Abstract
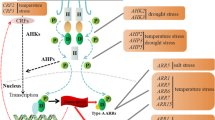
Mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) are known to get activated during various stress signals and transduce the message from the cell membrane to the nucleus for appropriate cellular reorganization. Though, a certain basal activity of MAPK is often observed in the control plants. Prolonged exposure of rice plants to lowered or elevated temperature exhibited a rhythm in the activation of MAPKs. We analyzed existence of a possible endogenous rhythm in the activity of MAPKs in rice plants. The plants growing at constant temperature entrained in 16/8 h day-night cycle showed diurnal rhythm in activity. When the activation of MAPK was tested under continuous conditions by shifting plants to continuous darkness for a period of 72 h, the periodic rhythm persisted and followed a circadian pattern. Analysis of the transcripts of group A, B and C members of MAPKs under above conditions by quantitative real time PCR revealed that the members of group C exhibit periodic rhythm. Our data indicates that the MAP kinase activity in rice follows rhythmic expression in a circadian manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canagarajah, B.J., Khokhlatchev, A., Cobb, M.H., and Goldsmith, E.J. (1997). Activation mechanism of the MAP kinase ERK2 by dual phosphorylation. Cell 90, 859–869.
Dunlap, J.C. (1999). Molecular bases for circadian clocks. Cell 96, 271–290.
Dunlap, J.C. (2004). Molecular biology of circadian pacemaker systems in chronobiology: biological time keeping, J.J. Loros, and P. DeCoursey, eds., (Sunderland: USA, Sinauer Associates), pp. 212–253.
Ehness, R., Ecker, M., Godt, D.E., and Roitsch, T. (1997). Glucose and stress independently regulate source and sink metabolism and defense mechanisms via signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation. Plant Cell 9, 1825–1841.
Eichberg, J., and Srinivas, I. (1996). Phosphorylation of myelin proteins: Recent advances. Neurochem. Res. 21, 527–535.
Hamel, L.P., Nicole, M.C., Sritubtim, S., Morency, M.J., Ellis, M., Ehlting, J., Beaudoin, N., Barbazuk, B., Klessig, D., Lee, J., et al. (2006). Ancient signals: comparative genomics of plant MAPK and MAPKK gene families. Trends Plant Sci. 11, 192–198.
Harada, Y., Sanada, K., and Yoshitaka, F. (2000). Circadian activation of bullfrog retinal mitogen-activated protein kinase associates with oscillator function. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 37078–37085.
Harauz, G., Ishiyama, N., and Bates, I. (2000). Analogous standard motifs in myelin basic protein and in MARCKS. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 209, 155–163.
Harmer, S.L., Hogenesch, J.B, Straume, M., Chang, H.S., Han, B., Zhu, T., Wang, X., Kreps, J.A., and Kay, S.A. (2000). Orchestrated transcription of key pathways in Arabidopsis by the circadian clock. Science 290, 2110–2113.
Jonak, C., Kiegerl, S., Ligterink, W., Barker, P.J., Huskisson, N.S., and Hirt, H. (1996). Stress signaling in plants: A mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is activated by cold and drought. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 11274–11279.
Jonak, C., Okresz, L., Bogre, L., and Hirt, H. (2002). Complexity, cross talk and integration of plant MAP kinase signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 5, 415–424.
Lee, M.O., Cho, K., Kim, S.H., Jeong, S.H., Kim, J.A., Jung, Y.H., Shim, J., Shibato, J., Rakwal, R., Tamogami, S., et al. (2008). Novel rice OsSIPK is a multiple stress responsive MAPK family member showing rhythmic expression at mRNA level. Planta 227, 981–990.
Link, V., Hofmann, M.G., Sinha, A.K., Ehness, R., Strnad, M., and Roitsch, T. (2002a). Biochemical evidence for the activation of distinct subsets of mitogen-activated protein kinases by voltage and defense-related stimuli. Plant Physiol. 128, 271–281.
Link, V., Sinha, A.K., Vashista, P., Hofmann, M.G., Proels, R.K., Ehness, R., and Roitsch, T. (2002b). A heat-activated MAP kinase in tomato: a possible regulator of the heat stress response. FEBS Lett. 531, 179–183.
Mishra, N.S., Tuteja, R., and Tuteja, N. (2006). Signaling through MAP kinase networks in plants. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 452, 55–68.
Mittag, M., Kiaulehn, S., and Johnson, C.H. (2005). The circadian clock in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. What is it for? What is it similar to? Plant Physiol. 137, 399–409.
Nakagami, H., Pitzschke, A., and Hirt, H. (2005). Emerging MAP kinase pathways in plant stress signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 10, 339–346.
Obrietan, K., Impey, S., and Storm, D.R. (1998). Light and circadian rhythmicity regulate MAP kinase activation in the suprachiasmatic nuclei. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 693–700.
Pittendrigh, C.S. (1993).Temporal organization: reflections of a Darwinian clock-watcher. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 55, 16–54.
Reuter, C.W., Catling, A.D., and Weber, M.J. (1995). Immune complex kinase assays for mitogen-activated protein kinase and MEK. Meth. Enzymol. 55, 245–256.
Sanada, K., Hayashi, Y., Harada, Y., Okano, T., and Fukada, F. (2000). Role of circadian activation of mitogen activated protein kinase in chick pineal clock oscillation. J. Neurosci. 20, 986–991.
Sangwan, V., Orvar, B.L., Beyerly, J., Hirt, H., and Dhindsa, R.S. (2002). Opposite changes in membrane fluidity mimic cold and heat stress activation of distinct plant MAP kinase pathways. Plant J. 3, 629–638.
Schaffer, R., Landgraf, J., Accerbi, M., Simon, V., Larson, M., and Wisman, E. (2001). Microarray analysis of diurnal and circadian regulated genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13, 113–123.
Tena, G., Asai, T., Chiu, W.L., and Sheen, J. (2001). Plant Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 74, 392–400.
Zhang, S., and Klessig, D.F. (1997). Salicylic acid activates a 48-kD MAPK kinase in tobacco. Plant Cell 9, 809–824.
Zhang, T., Liu, Y., Yang, T., Zhang, L., Xu, S., Xue, L., and An, L. (2006). Diverse signals converge at MAPK cascades in plant. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 44, 274–283.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, K.P., Vani, G., Kumar, K. et al. Rhythmic expression of mitogen activated protein kinase activity in rice. Mol Cells 28, 417–422 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0137-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0137-5