Abstract
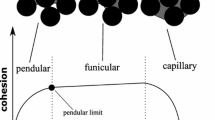
Shear cell simulations and experiments of weakly wetted particles (a few volume percent liquid binders) are compared, with the goal to understand their flow rheology. Application examples are cores for metal casting by core shooting made of sand and liquid binding materials. The experiments are carried out with a Couette-like rotating viscometer. The weakly wetted granular materials are made of quartz sand and small amounts of Newtonian liquids. For comparison, experiments on dry sand are also performed with a modified configuration of the viscometer. The numerical model involves spherical, monodisperse particles with contact forces and a simple liquid bridge model for individual capillary bridges between two particles. Different liquid content and properties lead to different flow rheology when measuring the shear stress-strain relations. In the experiments of the weakly wetted granular material, the apparent shear viscosity \(\eta _g\) scales inversely proportional to the inertial number \(I\), for all shear rates. On the contrary, in the dry case, an intermediate scaling regime inversely quadratic in \(I\) is observed for moderate shear rates. In the simulations, both scaling regimes are found for dry and wet granular material as well.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
MiDi, G.D.R.: On dense granular flows. Eur. Phys. J. E 14, 341–365 (2004)
Nakagawa, M., Luding, S.: Powders and grains 2009. AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1145, American institute of physics (2009)
Zhu, H.P., Zhou, Z.Y., Yang, R.Y., Yu, A.B.: Discrete particle simulation of particulate systems: theoretical developments. Chem. Eng. Sci. 62, 3378–3396 (2007)
van der Hoef, M.A., van Sint Annaland, M., Deen, N.G., Kuipers, J.A.M.: Numerical simulation of dense gas-solid fluidized beds: a multiscale modeling strategy. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 40, 4770 (2008)
Kafui, D.K., Johnson, S., Thornton, C., Seville, J.P.K.: Parallelization of a Lagrangian–Eulerian DEM/CFD code for application to fluidized beds. Powder Tech. 207, 270–278 (2011)
Voigtmann, T.: Yield stresses and flow curves in metallic glass formers and granular systems. Eur. Phys. J. E 34, 106 (2011)
Moorcroft, R.L., Cates, M.E., Fielding, S.M.: Age-dependent transient shear banding in soft glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 055502 (2011)
Mani, R., Kadau, D., Herrmann, H.J.: Fluid depletion in shear bands. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 248001 (2012)
Harireche, O., Faramarzi, A., Alani, A.: A toroidal approximation of capillary forces in polydisperse granular assemblies. Granul. Matter (2013). doi:10.1007/s10035-013-0425-9
Liu, P.Y., Yang, R.Y., Yu, A.B.: The effect of liquids on radial segregation of granular mixtures in rotating drums. Granul. Matter (2013). doi:10.1007/s10035-013-0392-1
Hsiau, S.S., Liao, C.C., Tai, C.H., Wang, C.Y.: The dynamics of wet granular matter under a vertical vibration bed. Granul. Matter (2013). doi:10.1007/s10035-013-0412-1
Zakerin, M., Kappl, M., Backus, E.H.G., Butt, H.J., Schonfeld, F.: Capillary forces between rigid spheres and elastic supports: the role of Young’s modulus and equilibrium vapor adsorption. Soft Matter 9, 4534–4543 (2013)
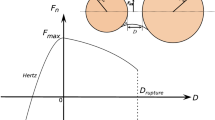
Lian, G., Thornton, C., Adams, M.J.: A theoretical study of the liquid bridge forces between two rigid spherical bodies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 161, 138–147 (1993)
Weigert, T., Rippberger, S.: Calculation of the liquid bridge volume and bulk saturation from the half-filling angle. Part. Part. Syst. Char. 16, 238–242 (1999)
Willett, C.D., Adams, M.J., Johnson, S.A., Seville, J.P.K.: Capillary bridges between two spherical bodies. Langmuir 16, 9396–9405 (2000)
Herminghaus, S.: Dynamics of wet granular matter. Adv. Phys. 54, 221–261 (2005)
Jop, P., Forterre, Y., Pouliquen, O.: A constitutive law for dense granular flows. Nature 441, 727–730 (2006)
Goddard, J.D.: A dissipative anisotropic fluid model for non-colloidal particle dispersions. J. Fluid Mech. 568, 1–17 (2006)
Gabrieli, F., Lambert, P., Cola, S., Calvetti, F.: Micromechanical modelling of erosion due to evaporation in a partially wet granular slope. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 36, 918–943 (2012)
Hayman, N.W., Ducloue, L., Foco, K.L., Daniels, K.E.: Granular controls on periodicity of stick-slip events: kinematics and force-chains in an experimental fault. Pure Appl. Geophys. 168, 2239–2257 (2011)
Pietsch, W.: Agglomeration Processes. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (2002)
Guo, Y., Wu, C.Y., Thornton, C.: The effects of air and particle density difference on segregation of powder mixtures during die filling. Chem. Eng. Sci. 66, 661–673 (2011)
Guo, Y., Wu, C.Y., Kafui, K.D., Thornton, C.: 3D DEM/CFD analysis of size-induced segregation during die filling. Powder Tech. 206, 177–188 (2011)
Beeley, P.R.: Foundry Technology. Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2001)
Schwarze, R., Rudert, A., Tilch, W., Bast, J.: Rheological behavior of sand-binder mixtures measured by a coaxial cylinder rheometer. I. Foundry Res. 60(3), 2–6 (2008)
Liao, C.-C., Hsiau, S.-S.: Experimental analysis of dynamic properties in wet sheared granular matter. Powder Tech. 197, 222–229 (2010)
Rudert, A., Schwarze, R., Tilch, W., Bast, J.: Computational fluid dynamics of the core shooting process. Foundry Trade J. Int. 185, 147–151 (2011)
Quarzwerke Frechen, Austria. www.quarzwerke.at/datenblaetter/Quarzsand_F32-F36.pdf
Fenistein, D., van de Meent, J.W., van Hecke, M.: Universal and wide shear zones in granular bulk flow. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 094301 (2004)
McCarthy, J.J.: Micro-modeling of cohesive mixing processes. Powder Technol. 138, 63–67 (2003)
Anand, A., Curtis, J.S., Wassgren, C.R., Hancock, B.C., Ketterhagen, W.R.: Segregation of cohesive granular materials during discharge from a rectangular hopper. Granul. Matter 12, 193–200 (2010)
Radl, S., Kalvoda, E., Glasser, B.J., Khinast, J.G.: Mixing characteristics of wet granular matter in a bladed mixer. Powder Technol. 200, 171–189 (2010)
Grima, P.W., Wypych, P.W.: Development and validation of calibration methods for discrete element modelling. Granul. Matter 13, 127–132 (2011)
Luding, S.: The effect of friction on wide shear bands. Part. Sci. Technol. 26, 33–42 (2008)
Luding, S.: Constitutive relations for the shear band evolution in granular matter under large strain. Particuology 6, 501–505 (2008)
Luding, S., Alonso-Marroquin, F.: The critical-state yield stress (termination locus) of adhesive powders from a single numerical experiment. Granul. Matter 13, 109–119 (2011)
Sadrekarimi, A., Olson, S.M.: A new ring shear device to measure the large displacement shearing behavior of sands. Geotech. Test. J. 32, 197–208 (2008)
Börzsönyi, T., Unger, T., Szabo, B., Wegner, S., Angenstein, F., Stannarius, R.: Reflection and exclusion of shear zones in inhomogeneous granular materials. Soft Matter 7, 8330–8336 (2011)
Dijksman, J.A., Wortel, G.H., van Dellen, L.T.H., Dauchot, O., van Hecke, M.: Jamming, yielding, and rheology of weakly vibrated granular media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 108303 (2011)
Börzsönyi, T., Szabo, B., Törös, G., Wegner, S., Török, J., Somfai, E., Bien, T., Stannarius, R.: Orientational order and alignment of elongated particles induced by shear. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 228302 (2012)
Wang, X., Zhu, H.P., Yu, A.B.: Microdynamic analysis of solid flow in a shear cell. Granul. Matter 14, 411–421 (2012)
Slotterback, S., Mailman, M., Ronaszegi, K., van Hecke, M., Girvan, M., Losert, W.: Onset of irreversibility in cyclic shear of granular packings. Phys. Rev. E 85, 021309 (2012)
Luding, S.: Cohesive frictional powders: contact models for tension. Granul. Matter 10, 235–246 (2008)
Göncü, F., Duran, O., Luding, S.: Constitutive relations for the isotropic deformation of frictionless packings of polydisperse spheres. Compt. Rend. Mec. 338, 570–586 (2010)
Shaebani, M.R., Madadi, M., Luding, S., Wolf, D.E.: Influence of polydispersity on micromechanics of granular materials. Phys. Rev. E 85, 011301 (2012)
Luding, S., Clément, E., Blumen, A., Rajchenbach, J., Duran, J.: Anomalous energy dissipation in molecular dynamics simulations of grains. Phys. Rev. E 50, 4113–4122 (1994)
Otsuki, M., Hayakawa, H., Luding, S.: Behavior of pressure and viscosity at high densities for two-dimensional hard and soft granular materials. Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 184, 110–133 (2010)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support of the ERASMUS program which allowed us to host FU during his Master study at the University of Twente. Helpful discussions with T. Weinhart, A. Singh, V. Magnanimo are appreciated. RS acknowledges the German Science Foundation (DFG) for funding parts of the work under Project No. SCHW 1168/6-1, and SL acknowledges the NWO/STW, VICI Grant 10828, and the DFG, project SPP1482 B12, for partial financial support. Finally, we acknowledge the constructive criticism of the referees of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarze, R., Gladkyy, A., Uhlig, F. et al. Rheology of weakly wetted granular materials: a comparison of experimental and numerical data. Granular Matter 15, 455–465 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-013-0430-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-013-0430-z