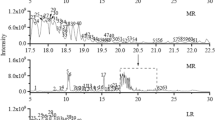
Abstract
Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) contains several types of saponins and ginsenosides, which are usually considered the major active components of ginseng. The types and quantities of saponins found in ginseng may differ depending on the region of cultivation. As a result, ginsengs produced in different areas of Korea have been unintentionally mislabeled and/or confused by Korean herbal markets owing to their complicated plant sources. Another concern is that 4- and 6-year-old ginseng roots, traditionally prescribed for different medicinal purposes, can vary in total saponin contents. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a reliable method for distinguishing different cultivation regions and ages of ginseng roots. A rapid resolution liquid chromatography-quadruple time of flight mass spectrometry (RRLC-QTOF/MS) based chemical profiling method was established for the rapid and global evaluation of Korean ginseng roots in this study. The method was successfully applied for the comparison of ginseng roots cultivated in different regions and of differing ages. Principal component analysis (PCA) of the data showed the clear separation of 4- and 6-year-old ginseng roots and of ginseng cultivated in 2 different areas of Korea, Ganghwa and Punggi.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akerele O. WHO guideline for assessment of herbal medicines. Fitoterapia 63: 99–118 (1992)
Cicero AFG, Vitale G, Savino G, Arletti R. Panax notoginseng (Burk.) effects on fibrinogen and lipid plasma level in rats fed on a high-fat diet. Phytother. Res. 17: 174–178 (2003)
Kim AJ, Kang SJ, Lee KH, Lee MS, Ha SD, Cha YS, Kim SY. The chemopreventive potential and anti-inflammatory activities of Korean black ginseng in colon 26-M3.1 carcinoma cells and macrophages. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 53: 101–105 (2010)
Attele AS, Wu JA, Yuan CS. Ginseng pharmacology: Multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem. Pharm. 58: 1685–1693 (1999)
Sun H, Yang Z, Ye Y. Structure and biological activity of protopanaxatriol-type saponins from the roots of Panax notoginseng. Int. Immunopharmacol. 6: 14–25 (2005)
Liu C X, Xiao PG. Recent advances on ginseng research in China. J. Ethnopharmacol. 36: 27–38 (1992)
Li W, Fitzolff JF. HPLC with evaporative light scattering detection as a tool to distinguish Asian ginseng (Panax ginseng) and North American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius). J. Liq. Chromatogr. R. T. 25: 17–27 (2002)
Hwang JB, Ha JH, Hawer WD, Nahmgung B, Lee BY. Ginsenoside contents of Korean white gingeng and taegeuk ginseng with various sizes and cultivation years. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 3: 508–512 (2005)
Lau AJ, Seo BH, Woo SO, Koh HL. High-performance liquid chromatographic method with quantitative comparisons of whole chromatograms of raw and steamed Panax notoginseng. J. Chromatogr. A 1057: 141–149 (2004)
Ji QC, Harkey MR, Henderson GL, Gershwin ME, Stern JS, Hackman RM. Quantitative determination of ginsenosides by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 12: 320–326 (2001)
Kwon SW, Han SB, Park IH, Kim, JM, Park MK, Park JH. Liquid chromatographic determination of less polar ginsenosides in processed ginseng. J. Chromatogr. A 921: 335–339 (2001)
Chan ECY, Yap SL, Lau AJ, Leow PC, Toh DF, Koh HL. Ultraperformance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry based metabolomics of raw and steamed Panax notoginseng. Rapid Commun. Mass Sp. 21: 519–528 (2007)
Eriksson L, Johansson E, Kettaneh Wold N, Wold S. Multi and Megavariate Data Analysis. Umetrics Academy, Umeå, Sweden. pp. 43–64 (2001)
Lee DY, Cho JG, Lee MK, Lee JW, Lee YH, Yang DC, Baek NI. Discrimination of Panax ginseng roots cultivated in different areas in Korea using HPLC-ELSD and principal component analysis. J. Ginseng. Res. 35: 31–38 (2011)
Cao XL, Tian YZ, Tian Y, Liu, QH, Jia LJ, Ito, Y. Separation of dammarane saponins from root of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F. H. Chen, by HSCCC coupled with evaporative light scattering detector. J. Liq. Chromatogr. R. T. 26: 1579–1591 (2003)
Zhao X, Wang J, Li J, Fu L, Gao J, Du X, Bi H, Zhou Y, Tai G. Highly selective biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to Rd by the phytopathogenic fungus Cladosporium fulvum (syn. Fulvia fulva). J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 36: 721–726 (2009)
Kim YH, Lee YG, Choi KJ, Uchida K, Suzuki Y. Transglycosylation to ginseng saponins by cyclomaltodextrin glucanotransferases. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 65: 875–883 (2001)
Ma XQ, Liang XM, Xu Q, Zhang XZ, Xiao HB. Identification of ginsenosides in roots of Panax ginseng by HPLC-APCI/MS. Phytochem. Anal. 16: 181–187 (2005)
Gao X, Dan M, Zhao A, Xie G, Jia W. Simultaneous determination of saponins in flower buds of Panax notoginseng using high performance liquid chromatography. Biomed. Chromatogr. 22: 244–249 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, DY., Cho, JG., Bang, MH. et al. Discrimination of Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng) roots using rapid resolution LC-QTOF/MS combined by multivariate statistical analysis. Food Sci Biotechnol 20, 1119–1124 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-011-0152-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-011-0152-0