Abstract
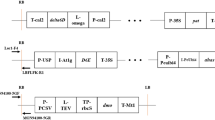
A multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method was developed to identify and distinguish 3 kinds of stacked genetically modified (GM) maize (MON810× MON863, NK603×MON863, and NK603×MON810× MON863). Four primer pairs, SSIIb JHF/JHR, C3b 5′/TAP1–3′, HS01/cry-CR01, and HS01/CTP164-3′ yielded 101, 129, 194, and 314 bp amplicons, respectively, Using the genomic DNA of the 3 stacked GM maize as templates, 3 or 4 corresponding PCR amplicons were amplified with similar band intensities by the multiplex PCR. The limit of detection (LOD) was approximately 0.5% for 3 kinds of stacked GM maize, using the multiplex PCR. The detection system using multiplex PCR developed in this study may be applicable to monitoring, identifying, and distinguishing not only the stacked GM maizes but also other stacked genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elenis DS, Kalogianni DP, Glynou K, Ioannou PC, Christopoulos TK. Advances in molecular techniques for the detection and quantification of genetically modified organisms. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 392: 347–354 (2008)
Engel KH, Frenzel T, Miller A. Current and future benefits from the use of GM technology in food production. Toxicol. Lett. 127: 329–336 (2002)
Chandler SF, Lu C-Y. Biotechnology in ornamental horticulture. In Vitro Cell. Dev.-Pl 41: 591–601 (2005)
Stephenson JR, Warnes A. Release of genetically modified microorganisms into the environment. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 65: 5–14 (1996)
Kim HY, Kim JH, Oh MH. Regulation and detection methods for genetically modified foods in Korea. Pure Appl. Chem. 82: 129–137 (2010)
Michelini E, Simoni P, Cevenini L, Mezzanotte L, Roda A. New trends in bioanalytical tools for the detection of genetically modified organisms: An update. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 392: 355–367 (2008)
Yang L, Pan A, Jia J, Ding J, Chen J, Cheng H, Zhang C, Zhang D. Validation of a tomato-specific gene, LAT52, used as an endogenous reference gene in qualitative and real-time quantitative PCR detection of transgenic tomatoes. J. Agr. Food Chem. 53: 183–190 (2005)
Forte VT, Di Pinto A, Martino C, Tantillo GM, Grasso G, Schena FP. A general multiplex-PCR assay for the general detection of genetically modified soya and maize. Food Control 16: 535–539 (2005)
Vollenhofer S, Burg K, Schmidt J, Kroath H. Genetically modified organisms in food-screening and specific detection by polymerase chain reaction. J. Agr. Food Chem. 47: 5038–5043 (1999)
Allmann M, Candrian U, Höfelein C, Lüthy J. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): A possible alternative to immunochemical methods assuring safety and quality of food: Detection of wheat contamination in non-wheat food products. Z. Lebensm. Unters. For. 196: 248–251 (1993)
Meyer R, Chardonnens F, Hübner P, Lüthy J. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in the quality and safety assurance of food: Detection of soya in processed meat products. Z. Lebensm. Unters. For. 203: 339–344 (1996)
Holst-Jensen A, Rønning SB, Løvseth A, Berdal KG. PCR technology for screening and quantification of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 375: 985–993 (2003)
De Schrijver A, Devos Y, Van den Bulcke M, Cadot P, De Loose M, Reheul D, Sneyers M. Risk assessment of GM stacked events obtained from crosses between GM events. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 18: 101–109 (2007)
Akiyama H, Watanabe T, Wakabayashi K, Nakade S, Yasui S, Sakata K, Chiba R, Spiegelhalter F, Hino A, Maitani T. Quantitative detection system for maize sample containing combined-trait genetically modified maize. Anal. Chem. 77: 7421–7428 (2005)
Lee B, Kim CG, Park JY, Park KW, Kim HJ, Yi H, Jeong SC, Yoon WK, Kim HM. Monitoring the occurrence of genetically modified soybean and maize in cultivated fields and along the transportation routes of the Incheon Port in South Korea. Food Control 20: 250–254 (2009)
Xu WT, Yuan YF, Luo YB, Bai WB, Zhang CJ, Huang KL. Eventspecific detection of stacked genetically modified maize Bt11×GA21 by UP-M-PCR and real-time PCR. J. Agr. Food Chem. 57: 395–402 (2009)
Rudi K, Rud I, Holck A. A novel multiplex quantitative DNA array based PCR (MQDA-PCR) for quantification of transgenic maize in food and feed. Nucleic Acids Res. 31: e62 (2003)
Höhne M, Santisi CR, Meyer R. Real-time multiplex PCR: An accurate method for the detection and quantification of 35S-CaMV promoter in genetically modified maize-containing food. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 215: 59–64 (2002)
Mano J, Shigemitsu N, Futo S, Akiyama H, Teshima R, Hino A, Furui S, Kitta K. Real-time PCR array as a universal platform for the detection of genetically modified crops and its application in identifying unapproved genetically modified crops in Japan. J. Agr. Food Chem. 57: 26–37 (2009)
Xu J, Zhu S, Miao H, Huang W, Qiu M, Huang Y, Fu X, Li Y. Event-specific detection of seven genetically modified soybean and maizes using multiplex-PCR coupled with oligonucleotide microarray. J. Agr. Food Chem. 55: 5575–5579 (2007)
Gruère GP, Carter CA, Hossein Farzin Y. Explaining international differences in genetically modified food labeling policies. Rev. Int. Econ. 17: 393–408 (2009)
Kim JH, Kim HY. Event-specific detection methods for genetically modified maize MIR604 using real-time PCR. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 18: 1118–1123 (2009)
Kim JH, Park SH, Kim HY. Multiplex PCR detection of four events of GM maize (Event 3272, LY038, MIR162, and MON88017). J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 52: 105–107 (2009)
Matsuoka T, Kawashima Y, Akiyama H, Miura H, Goda Y, Kusakabe Y, Isshiki K, Toyoda M, Hino A. A method of detecting recombinant DNAs from four lines of genetically modified maize. J Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 41: 137–143 (2000)
Kim JH, Song HS, Heo MS, Lee WY, Lee SH, Park SH, Park HK, Kim MC, Kim HY. Detection of eight different events of genetically modified maize by multiplex PCR method. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 15: 148–151 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SY., Kim, JH., Lee, H. et al. Detection system of stacked genetically modified maize using multiplex PCR. Food Sci Biotechnol 19, 1029–1033 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-010-0144-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-010-0144-5