Abstract
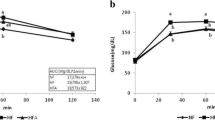
This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of ginseng vinegar (GV) for preventing and ameliorating the obesity and inflammation. Oral administrations of GV with different doses were conducted for 10 weeks in the preventive model and therapeutic model. In the preventive model, above GV-medium dose significantly reduced body weight gain, epididymal fat weight, triglycerides, and total cholesterol compared to control. GV-high dose effectively improved the inflammatory factors (tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin 6) in serum, liver, and adipose tissue. In the therapeutic model, all GV groups showed significantly decreased body weight gain, epididymal fat weight, triglycerides, and total cholesterol. Reductions of the TNF-α level in the serum and liver were observed in all GV groups, and the CRP levels in the liver of all GV groups were significantly decreased with different trend from the preventive model. These results suggest that GV is more effective in therapeutic model and is a potential food for obesity and associated inflammation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C, Kim MJ, Caron M, Vidal H, Feve B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 17: 4–12 (2006)
Cesari M, Penninx BW, Newman AB, Kritchevsky SB, Nicklas BJ, Sutton-Tyrrell K, Harris TB. Inflammatory markers and onset of cardiovascular events results from the Health ABC Study. Circulation 108: 2317–2322 (2003)
Choi YH, Kim KO, Baek EJ, Hur BS. Simultaneous two-step fermentation ginseng black vinegar and method for manufacturing the same. Korea Patent 10-1749990 (2017)
Chou CH, Liu CW, Yang DJ, Wu YHS, Chen YC. Amino acid, mineral, and polyphenolic profiles of black vinegar, and its lipid lowering and antioxidant effects in vivo. Food Chem. 168: 63–69 (2015)
Fushimi T, Sato Y. Effect of acetic acid feeding on the circadian changes in glycogen and metabolites of glucose and lipid in liver and skeletal muscle of rats. Br. J. Nutr. 94: 714–719 (2005)
Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444: 860–867 (2006)
Hwang JT, Kim SH, Lee MS, Kim SH, Yang HJ, Kim MJ, Kwon DY. Anti-obesity effects of ginsenoside Rh 2 are associated with the activation of AMPK signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocyte. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 364: 1002–1008 (2007)
Kim DK, Baik MY, Kim HK, Hahm YT, Kim BY. Manufacture of the red ginseng vinegar fermented with red ginseng concentrate and rice wine, and its quality evaluation. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 44: 179–184 (2012)
Ko SK, Lee KH, Hong JK, Kang SA, Sohn UD, Im BO, Han ST, Yang BW, Chung SH, Lee BY. Change of ginsenoside composition in ginseng extract by vinegar process. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 14: 509–513 (2005)
Koukkunen H, Penttilä K, Kemppainen A, Halinen M, Penttilä I, Rantanen T, Pyörälä K. C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor-α in the prognostic classification of unstable angina pectoris. Ann. Med. 33: 37–47 (2001)
Lee JH, Cho HD, Jeong JH, Lee MK, Jeong YK, Shim KH, Seo KI. New vinegar produced by tomato suppresses adipocyte differentiation and fat accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells and obese rat model. Food Chem. 141: 3241–3249 (2013)
Lim S, Yoon JW, Choi SH, Cho BJ, Kim JT, Chang HS, Kim YB. Effect of ginsam, a vinegar extract from Panax ginseng, on body weight and glucose homeostasis in an obese insulin-resistant rat model. Metabolism 58: 8–15 (2009)
Lin WW, Karin M. A cytokine-mediated link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 117: 1175–1183 (2007)
Moon YJ, Choi DS, Oh SH, Song YS, Cha, YS. Effects of persimmon-vinegar on lipid and carnitine profiles in mice. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 19: 343–348 (2010)
Nam YR, Won SB, Chung YS, Kwak CS, Kwon YH. Inhibitory effects of Doenjang, Korean traditional fermented soybean paste, on oxidative stress and inflammation in adipose tissue of mice fed a high-fat diet. Nutr. Res. Pract. 9: 235–241 (2015)
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey Jr GC. AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J. Nutr. 123: 1939–1951(1993)
Samad A, Azlan A, Ismail A. Therapeutic effects of vinegar: a review. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 8: 56–61 (2016)
Sengun IY, Karapinar M. Effectiveness of household natural sanitizers in the elimination of Salmonella typhimurium on rocket (Eruca sativa Miller) and spring onion (Allium cepa L.). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 98: 319–323 (2005)
Seo KI, Lee J, Choi RY, Lee HI, Lee JH, Jeong YK, Lee MK. Anti-obesity and anti-insulin resistance effects of tomato vinegar beverage in diet-induced obese mice. Food Funct. 5: 1579–1586 (2014)
Shang W, Yang Y, Jiang B, Jin H, Zhou L, Liu S, Chen M. Ginsenoside Rb 1 promotes adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells by enhancing PPARγ 2 and C/EBPα gene expression. Life Sci. 80: 618–625 (2007)
Song YB, An YR, Kim SJ, Park HW, Jung JW, Kyung JS, Hwang SY, Kim YS. Lipid metabolic effect of Korean red ginseng extract in mice fed on a high‐fat diet. J. Sci. Food Agric. 92: 388–396 (2010)
Wu Y, Yu Y, Szabo A, Han M, Huang XF. Central inflammation and leptin resistance are attenuated by ginsenoside Rb 1 treatment in obese mice fed a high-fat diet. PLoS ONE 9: e92618 (2014)
Yun SN, Ko SK, Lee KH, Chung SH. Vinegar-processed ginseng radix improves metabolic syndrome induced by a high fat diet in ICR mice. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 30: 587–595 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MOTIE), Korea, under the “Regional Specialized Industry Development Program” (R0002329) supervised by the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, I., Baek, E.J., Lee, DH. et al. Anti-obesity and anti-inflammatory effects of ginseng vinegar in high-fat diet fed mice. Food Sci Biotechnol 28, 1829–1836 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00624-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00624-6