Abstract
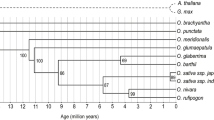
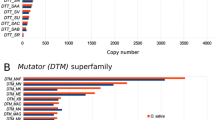
MUG1 is a MULE transposon-related domesticated gene in plants. We assessed the sequence diversity, neutrality, expression, and phylogenetics of the MUG1 gene among Oryza ssp. We found MUG1 expression in all tissues analyzed, with different levels in O. sativa. There were 408 variation sites in the 3886 bp of MUG1 locus. The nucleotide diversity of the MUG1 was higher than functionally known genes in rice. The nucleotide diversity (π) in the domains was lower than the average nucleotide diversity in whole coding region. The π values in nonsynonymous sites were lower than those of synonymous sites. Tajima D and Fu and Li D* values were mostly negative values, suggesting purifying selection in MUG1 sequences of Oryza ssp. Genome-specific variation and phylogenetic analyses show a general grouping of MUG1 sequences congruent with Oryza ssp. biogeography; however, our MUG1 phylogenetic results, in combination with separate B and D genome studies, might suggest an early divergence of the Oryza ssp. by continental drift of Gondwanaland. O. longistaminata MUG1 divergence from other AA diploids suggests that it might not be a direct ancestor of the African rice species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, A., Eastman, Q.M., and Schatz, D.G. (1998). Transposition mediated by RAG1 and RAG2 and its implications for the evolution of the immune system. Nature 394, 744–751.
Benito, M.I., and Walbot, V. (1997). Characterization of the maize Mutator transposable element MURA transposase as a DNA-binding protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 5165–5175.
Chang, T.T. (1976). The origin, evolution, cultivation, dissemination, and diversification of Asian and African rices. Euphytica 25, 425–441.
Chung, H.J., and Ferl, R.J. (1999). Arabidopsis alcohol dehydrogenase expression in both shoots and roots is conditioned by root growth environment. Plant Physiol. 121, 429–436.
Cowan, R.K., Hoen, D.R., Schoen, D.J., and Bureau, T.E. (2005). MUSTANG is a novel family of domesticated transposase genes found in diverse angiosperms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 22, 2084–2089.
Dellaporta, S., Wood, J., and Hicks, J. (1983). A simple and rapid method for plant DNA preparation. Version II. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1, 19–21.
Dolferus, R., Jacobs, M., Peacock, W.J., and Dennis, E.S. (1994). Differential interactions of promoter elements in stress responses of the Arabidopsis Adh gene. Plant Physiol. 105, 1075–1087.
Fu, Y.X., and Li, W.H. (1993). Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations. Genetics 133, 693–709.
Ge, S., Sang, T., Lu, B.R., and Hong, D.Y. (1999). Phylogeny of rice genomes with emphasis on origins of allotetraploid species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 14400–14405.
Guo, Y., and Ge, S. (2005). Molecular phylogeny of Oryzeae (Poaceae) based on DNA sequences from chloroplast, mitochondrial, and nuclear genomes1. Am. J. Bot. 92, 1548–1558.
Hoen, D.R., Park, K.C., Elrouby, N., Yu, Z., Mohabir, N., Cowan, R.K., and Bureau, T.E. (2006). Transposon-mediated expansion and diversification of a family of ULP-like genes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 23, 1254–1268.
Hudson, M.E., Lisch, D.R., and Quail, P.H. (2003). The FHY3 and FAR1 genes encode transposase-related proteins involved in regulation of gene expression by the phytochrome A-signaling pathway. Plant J. 34, 453–471.
Khush, G.S. (1997). Origin, dispersal, cultivation and variation of rice. Plant. Mol. Biol. 35, 25–34.
Kidwell, M.G., and Lisch, D.R. (2001). Perspective: transposable elements, parasitic DNA, and genome evolution. Evolution 55, 1–24.
Kim, N.H., Lee, J.K., Shin, Y.B., Park, C.H., Cho, E.G., and Kim, N.S. (2003). Phylogenetic relationship and genetic variation among Oryza species revealed by AFLP analysis. Kor. J. Breed. 35, 78–85.
Kumar, S., Tamura, K., Jakobsen, I.B., and Nei, M. (2001). MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17, 1244–1245.
Lin, R., Ding, L., Casola, C., Ripoll, D.R., Feschotte, C., and Wang, H. (2007). Transposase-derived transcription factors regulate light signaling in Arabidopsis. Science 151, 1302–1305.
Lisch, D., Girard, L., Donlin, M., and Freeling, M. (1999). Functional analysis of deletion derivatives of the maize transposon MuDR delineates roles for the MURA and MURB proteins. Genetics 151, 331–341.
Ma, J., and Bennetzen, J.L. (2004). Rapid recent growth and divergence of rice nuclear genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 12404–12410.
Panaud, O., Vitte, C., Hivert, J., Muzlak, S., Talag, J., Brar, D., and Sarr, A. (2002). Characterization of transposable elements in the genome of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using representational difference analysis (RDA). Mol. Genet. Genomics 268, 113–121.
Park, K.C., Lee, J.K., Kim, N.H., Shin, Y.B., Lee, J.H., and Kim, N.S. (2003). Genetic variation in Oryza species detected by MITEAFLP. Genes Genet. Syst. 78, 235–243.
Rozas, J., and Rozas, R. (1999). DnaSP version 3: an integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics 15, 174–175.
Tajima, F. (1989). Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123, 585–595.
Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., and Higgins, D.G. (1997). The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 4876–4882.
Vaughan, D. (1994) The wild relatives of rice, IRRI Manila, Philippines.
Vaughan, D., Kadowaki, K., Kaga, A., and Tomooka, N. (2005). On the phylogeny and biogeography of the genus Oryza. Breed. Sci. 55, 113–122.
Vaughan, D., Lu, B., and Tomooka, N. (2008). The evolving story of rice evolution. Plant Sci. 174, 394–408.
Wang, Z., Second, G., and Tanksley, S. (1992). Polymorphism and phylogenetic relationships among species in the genus Oryza as determined by analysis of nuclear RFLPs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83, 565–581.
Watterson, G.A. (1975). On the number of segregating sites in genetical models without recombination. Theor. Popul. Biol. 7, 256–276.
Yoshida, K., Miyashita, N.T., and Ishii, T. (2004). Nucleotide polymorphism in the Adh1 locus region of the wild rice Oryza rufipogon. Theor. Appl. Genet. 109, 1406–1416.
You, M.K., Oh, S.I., Ok, S.H., Cho, S.K., Shin, H.Y., Jeung, J.U., and Shin, J.S. (2007). Identification of putative MAPK kinases in Oryza minuta and O. sativa responsive to biotic stresses. Mol. Cells 23, 108–114.
Yu, Z., Wright, S.I., and Bureau, T.E. (2000). Mutator-like elements in Arabidopsis thaliana: Structure, diversity and evolution. Genetics 156, 2019–2031.
Zhu, Q., Zheng, X., Luo, J., Gaut, B.S., and Ge, S. (2007). Multilocus analysis of nucleotide variation of Oryza sativa and its wild relatives: severe bottleneck during domestication of rice. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 875–888.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, SJ., Park, KC., Son, JH. et al. Sequence diversity of a domesticated transposase gene, MUG1, in Oryza species. Mol Cells 27, 459–465 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0061-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0061-8