Abstract
Objective
Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) is an auto-inflammatory disease that is also characterized with some of the common musculoskeletal features of spondyloarthritis (SpA). Enthesitis is the hallmark of SpA. Recently, it was postulated that exertional leg pain is a possible sign of lower extremity enthesitis associated with FMF severity. In this study, we have evaluated the association between the enthesitis, enthesitis score and disease severity in FMF patients.
Methods
We enrolled 238 FMF patients that fulfilled the modified Tel-Hashomer criteria. We assessed the presence of enthesitis at the Maastricht Ankylosing Spondylitis Enthesitis Score (MASES) defined sites with standard palpation method. Then, FMF patients dichotomised two groups as enthesitis group and controls. Herein, we evaluated the enthesis extensity with MASES. FMF disease severity was determined via the international severity scoring system for FMF (ISSF). Firstly, we have compared demographic properties, disease-related features and ISSF scores of the groups. Then, we have correlated ISSF with MASES in enthesitis group.
Results
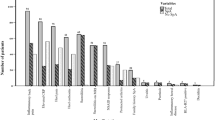
We showed that 54 (22.6%) of 238 patients had enthesitis. The demographic features were similar between the groups. The enthesitis group had higher ISSF scores (p < 0.001); higher frequency of fever (p = 0.004), exertional leg pain (p < 0.001), myalgia (p < 0.001) and arthritis (p = 0.01); and more intense, widespread, frequent and longer attacks compared with controls. Moreover, there was a weak correlation between ISSF and MASES in the patients with enthesitis.
Conclusion
Enthesitis may be a sign of more severe FMF phenotype and frequently associated with other musculoskeletal manifestations resemble SpA.
Key points •More than one-fifth of the patients with FMF would suffer from enthesitis. •The FMF patients with enthesitis had higher ISSF scores; higher frequency of fever, exertional leg pain, myalgia and arthritis; and more intense, widespread, frequent and longer attacks as compared with controls. •Enthesitis may be a sign of more severe FMF phenotype and frequently associated with other SpA-like musculoskeletal feature. |
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials would be available if needed.
References
Ben-Chetrit E, Levy M (1998) Familial Mediterranean fever. Lancet 351(9103):659–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(97)09408-7
Brik R, Shinawi M, Kasinetz L, Gershoni-Baruch R (2001) The musculoskeletal manifestations of familial Mediterranean fever in children genetically diagnosed with the disease. Arthritis Rheum 44(6):1416–1419. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(200106)44:6<1416::AID-ART236>3.0.CO;2-6
Akar S, Soysal O, Balci A, Solmaz D, Gerdan V, Onen F, Tunca M, Akkoc N (2013) High prevalence of spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis among familial Mediterranean fever patients and their first-degree relatives: further evidence for the connection. Arthritis Research & Therapy 15(1):R21. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4154
Eshed I, Rosman Y, Livneh A, Kedem R, Langevitz P, Ben-Zvi I, Lidar M (2014) Exertional leg pain in familial Mediterranean fever: a manifestation of an underlying enthesopathy and a marker of more severe disease. Arthritis & Rheumatology 66(11):3221–3226. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38797
Slobodin G, Rosner I (2017) Enthesis as a target organ in rheumatic diseases: an expanding frontier. Clin Rheumatol 36(10):2163–2165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3749-8
McGonagle D, McDermott MF (2006) A proposed classification of the immunological diseases. PLoS Med 3(8):e297. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0030297
Tufan A, Mercan R, Tezcan ME, Kaya A, Bitik B, Ozturk MA, Haznedaroglu S, Goker B (2013) Enthesopathy in patients with familial Mediterranean fever: increased prevalence in M694 V variant. Rheumatol Int 33(8):1933–1937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2669-4
Ozkan F, Cetin GY, Inci MF, Bakan B, Yuksel M, Ekerbicer HC, Sayarlioglu M (2013) Increased enthesopathy in patients with familial Mediterranean fever: evaluation with a new sonographic enthesitis index. Journal of ultrasound in medicine : official journal of the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine 32(2):325–332. https://doi.org/10.7863/jum.2013.32.2.325
Rigante D, La Torraca I, Ansuini V, Compagnone A, Salli A, Stabile A (2006) The multi-face expression of familial Mediterranean fever in the child. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 10(4):163–171
Aktas A, Karadavut M, Cansu DU, Korkmaz C (2019) The influence of genotype on disease severity and concomitant diseases in familial Mediterranean fever patients. Clinical and experimental rheumatology 37 Suppl 121 (6):93–97
Livneh A, Langevitz P, Zemer D, Zaks N, Kees S, Lidar T, Migdal A, Padeh S, Pras M (1997) Criteria for the diagnosis of familial Mediterranean fever. Arthritis Rheum 40(10):1879–1885. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(199710)40:10<1879::AID-ART23>3.0.CO;2-M
Kristensen S, Christensen JH, Schmidt EB, Olesen JL, Johansen MB, Arvesen KB, Schlemmer A (2016) Assessment of enthesitis in patients with psoriatic arthritis using clinical examination and ultrasound. Muscles, ligaments and tendons journal 6(2):241–247. https://doi.org/10.11138/mltj/2016.6.2.241
Heuft-Dorenbosch L, Spoorenberg A, van Tubergen A, Landewe R, van ver Tempel H, Mielants H, Dougados M, van der Heijde D (2003) Assessment of enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 62(2):127–132. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.62.2.127
Demirkaya E, Acikel C, Hashkes P, Gattorno M, Gul A, Ozdogan H, Turker T, Karadag O, Livneh A, Ben-Chetrit E, Ozen S, Vasculitis FMFA, Orphan disease Research in pediatric r (2016) Development and initial validation of international severity scoring system for familial Mediterranean fever (ISSF). Ann Rheum Dis 75(6):1051–1056. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208671
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Akkoc N, Brandt J, Chou CT, Dougados M, Huang F, Gu J, Kirazli Y, Van den Bosch F, Olivieri I, Roussou E, Scarpato S, Sorensen IJ, Valle-Onate R, Weber U, Wei J, Sieper J (2011) The assessment of spondyloarthritis international society classification criteria for peripheral spondyloarthritis and for spondyloarthritis in general. Ann Rheum Dis 70(1):25–31. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2010.133645
Langevitz P, Livneh A, Zemer D, Shemer J, Pras M (1997) Seronegative spondyloarthropathy in familial Mediterranean fever. Semin Arthritis Rheum 27(2):67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0049-0172(97)80007-8
Akkoc N, Gul A (2011) Familial Mediterranean fever and seronegative arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 13(5):388–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-011-0191-9
Borman P, Gokoglu F, Tasbas O, Yilmaz M, Yorgancioglu ZR (2009) Familial Mediterranean fever-related spondyloarthropathy. Singap Med J 50(3):e116–e119
Ozdel S, Baglan E, Cakici EK, Yazilitas F, Gur G, Celikkaya E, Gungor T, Bulbul M (2020) Similarities between pediatric FMF patients with sacroiliitis and pediatric juvenile spondyloarthropathy patients with sacroiliitis: a preliminary study. Acta Clin Belg:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/17843286.2020.1724450
Atas N, Armagan B, Bodakci E, Satis H, Sari A, Bilge NSY, Salman RB, Yardimci GK, Babaoglu H, Guler AA, Karadeniz H, Kilic L, Ozturk MA, Goker B, Haznedaroglu S, Kalyoncu U, Kasifoglu T, Tufan A (2020) Familial Mediterranean fever is associated with a wide spectrum of inflammatory disorders: results from a large cohort study. Rheumatol Int 40(1):41–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04412-7
Yildiz M, Adrovic A, Tasdemir E, Baba-Zada K, Aydin M, Koker O, Sahin S, Barut K, Kasapcopur O (2020) Evaluation of co-existing diseases in children with familial Mediterranean fever. Rheumatol Int 40(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04391-9
Ozer E, Seker D, Taner E, Adrovic A, Sahin S, Barut K, Kasapcopur O (2018) The frequency of juvenile spondyloarthropathies in childhood familial Mediterranean fever. Clin Exp Rheumatol 36(6 Suppl 115):141–145
McGonagle D, Khan MA, Marzo-Ortega H, O'Connor P, Gibbon W, Emery P (1999) Enthesitis in spondyloarthropathy. Curr Opin Rheumatol 11(4):244–250. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002281-199907000-00004
Masters SL, Simon A, Aksentijevich I, Kastner DL (2009) Horror autoinflammaticus: the molecular pathophysiology of autoinflammatory disease (*). Annu Rev Immunol 27:621–668. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141627
Sims AM, Timms AE, Bruges-Armas J, Burgos-Vargas R, Chou CT, Doan T, Dowling A, Fialho RN, Gergely P, Gladman DD, Inman R, Kauppi M, Kaarela K, Laiho K, Maksymowych W, Pointon JJ, Rahman P, Reveille JD, Sorrentino R, Tuomilehto J, Vargas-Alarcon G, Wordsworth BP, Xu H, Brown MA, International Genetics of Ankylosing S (2008) Prospective meta-analysis of interleukin 1 gene complex polymorphisms confirms associations with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 67(9):1305–1309. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2007.081364
Wellcome Trust Case Control C, Australo-Anglo-American Spondylitis C, Burton PR, Clayton DG, Cardon LR, Craddock N, Deloukas P, Duncanson A, Kwiatkowski DP, McCarthy MI, Ouwehand WH, Samani NJ, Todd JA, Donnelly P, Barrett JC, Davison D, Easton D, Evans DM, Leung HT, Marchini JL, Morris AP, Spencer CC, Tobin MD, Attwood AP, Boorman JP, Cant B, Everson U, Hussey JM, Jolley JD, Knight AS, Koch K, Meech E, Nutland S, Prowse CV, Stevens HE, Taylor NC, Walters GR, Walker NM, Watkins NA, Winzer T, Jones RW, McArdle WL, Ring SM, Strachan DP, Pembrey M, Breen G, St Clair D, Caesar S, Gordon-Smith K, Jones L, Fraser C, Green EK, Grozeva D, Hamshere ML, Holmans PA, Jones IR, Kirov G, Moskivina V, Nikolov I, O'Donovan MC, Owen MJ, Collier DA, Elkin A, Farmer A, Williamson R, McGuffin P, Young AH, Ferrier IN, Ball SG, Balmforth AJ, Barrett JH, Bishop TD, Iles MM, Maqbool A, Yuldasheva N, Hall AS, Braund PS, Dixon RJ, Mangino M, Stevens S, Thompson JR, Bredin F, Tremelling M, Parkes M, Drummond H, Lees CW, Nimmo ER, Satsangi J, Fisher SA, Forbes A, Lewis CM, Onnie CM, Prescott NJ, Sanderson J, Matthew CG, Barbour J, Mohiuddin MK, Todhunter CE, Mansfield JC, Ahmad T, Cummings FR, Jewell DP, Webster J, Brown MJ, Lathrop MG, Connell J, Dominiczak A, Marcano CA, Burke B, Dobson R, Gungadoo J, Lee KL, Munroe PB, Newhouse SJ, Onipinla A, Wallace C, Xue M, Caulfield M, Farrall M, Barton A, Biologics in RAG, Genomics Study Syndicate Steering C, Bruce IN, Donovan H, Eyre S, Gilbert PD, Hilder SL, Hinks AM, John SL, Potter C, Silman AJ, Symmons DP, Thomson W, Worthington J, Dunger DB, Widmer B, Frayling TM, Freathy RM, Lango H, Perry JR, Shields BM, Weedon MN, Hattersley AT, Hitman GA, Walker M, Elliott KS, Groves CJ, Lindgren CM, Rayner NW, Timpson NJ, Zeggini E, Newport M, Sirugo G, Lyons E, Vannberg F, Hill AV, Bradbury LA, Farrar C, Pointon JJ, Wordsworth P, Brown MA, Franklyn JA, Heward JM, Simmonds MJ, Gough SC, Seal S, Breast Cancer Susceptibility C, Stratton MR, Rahman N, Ban M, Goris A, Sawcer SJ, Compston A, Conway D, Jallow M, Newport M, Sirugo G, Rockett KA, Bumpstead SJ, Chaney A, Downes K, Ghori MJ, Gwilliam R, Hunt SE, Inouye M, Keniry A, King E, McGinnis R, Potter S, Ravindrarajah R, Whittaker P, Widden C, Withers D, Cardin NJ, Davison D, Ferreira T, Pereira-Gale J, Hallgrimsdo'ttir IB, Howie BN, Su Z, Teo YY, Vukcevic D, Bentley D, Brown MA, Compston A, Farrall M, Hall AS, Hattersley AT, Hill AV, Parkes M, Pembrey M, Stratton MR, Mitchell SL, Newby PR, Brand OJ, Carr-Smith J, Pearce SH, McGinnis R, Keniry A, Deloukas P, Reveille JD, Zhou X, Sims AM, Dowling A, Taylor J, Doan T, Davis JC, Savage L, Ward MM, Learch TL, Weisman MH, Brown M (2007) Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat Genet 39(11):1329–1337. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2007.17
Watad A, Bragazzi NL, Adawi M, Shoenfeld Y, Comaneshter D, Cohen AD, McGonagle D, Amital H (2019) FMF is associated with a wide spectrum of MHC class I- and allied SpA disorders but not with classical MHC class II-associated autoimmune disease: insights from a large cohort study. Front Immunol 10:2733. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02733
Kasifoglu T, Calisir C, Cansu DU, Korkmaz C (2009) The frequency of sacroiliitis in familial Mediterranean fever and the role of HLA-B27 and MEFV mutations in the development of sacroiliitis. Clin Rheumatol 28(1):41–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0980-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NS: Provide important contributions to conceptual or planning stages of the study or collection/processing, analysis or interpretation of the data. MY: Taking responsibility in patient follow-up, collection of relevant biological materials, data management and reporting, execution of the experiments. RM: Taking responsibility in logical interpretation and conclusion of the results. OM: Planning methodology to reach the conclusions. SYO: Reviewing the article before submission scientifically besides spelling and grammar. ET: Taking responsibility in patient follow-up, collection of relevant biological materials, data management and reporting, execution of the experiments. MET: Main writer, planning methodology to reach the conclusions and reviewing the article before submission scientifically besides spelling and grammar
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Local Research Ethics Committee and carried out in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration.
Consent to participate
All the patients gave written informed consent.
Consent for publication
All authors has a consent for publication.
Code availability
Statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS Version 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, N., Yilmaz, M., Mercan, R. et al. Enthesitis may be one of the signs of severe disease in familial Mediterranean fever. Clin Rheumatol 40, 1479–1485 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05392-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05392-x