Abstract
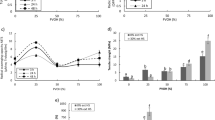
Solid fat was developed by blending fully hydrogenated soybean oil, palm oil, and canola oil, and organogels were prepared using selected solid fats and ethylcellulose. The oxidative stability of organogel was tested at 100 and 180°C using a headspace oxygen assay. Addition of ethylcellulose produced a firmer organogel solid state in selected solid fats ranging from 15.8 to 24.6% saturation at room temperature. Addition of ethylcellulose generally decreased the oxidative stability of organogels prepared using canola oil. The oxidative stability of some organogels made using solid fats changed depending on the concentration of added ethylcellulose (10 or 15%, w/w), and the oxidation temperature. Development of an organogel with a relatively low saturation and a high oxidative stability suitable as a food ingredient is possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu FB, Stampfer MJ, Manson JE, Ascherio A, Colditz GA, Speizer FE, Hennekens CH, Willett WC. Dietary saturated fats and their food sources in relation to the risk of coronary heart disease in women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 70: 1001–1008 (1999)
Mensink RP, Zock PL, Kester AD, Katan MB. Effects of dietary fatty acids and carbohydrates on the ratio of serum total to HDL cholesterol and on serum lipids and apolipoproteins: a meta-analysis of 60 controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 77: 1146–1155 (2003)
Grundy SM. Influence of stearic acid on cholesterol metabolism relative to other long-chain fatty acids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 60: 986S–990S (1994)
Sundram K, Hayes KC, Siru OH. Dietary palmitic acid results in lower serum cholesterol than does a lauric-myristic acid combination in normolipemic humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 59: 841–846 (1994)
Edmund DC, Alejandro G, Marangoni AG. Organogels: An alternative edible oil-structuring method. J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 89: 749–780 (2012)
Gravelle AJ, Barbut S, Marangoni AG. Fractionation of ethylcellulose oleogels during setting. Food Funct. 4: 153–161 (2013)
Zetzl AK, Marangoni AG, Barbut S. Mechanical properties of ethylcellulose oleogels and their potential for saturated fat reduction in frankfurters. Food Funct. 3: 327–337 (2012)
Mensink RP, Katan MB. Effect of dietary trans fatty acids on high-density and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in healthy subjects. New Engl. J. Med. 323: 439–445 (1990)
AOCS. Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the AOCS. 4th ed. Method Ce 6-22. American Oil Chemists’ Society, Champaign, IL, USA (2006)
Lee JH, Min DB. Effects of photooxidation and chlorophyll photosensitization on the formation of volatile compounds in lard model systems. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 18: 413–418 (2009)
Min DB, Boff JM. Chemistry and reaction of singlet oxygen in foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F. 1: 58–72 (2002)
Gunstone FD. Reaction of oxygen and unsaturated fatty acids. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 61: 441–447 (1984)
Neff WE, Selke E, Mounts TL, Rinsch W, Frankel EN, Zeitoun MAM. Effect of triacylglycerol composition and structure on oxidative stability of oils from selected soybean germplasm. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 49: 111–118 (1992)
Kim JY, Yi BR, Kim MJ, Lee JH. Oxidative stability in bulk oil containing carbohydrates such as glucose, sucrose, maltose, mannitol, and starch. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 91: 1387–1395 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.Y., Yi, B., Kim, MJ. et al. Oxidative stability of solid fats containing ethylcellulose determined based on the headspace oxygen content. Food Sci Biotechnol 23, 1779–1784 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0243-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0243-9