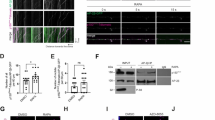
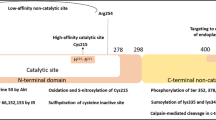
Abstract
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) is a master regulator of cell growth and autophagy. Its activity is regulated by the availability of amino acids and growth factors. The activation of mTORC1 by growth factors, such as insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), is mediated by tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) 1 and 2 and Rheb GTPase. Relative to the growth factor-regulated mTORC1 pathway, the evolutionarily ancient amino acid-mTORC1 pathway remains not yet clearly defined. The amino acid-mTORC1 pathway is mediated by Rag GTPase heterodimers. Several binding proteins of Rag GTPases were discovered in recent studies. Here, we discuss the functions and mechanisms of the newly-identified binders of Rag GTPases. In particular, this review focuses on SH3 binding protein 4 (SH3BP4), the protein recently identifed as a negative regulator of Rag GTPases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar-Peled, L., Schweitzer, L.D., Zoncu, R., and Sabatini, D.M. (2012). Ragulator is a GEF for the rag GTPases that signal amino acid levels to mTORC1. Cell 150, 1196–1208.
Beroukhim, R., Getz, G., Nghiemphu, L., Barretina, J., Hsueh, T., Linhart, D., Vivanco, I., Lee, J.C., Huang, J.H., et al. (2007). Assessing the significance of chromosomal aberrations in cancer: methodology and application to glioma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 20007–20012.
Beroukhim, R., Mermel, C.H., Porter, D., Wei, G., Raychaudhuri, S., Donovan, J., Barretina, J., Boehm, J.S., Dobson, J., Urashima, M., et al. (2010). The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature 463, 899–905.
Binda, M., Peli-Gulli, M.P., Bonfils, G., Panchaud, N., Urban, J., Sturgill, T.W., Loewith, R., and De Virgilio, C. (2009). The Vam6 GEF controls TORC1 by activating the EGO complex. Mol. Cell 35, 563–573.
Bonfils, G., Jaquenoud, M., Bontron, S., Ostrowicz, C., Ungermann, C., and De Virgilio, C. (2012). Leucyl-tRNA synthetase controls TORC1 via the EGO complex. Mol. Cell 46, 105–110.
Bryk, B., Hahn, K., Cohen, S.M., and Teleman, A.A. (2010). MAP4K3 regulates body size and metabolism in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 344, 150–157.
Chen, R.Q., Yang, Q.K., Lu, B.W., Yi, W., Cantin, G., Chen, Y.L., Fearns, C., Yates, J.R., 3rd, and Lee, J.D. (2009). CDC25B mediates rapamycin-induced oncogenic responses in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 69, 2663–2668.
Chiba, S., Tokuhara, M., Morita, E.H., and Abe, S. (2009). TTP at Ser245 phosphorylation by AKT is required for binding to 14-3-3. J. Biochem. 145, 403–409.
Dubouloz, F., Deloche, O., Wanke, V., Cameroni, E., and De Virgilio, C. (2005). The TOR and EGO protein complexes orchestrate microautophagy in yeast. Mol. Cell 19, 15–26.
Duran, A., Amanchy, R., Linares, J.F., Joshi, J., Abu-Baker, S., Porollo, A., Hansen, M., Moscat, J., and Diaz-Meco, M.T. (2011). p62 is a key regulator of nutrient sensing in the mTORC1 pathway. Mol. Cell 44, 134–146.
Findlay, G.M., Yan, L., Procter, J., Mieulet, V., and Lamb, R.F. (2007). A MAP4 kinase related to Ste20 is a nutrient-sensitive regulator of mTOR signalling. Biochem. J. 403, 13–20.
Flinn, R.J., Yan, Y., Goswami, S., Parker, P.J., and Backer, J.M. (2010). The late endosome is essential for mTORC1 signaling. Mol. Biol. Cell 21, 833–841.
Goberdhan, D.C., and Boyd, C.A. (2009). mTOR: dissecting regulation and mechanism of action to understand human disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 37, 213–216.
Gong, R., Li, L., Liu, Y., Wang, P., Yang, H., Wang, L., Cheng, J., Guan, K.L., and Xu, Y. (2011). Crystal structure of the Gtr1p-Gtr2p complex reveals new insights into the amino acid-induced TORC1 activation. Genes Dev. 25, 1668–1673.
Han, J.M., Jeong, S.J., Park, M.C., Kim, G., Kwon, N.H., Kim, H.K., Ha, S.H., Ryu, S.H., and Kim, S. (2012). Leucyl-tRNA Synthetase is an intracellular leucine sensor for the mTORC1-signaling pathway. Cell 149, 410–424.
Hara, K., Maruki, Y., Long, X., Yoshino, K., Oshiro, N., Hidayat, S., Tokunaga, C., Avruch, J., and Yonezawa, K. (2002). Raptor, a binding partner of target of rapamycin (TOR), mediates TOR action. Cell 110, 177–189.
Harrison, D.E., Strong, R., Sharp, Z.D., Nelson, J.F., Astle, C.M., Flurkey, K., Nadon, N.L., Wilkinson, J.E., Frenkel, K., Carter, C. S., et al. (2009). Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in genetically heterogeneous mice. Nature 460, 392–395.
Hennig, K.M., Colombani, J., and Neufeld, T.P. (2006). TOR coordinates bulk and targeted endocytosis in the Drosophila melanogaster fat body to regulate cell growth. J. Cell Biol. 173, 963–974.
Hirose, E., Nakashima, N., Sekiguchi, T., and Nishimoto, T. (1998). RagA is a functional homologue of S. cerevisiae Gtr1p involved in the Ran/Gsp1-GTPase pathway. J. Cell Sci. 111(Pt 1), 11–21.
Inoki, K., Li, Y., Zhu, T., Wu, J., and Guan, K.L. (2002). TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 648–657.
Jeong, J.H., Lee, K.H., Kim, Y.M., Kim, D.H., Oh, B.H., and Kim, Y.G. (2012). Crystal structure of the Gtr1pGTP-Gtr2pGDP protein complex reveals large structural rearrangements triggered by GTP-to-GDP conversion. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 29648–29653.
Jung, C.H., Ro, S.H., Cao, J., Otto, N.M., and Kim, D.H. (2010). mTOR regulation of autophagy. FEBS Lett. 584, 1287–1295.
Kim, E., and Guan, K.L. (2009). RAG GTPases in nutrient-mediated TOR signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 8, 1014–1018.
Kim, D.H., Sarbassov, D.D., Ali, S.M., King, J.E., Latek, R.R., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P., and Sabatini, D.M. (2002). mTOR interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell 110, 163–175.
Kim, E., Goraksha-Hicks, P., Li, L., Neufeld, T.P., and Guan, K.L. (2008). Regulation of TORC1 by Rag GTPases in nutrient response. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 935–945.
Kim, Y.M., Stone, M., Hwang, T.H., Kim, Y.G., Dunlevy, J.R., Griffin, T.J., and Kim, D.H. (2012). SH3BP4 is a negative regulator of amino acid-Rag GTPase-mTORC1 signaling. Mol. Cell 46, 833–846.
Li, L., Kim, E., Yuan, H., Inoki, K., Goraksha-Hicks, P., Schiesher, R.L., Neufeld, T.P., and Guan, K.L. (2010). Regulation of mTORC1 by the Rab and Arf GTPases. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 19705–19709.
Loewith, R., Jacinto, E., Wullschleger, S., Lorberg, A., Crespo, J.L., Bonenfant, D., Oppliger, W., Jenoe, P., and Hall, M.N. (2002). Two TOR complexes, only one of which is rapamycin sensitive, have distinct roles in cell growth control. Mol. Cell 10, 457–468.
Long, X., Lin, Y., Ortiz-Vega, S., Yonezawa, K., and Avruch, J. (2005). Rheb binds and regulates the mTOR kinase. Curr. Biol. 15, 702–713.
Manning, B.D., and Cantley, L.C. (2003). Rheb fills a GAP between TSC and TOR. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28, 573–576.
Narita, M., Young, A.R., Arakawa, S., Samarajiwa, S.A., Nakashima, T., Yoshida, S., Hong, S., Berry, L.S., Reichelt, S., Ferreira, M., et al. (2011). Spatial coupling of mTOR and autophagy augments secretory phenotypes. Science 332, 966–970.
Nelson, N., Perzov, N., Cohen, A., Hagai, K., Padler, V., and Nelson, H. (2000). The cellular biology of proton-motive force generation by V-ATPases. J. Exp. Biol. 203, 89–95.
Nicklin, P., Bergman, P., Zhang, B., Triantafellow, E., Wang, H., Nyfeler, B., Yang, H., Hild, M., Kung, C., Wilson, C., et al. (2009). Bidirectional transport of amino acids regulates mTOR and autophagy. Cell 136, 521–534.
Pan, C., Gnad, F., Olsen, J.V., and Mann, M. (2008). Quantitative phosphoproteome analysis of a mouse liver cell line reveals specificity of phosphatase inhibitors. Proteomics 8, 4534–4546.
Reddy, N.M., Potteti, H.R., Mariani, T.J., Biswal, S., and Reddy, S.P. (2011). Conditional deletion of Nrf2 in airway epithelium exacerbates acute lung injury and impairs the resolution of inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 45, 1161–1168.
Resnik-Docampo, M., and de Celis, J.F. (2011). MAP4K3 is a component of the TORC1 signalling complex that modulates cell growth and viability in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS One 6, e14528.
Sancak, Y., Thoreen, C.C., Peterson, T.R., Lindquist, R.A., Kang, S.A., Spooner, E., Carr, S.A., and Sabatini, D.M. (2007). PRAS40 is an insulin-regulated inhibitor of the mTORC1 protein kinase. Mol. Cell 25, 903–915.
Sancak, Y., Peterson, T.R., Shaul, Y.D., Lindquist, R.A., Thoreen, C.C., Bar-Peled, L., and Sabatini, D.M. (2008). The Rag GTPases bind raptor and mediate amino acid signaling to mTORC1. Science 320, 1496–1501.
Sancak, Y., Bar-Peled, L., Zoncu, R., Markhard, A.L., Nada, S., and Sabatini, D.M. (2010). Ragulator-Rag complex targets mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface and is necessary for its activation by amino acids. Cell 141, 290–303.
Sekiguchi, T., Hirose, E., Nakashima, N., Ii, M., and Nishimoto, T. (2001). Novel G proteins, Rag C and Rag D, interact with GTPbinding proteins, Rag A and Rag B. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 7246–7257.
Selman, C., Tullet, J.M., Wieser, D., Irvine, E., Lingard, S.J., Choudhury, A.I., Claret, M., Al-Qassab, H., Carmignac, D., Ramadani, F., et al. (2009). Ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 signaling regulates mammalian life span. Science 326, 140–144.
Tee, A.R., Manning, B.D., Roux, P.P., Cantley, L.C., and Blenis, J. (2003). Tuberous sclerosis complex gene products, Tuberin and Hamartin, control mTOR signaling by acting as a GTPase-activating protein complex toward Rheb. Curr. Biol. 13, 1259–1268.
Tosoni, D., Puri, C., Confalonieri, S., Salcini, A.E., De Camilli, P., Tacchetti, C., and Di Fiore, P.P. (2005). TTP specifically regulates the internalization of the transferrin receptor. Cell 123, 875–888.
Um, S.H., Frigerio, F., Watanabe, M., Picard, F., Joaquin, M., Sticker, M., Fumagalli, S., Allegrini, P.R., Kozma, S.C., Auwerx, J., et al. (2004). Absence of S6K1 protects against age- and diet-induced obesity while enhancing insulin sensitivity. Nature 431, 200–205.
Valbuena, N., Guan, K.L., and Moreno, S. (2012). The Vam6 and Gtr1-Gtr2 pathway activates TORC1 in response to amino acids in fission yeast. J. Cell Sci. 125, 1920–1928.
Vander Haar, E., Lee, S.I., Bandhakavi, S., Griffin, T.J., and Kim, D.H. (2007). Insulin signalling to mTOR mediated by the Akt/PKB substrate PRAS40. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 316–323.
Wullschleger, S., Loewith, R., and Hall, M.N. (2006). TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 124, 471–484.
Wurmser, A.E., Sato, T.K., and Emr, S.D. (2000). New component of the vacuolar class C-Vps complex couples nucleotide exchange on the Ypt7 GTPase to SNARE-dependent docking and fusion. J. Cell Biol. 151, 551–562.
Yan, L., Mieulet, V., Burgess, D., Findlay, G.M., Sully, K., Procter, J., Goris, J., Janssens, V., Morrice, N.A., and Lamb, R.F. (2010). PP2A T61 epsilon is an inhibitor of MAP4K3 in nutrient signaling to mTOR. Mol. Cell 37, 633–642.
Yu, L., McPhee, C.K., Zheng, L., Mardones, G.A., Rong, Y., Peng, J., Mi, N., Zhao, Y., Liu, Z., Wan, F., et al. (2010). Termination of autophagy and reformation of lysosomes regulated by mTOR. Nature 465, 942–946.
Zhang, Y., Gao, X., Saucedo, L.J., Ru, B., Edgar, B.A., and Pan, D. (2003). Rheb is a direct target of the tuberous sclerosis tumour suppressor proteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 5, 578–581.
Zoncu, R., Bar-Peled, L., Efeyan, A., Wang, S., Sancak, Y., and Sabatini, D.M. (2011). mTORC1 senses lysosomal amino acids through an inside-out mechanism that requires the vacuolar HATPase. Science 334, 678–683.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YM., Kim, DH. dRAGging amino Acid-mTORC1 signaling by SH3BP4. Mol Cells 35, 1–6 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-2249-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-013-2249-1