone on osmotic-induced demyelination in rats. Exp Neurol 192:178–183
Dewitt LD, Buonanno FS, Kistler JP et al (1984) Central pontine myelinolysis: demonstration by nuclear magnetic resonance. Neurology 34:570–576
Miller GM, Baker HL, Okazaki H et al (1988) Central pontine myelinolysis and its imitators: MR findings. Radiology 168:795–802
Kimberly AR, Norbert GC, Gary MM (2004) Early diagnosis of central pontine myelinolysis with diffusion-weighted imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 25:210–213
Chu K, Kang DW, Ko SB et al (2011) Diffusion-weighted MR findings of central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Acta Neurol Scand 104:385–388
Waragai M, Satoh T (1998) Serial MRI of extrapontine myelinolysis of the basal ganglia: a case report. J Neuro Sci 161:173–175
Choe WJ, Cho BK, Kim IO et al (1998) Extrapontine myelinolysis caused by electrolyte imbalance during the management of suprasellar germ cell tumors. Report of two cases. Childs Nerv Syst 14:155–158
Ho VB, Fitz CR, Yoder CC et al (1998) Resolving MR features in osmotic myelinolysis (general pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis). AJNR 1993 14:163–167
Seok Jung Im, Youn Jinyoung, Chung EunJoo et al (2006) Sequential observation of movement disorders and brain images in the case of central pontine myelinolysis and extrapontine myelinolysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 12:462–464
Koenig SH (1991) Cholesterol of myelin in the determinant of gray-white contrast in MRI of brain. Magn Reson Med 20:285–291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, Y., An, Dh., Xing, Y. et al. Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis associated with acute hepatic dysfunction. Neurol Sci 33, 673–676 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0838-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-011-0838-3