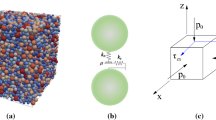
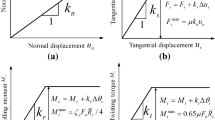
Abstract
The mechanical behaviors of granular soils at different initial densities and confining pressures in the drained and undrained triaxial tests are investigated micromechanically by three-dimensional discrete element method (DEM). The evolutions of the microstructure in the numerical specimen, including coordination number, contact force and anisotropies of contact normal and contact force, are monitored during the shearing. The typical shear behaviors of granular soils (e.g. strain softening, phase transformation, static liquefaction and critical state behavior) are successfully captured in the DEM simulation. It is found that the anisotropies of contact normal, normal and tangential contact forces comprise the shear resistance and show different evolution features during shearing. After large strain shearing, the microstructure of the soil will finally reach a critical state, although the evolution path depends on the soil density and loading mode. Similar to the macroscopic void ratio \(e\) and deviatoric stress \(q\), the coordination number and anisotropies of contact normal and contact force at the critical state also depend on the mean normal effective stress \(P^{\prime }\) at the critical state.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Been, K., Jefferies, M.G.: A state parameter for sands. Géotechnique 35(2), 99–112 (1985)
Poulos, S.J.: The steady state of deformation. J. Geotech. Eng. Div. ASCE 107(5), 553–562 (1981)
Verdugo, R., Ishihara, K.: The steady state of sandy soils. Soils Found. 36(2), 81–91 (1996)
Doanh, T., Ibraim, E., Matiotti, R.: Undrained instability of very loose Hostun sand in triaxial compression and extension. Part 1: experimental observations. Mech. Cohes.-Frict. Mat. 2(1), 47–70 (1997)
Yamamuro, J.A., Lade, P.V.: Static liquefaction of very loose sands. Can. Geotech. J. 34, 905–917 (1997)
Yamamuro, J.A., Lade, P.V.: Steady-state concepts and static liquefaction of silty sands. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. ASCE 124(9), 868–877 (1998)
Rahman, M.M., Lo, S.R.: Predicting the onset of static liquefaction of loose sand with fines. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. ASCE 138(8), 1037–1041 (2011)
Oda, M., Nemat-Nasser, S., Konishi, J.: Stress-induced anisotropy in granular masses. Soils Found. 25(3), 85–97 (1985)
Majmudar, T.S., Behringer, R.P.: Contact force measurements and stress-induced anisotropy in granular materials. Nature 435, 1079–1082 (2005)
Yang, Z.X., Li, X.S., Yang, J.: Quantifying and modelling fabric anisotropy of granular soils. Géotechnique 58(4), 237–248 (2008)
Cundall, P.A., Strack, O.D.L.: A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Géotechnique 29(1), 47–65 (1979)
Dobry, R., Ng, T.T.: Discrete modeling of stress–strain behavior of granular media at small and large strains. Eng. Comput. 9, 129–143 (1992)
Radjai, F., Jean, M., Moreau, J.-J., Roux, S.: Force distributions in dense two-dimensional granular systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(2), 274–277 (1996)
Radjai, F., Wolf, D.E., Jean, M., Moreau, J.-J.: Bimodal character of stress transmission in granular packings. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80(1), 61–64 (1998)
Thornton, C.: Numerical simulations of deviatoric shear deformation of granular media. Géotechnique 50(1), 43–53 (2000)
Sitharam, T.G., Dinesh, S.V., Shimizu, N.: Micromechanical modeling of monotonic drained and undrained shear behavior of granular media using three-dimensional DEM. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 26, 1167–1189 (2002)
Sitharam, T.G., Vinod, J.S., Ravishankar, B.V.: Post-liquefaction undrained monotonic behavior of sands: experiments and DEM simulations. Géotechnique 59(9), 739–749 (2009)
Alonso-Marroquin, F., Luding, S., Herrmann, H.J., Vardoulakis, I.: Role of anisotropy in the elastoplastic response of a polygonal packing. Phys. Rev. E 71(5), 051304 (2005)
Yan, W.M., Dong, J.J.: Effect of particle grading on the response of an idealized granular assemblage. Int. J. Geomech. 11(4), 276–285 (2010)
Yimsiri, S., Soga, K.: DEM analysis of soil fabric effects on behavior of sand. Géotechnique 60(6), 483–495 (2010)
Huang, X., Kwok, C.Y., O’sullivan, C., Tham, L.G.: DEM modeling of the critical-state behavior of a granular material. In: Choi, C.-K. (ed.) Proceeding of the 2012 World Congress on Advances in Civil, Environmental, and Materials Research, pp. 597–611, Seoul, Korea (2012)
Zhao, X., Evans, T.M.: Numerical analysis of critical state behaviors of granular soils under different loading conditions. Granul. Matter 13(6), 751–764 (2011)
Guo, N., Zhao, J.D.: The signature of shear-induced anisotropy in granular media. Comput. Geotech. 47, 1–15 (2013)
Muir Wood, D., Maeda, K.: Changing grading of soil: effect on critical states. Acta Geotech. 3, 3–14 (2008)
Itasca: Particle Flow Code (PFC3D) Manual. Itasca Consulting Group Inc., Minn (2009)
Yan, W.M.: Particle elongation and deposition effect to macroscopic and microscopic responses of numerical direct shear tests. Geotech. Test. J. 34(3), 238–249 (2011)
Andrade, J.E., Chen, Q., Le, P.H., Avila, C.F., Evans, T.M.: On the rheology of dilative granular media: bridging solid- and fluid-like behavior. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 60, 1122–1136 (2012)
Duffy, J., Mindlin, R.D.: Stress–strain relations and vibrations of a granular medium. J. Appl. Mech. 24, 585–593 (1957)
Yang, J., Gu, X.Q.: Shear stiffness of granular material at small strain: does it depend on grain size? Geotechnique 63(2), 165–179 (2012)
Sze, H.Y.: Initial Shear and Confining Stress Effects on Cyclic Behavior and Liquefaction Resistance of Sands. PhD thesis, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong (2010)
Li, X.: Micro-scale Investigation of the Quasi-Static Behavior of Granular Material. PhD thesis, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong (2006)
Alonso-Marroquin, Vardoulakis, I., Herrmann, H.J., Weatherley, D., Mora, P.: Effect of rolling on dissipation in fault gouge. Phys. Rev. E 74(3), 031306 (2006)
Ishihara, K.: Liquefaction and flow failure during earthquakes. Géotechnique 43(3), 351–415 (1993)
Been, K., Jefferies, M.G., Hachey, J.: The critical sate of sands. Géotechnique 41(3), 365–381 (1991)
Marsal, R.J.: Mechanical Properties of Rockfill. Embankment Dam Engineering, pp. 109–145 (1973)
Oda, M.: Co-ordination number and its relation to shear strength of granular materials. Soils Found. 14(4), 109–145 (1977)
Agnolin, I., Roux, J.-N.: Internal states of model isotropic granular packings. I. Assembling process, geometry, and contact networks. Phys. Rev. E 76(6), 061302 (2007)
Magnanimo, V., Rigione, L.L.A., Jenkins, J.T., Wang, P., Makse, H.A.: Characterizing the shear and bulk moduli of an idealized granular material. Europhys. Lett. 81, 34006 (2008)
De Alba, P., Baldwin, K., Janoo, V., Roe, G., Celikkol, B.: Elastic-wave velocities and liquefaction potential. Geotech. Test. J. 7(2), 77–87 (1984)
Ishibashi, I., Capar, O.F.: Anisotropy and its relation to liquefaction resistance of granular material. Soils Found. 43(5), 149–159 (2003)
Agnolin, I., Roux, J.-N.: Internal states of model isotropic granular packings. III. Elastic properties. Phys. Rev. E 76(6), 061304 (2007)
Gu, X.Q., Yang, J.: A discrete element analysis of elastic properties of granular materials. Granul. Matter 15(2), 139–147 (2013)
Gu, X.Q., Yang, J., Huang, M.S.: DEM simulations of the small strain stiffness of granular soils: effect of stress ratio. Granul. Matter 15(3), 287–298 (2013)
Kumar, N., Imole, I.O., Magnanimo, V., Luding, S.: Effects of polydispersity on the micro-macro behavior of granular assemblies under different deformation paths. Particuology (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2013.07.011
Yang, J., Dai, B.B.: Is the quasi-steady state a real behavior? A micromechanical perspective. Géotechnique 61(2), 175–183 (2009)
Gong, G.B.: DEM Simulation of Drained and Undrained Behavior. PhD thesis, The University of Birmingham, UK (2008)
Duran, O., Kruyt, N.P., Luding, S.: Micro-mechanical analysis of deformation characteristics of three-dimensional granular materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 47(17), 2234–2245 (2010)
Rothenburg, L., Kruyt, N.P.: Critical state and evolution of coordination number in simulated granular materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41, 5763–5774 (2004)
Azeme, E., Radjai, F.: Stress–strain behavior and geometrical properties of packings of elongated particles. Phys. Rev. E 81(5), 051304 (2010)
Azeme, E., Radjai, F.: Force chains and contact network topology in sheared packings of elongated particles. Phys. Rev. E 85(3), 031303 (2012)
Chang, C.S., Misra, A., Sundaram, S.S.: Properties of granular packing under low amplitude cyclic loading. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 10(4), 201–211 (1991)
Kuhn, M.R.: Structured deformation in granular materials. Mech. Mater 31, 407–419 (1999)
Rothenburg, L., Bathurst, R.J.: Analytical study of induced anisotropy in idealized granular materials. Géotechnique 39(4), 601–614 (1989)
Azeme, E., Radjai, F., Saint-Cyr, B., Delenne, J.-Y., Sornay, P.: Rheology of three-dimensional packings of aggregates: microstructure and effects of nonconvexity. Phys. Rev. E 87(5), 052205 (2013)
Imole, I.O., Magnanimo, V., Luding, S.: Micro-macro correlations and anisotropy in granular assemblies under uniaxial loading and unloading. Phys. Rev. E. (2013) (submitted)
Chantawarungal, K.: Numerical Simulations of Three Dimensional Granular Assemblies. PhD thesis, University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada (1993)
Masin, D.: Asymptotic behaviour of granular materials. Granul. Matter 14(6), 759–774 (2012)
Dafalias, Y.F., Paradimitriou, A.G., Li, X.S.: Sand plasticity model accounting for inherent fabric anisotropy. J. Eng. Mech. 130(11), 1319–1333 (2004)
Li, X.S., Dafalias, Y.F.: anisotropic critical state theory: role of fabric. J. Eng. Mech. 138(3), 263–275 (2012)
Qian, J.G., You, Z.P., Huang, M.S., Gu, X.Q.: A micromechanics-based model for estimating localized failure with effects of fabric anisotropy. Comp. Geotech. 50, 90–100 (2013)
Lätzel, M., Luding, S., Herrmann, H.J.: Macroscopic material properties from quasi-static, microscopic simulations of a two-dimensional shear-cell. Granul. Matter 2(3), 123–135 (2000)
Tordesillas, A., Muthuswamy, M.: On the modeling of confined buckling of force chains. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 57(4), 706–727 (2009)
Sykut, J., Molenda, M., Horabik, J.: DEM simulation of the packing structure and wall load in a 2-dimensional silo. Granul. Matter 10(4), 273–278 (2008)
Nicot, F., Sibille, L., Donze, F., Darve, F.: From microscopic to macroscopic second-order work in granular assemblies. Mech. Mater. 39, 664–684 (2007)
Katagiri, J., Matsushima, T., Yamada, Y.: Simple shear simulation of 3D irregularly-shaped particles by image-based DEM. Granul. Matter 12(5), 491–497 (2010)
Lu, Y., Frost, D.: Three-dimensional DEM modeling of triaxial compression of sands. In: Proceeding of Geoshanghai 2010 International Conference, pp. 220–226 (2010)
Minh, N.H., Cheng, Y.P.: A DEM investigation of the effect of particle-size distribution on one-dimensional compression. Géotechnique 63(1), 44–53 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The work presented in this paper is supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, Grant No. 2012CB719803), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51308408, 11372228, 41272291 and 51238009) and Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2013M541543). The authors are also very grateful to the reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, X., Huang, M. & Qian, J. DEM investigation on the evolution of microstructure in granular soils under shearing. Granular Matter 16, 91–106 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-013-0467-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-013-0467-z