Abstract
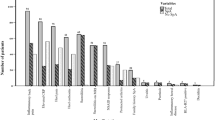
Enthesopathy is pathology of bony insertions of tendons, ligaments or joint capsules. It is a frequent finding in rheumatic diseases, like ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and Behçet’s disease. Musculoskeletal complaints are common in patients with familial Mediterranean fever (FMF), and these could be a clinical manifestation of enthesopathy. Hence, we investigated the possible association between FMF and enthesopathy. Fifty-six patients with FMF and 11 patients with FMF-associated spondyloarthropathy (FMFS) were enrolled. Forty-seven healthy individuals and 36 patients with AS formed the healthy and diseased control groups. Musculoskeletal complaints were meticulously questioned, and all patients underwent a detailed physical and ultrasonographic (US) examination of the lower limbs. US scorings of enthesopathy was performed according to the Glasgow Ultrasound Enthesitis Scoring System (GUESS). Demographic data, disease characteristics, MEFV genotypes and HLA B27 results were retrieved from the medical records. Patient-reported pain and physical examination findings consistent with enthesopathy were frequent in all groups with the highest prevalence in the FMFS group. Heel was the most common region affected in all patient groups. FMF patients harboring M694 V variant had higher GUESS scores compared to patients with other variants (2.78 ± 2.43 vs. 1.37 ± 1.67, p = 0.026). There was no statistically significant difference in the mean ± SD GUESS scores between healthy subjects and those FMF patients with genetic variants other than M694 V (1.38 ± 1.42 vs. 1.37 ± 1.67, p > 0.05). Enthesopathy may not be a feature of general FMF population; rather, it might be specifically associated with the presence of M694 V variant. Our results further support the previous evidence regarding M694 V mutation and spondyloarthropathy association.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Onen F (2006) Familial Mediterranean fever. Rheumatol Int 26(6):489–496. doi:10.1007/s00296-005-0074-3
Brik R, Shinawi M, Kasinetz L, Gershoni-Baruch R (2001) The musculoskeletal manifestations of familial Mediterranean fever in children genetically diagnosed with the disease. Arthritis Rheum 44(6):1416–1419. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200106)44:6<1416:AID-ART236>3.0.CO;2-6
Majeed HA, Al-Qudah AK, Qubain H, Shahin HM (2000) The clinical patterns of myalgia in children with familial Mediterranean fever. Semin Arthritis Rheum 30(2):138–143. doi:10.1053/sarh.2000.16646
Benjamin M, Toumi H, Ralphs JR, Bydder G, Best TM, Milz S (2006) Where tendons and ligaments meet bone: attachment sites (‘entheses’) in relation to exercise and/or mechanical load. J Anat 208(4):471–490. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2006.00540.x
D’Agostino MA, Olivieri I (2006) Enthesitis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 20(3):473–486. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2006.03.007
Francois RJ, Braun J, Khan MA (2001) Entheses and enthesitis: a histopathologic review and relevance to spondyloarthritides. Curr Opin Rheumatol 13(4):255–264
McGonagle D, Marzo-Ortega H, O’Connor P, Gibbon W, Pease C, Reece R, Emery P (2002) The role of biomechanical factors and HLA-B27 in magnetic resonance imaging-determined bone changes in plantar fascia enthesopathy. Arthritis Rheum 46(2):489–493
Slobodin G, Rozenbaum M, Boulman N, Rosner I (2007) Varied presentations of enthesopathy. Semin Arthritis Rheum 37(2):119–126. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2007.01.004
Akkoc N, Gul A (2011) Familial Mediterranean fever and seronegative arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 13(5):388–394. doi:10.1007/s11926-011-0191-9
Cosan F, Ustek D, Oku B, Duymaz-Tozkir J, Cakiris A, Abaci N, Ocal L, Aral O, Gul A (2010) Association of familial Mediterranean fever-related MEFV variations with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 62(11):3232–3236. doi:10.1002/art.27683
Livneh A, Langevitz P, Zemer D, Zaks N, Kees S, Lidar T, Migdal A, Padeh S, Pras M (1997) Criteria for the diagnosis of familial Mediterranean fever. Arthritis Rheum 40(10):1879–1885. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199710)40:10<1879:AID-ART23>3.0.CO;2-M
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27(4):361–368
Balint PV, Kane D, Wilson H, McInnes IB, Sturrock RD (2002) Ultrasonography of entheseal insertions in the lower limb in spondyloarthropathy. Ann Rheum Dis 61(10):905–910
Braem K, Lories RJ (2011) Insights into the pathophysiology of ankylosing spondylitis: contributions from animal models. Joint Bone Spine. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.09.008
Touitou I (2001) The spectrum of Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) mutations. Eur J Hum Genet 9(7):473–483. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200658
Ureten K, Gonulalan G, Akbal E, Gunes F, Akyurek O, Ozbek M, Ozturk MA (2010) Demographic, clinical and mutational characteristics of Turkish familial Mediterranean fever patients: results of a single center in Central Anatolia. Rheumatol Int 30(7):911–915. doi:10.1007/s00296-009-1073-6
Chae JJ, Wood G, Masters SL, Richard K, Park G, Smith BJ, Kastner DL (2006) The B30.2 domain of pyrin, the familial Mediterranean fever protein, interacts directly with caspase-1 to modulate IL-1beta production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(26):9982–9987. doi:10.1073/pnas.0602081103
Reveille JD, Sims AM, Danoy P, Evans DM, Leo P, Pointon JJ, Jin R, Zhou X, Bradbury LA, Appleton LH, Davis JC, Diekman L, Doan T, Dowling A, Duan R, Duncan EL, Farrar C, Hadler J, Harvey D, Karaderi T, Mogg R, Pomeroy E, Pryce K, Taylor J, Savage L, Deloukas P, Kumanduri V, Peltonen L, Ring SM, Whittaker P, Glazov E, Thomas GP, Maksymowych WP, Inman RD, Ward MM, Stone MA, Weisman MH, Wordsworth BP, Brown MA (2010) Genome-wide association study of ankylosing spondylitis identifies non-MHC susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 42(2):123–127. doi:10.1038/ng.513
Tan AL, Marzo-Ortega H, O’Connor P, Fraser A, Emery P, McGonagle D (2004) Efficacy of anakinra in active ankylosing spondylitis: a clinical and magnetic resonance imaging study. Ann Rheum Dis 63(9):1041–1045. doi:10.1136/ard.2004.020800
de Miguel E, Cobo T, Munoz-Fernandez S, Naredo E, Uson J, Acebes JC, Andreu JL, Martin-Mola E (2009) Validity of enthesis ultrasound assessment in spondyloarthropathy. Ann Rheum Dis 68(2):169–174. doi:10.1136/ard.2007.084251
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tufan, A., Mercan, R., Tezcan, M.E. et al. Enthesopathy in patients with familial Mediterranean fever: increased prevalence in M694 V variant. Rheumatol Int 33, 1933–1937 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2669-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2669-4