Abstract
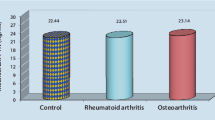
The goal of this study is to determine and compare the β-endorphin levels in the synovial fluid of patients with different joint disorders (avascular necrosis, AVN; osteoarthritis, OA; and rheumatoid arthritis, RA of the hip or knee). Eighty-seven patients were involved in our study with an average age of 62 years. Thirty-three patients had AVN (18 hips, 15 knees). Twenty-three patients were diagnosed with OA (14 hips, 9 knees), and 31 patients suffered from RA (12 hips, 19 knees). We measured the β-endorphin levels of the synovial fluids -harvested from surgery—with radioimmunoassay. No significant difference was found in the β-endorphin levels of the synovial fluid from AVN comparing to OA and RA, however β-endorphin level was significantly higher in RA group than among patients with OA (p = 0.01). Synovial β-endorphin level was slightly lower in knee comparing to hip joint p = (0.06). When examining the different joints separately in compliance with diagnoses, we concluded that the synovial β-endorphin level from AVN was between the values of OA and RA without significant difference, whereas it was significantly higher in the knee of RA, than of OA groups (p = 0.05 knee, p = 0.2 hip). Our results confirmed those experiments which stated that there is a significant increase in synovial β-endorphin level in patients with inflammatory autoimmune diseases (e.g., RA), comparing to the level measured in degenerative conditions (e.g., OA).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Majithia V, Geraci SA (2007) Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis and management. Am J Med 120:936–939
Lafforgue P (2006) Pathophysiology and natural history of avascular necrosis of bone. Joint Bone Spine 73:500–507
Holden JE, Jeong Y, Forrest JM (2005) The endogenous opioid system and clinical pain management. AACN Clin Isssues 16:291–301
Takeba Y, Suzuki N, Kaneko A, Asai T, Sakane T (2001) Endorphin and enkephalin ameliorate excessive synovial cell functions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 28:2176–2183
Steinberg ME, Hayken GD, Steinberg DR (1995) A quantitative system for staging avascular necrosis. J Bone Jt Surg 77B:34–41
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS (1957) Radiological assessment of osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 16:494–502
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987. Revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, Bole D, Borenstein K, Brandt K et al (1986) Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum 29:1039–1049
Barna I, Koenig JI (1992) Effects of mediobasal hypothalamic lesion on immunoreactive ACTH/beta-endorphin levels in cerebrospinal fluid, in discrete brain regions, in plasma, and in pituitary of the rat. Brain Res 593:69–76
Senolt L, Polanska M, Filkova M, Oslejskova L, Pavelka K, Gay S, Haluzik M, Vencovsky J (2009) Vaspin and omentin: new adipokines differentially regulated at the site of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1410–1411. doi:10.1136/ard.2009.119735
Davies MR, Ribeiro LR, Downey-Jones M, Needham MR, Oakley C, Wardale J (2009) Ligands for retinoic acid receptors are elevated in osteoarthritis and may contribute to pathologic processes in the osteoarthritic joint. Arthritis Rheum 60:1722–1732
Kato S, Yamada H, Terada N, Masuda K, Lenz ME, Morita M, Yoshihara Y, Henmi O (2005) Joint biomarkers in idiopathic femoral head osteonecrosis: comparison with hip osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol 32:1518–1523
Iwase T, Hasegawa Y, Ishiguro N, Ito T, Iwasada S, Kitamura S, Iwata H (1998) Synovial fluid cartilage metabolism marker concentrations in osteonecrosis of the femoral head compared with osteoarthrosis of the hip. J Rheumatol 25:527–531
Saito T, Takeuchi R, Mitsuhashi S, Uesugi M, Yoshida T, Koshino T (2002) Use of joint fluid analysis for determining cartilage damage in osteonecrosis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum 46:1813–1819
Huffman KM, Bowers JR, Dailiana Z, Huebner JL, Urbaniak JR, Kraus VB (2007) Synovial fluid metabolites in osteonecrosis. Rheumatology 46:523–528
Bender T, Barna I, Geher P (1999) Synovial immunoreactive beta-endorphin levels in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 17:630
Zhong Q, Sridhar S, Ruan L, Ding KH, Xie D, Insogna K, Kang B, Xu J, Bollag RJ, Isales CM (2005) Multiple melanocortin receptors are expressed in bone cells. Bone 36:820–831
Cerinic MM, Konttinen Y, Generini S, Cutolo M (1998) Neuropeptides and steroid hormones in arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 10:220–235
Stein C, Hassan AH, Lehrberger K, Giefing J, Yassouridis A (1993) Local analgesic effect of endogenous opioid peptides. Lancet 342:321–324
Pessler F, Dai L, Diaz-Torne C, Gomez-Vaquero C, Paessler ME, Zheng DH, Einhorn E, Range U, Scanzello C, Schumacher HR (2008) The synovitis of “non-inflammatory” orthopaedic arthropathies: a quantitative histological and immunohistochemical analysis. Annals Rheum Dis 67:1184–1187
Mousa SA, Straub RH, Schäfer M, Stein C (2007) Beta-endorphin, Met-enkephalin and corresponding opioid receptors within synovium of patients with joint trauma, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:871–879
Smith HS (2008) Peripherally-acting opioids. Pain Physician 11(2 Suppl):121–132
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toth, K., Barna, I., Nagy, G. et al. Synovial fluid β-endorphin level in avascular necrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoarthritis of the femoral head and knee. A controlled pilot study. Clin Rheumatol 30, 537–540 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-010-1573-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-010-1573-5