Abstract
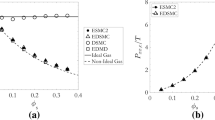
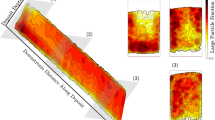
Flux models play a crucial role in understanding clustering behavior of compartmentalized granular gases. In this work we propose a method to measure the flux of mono-disperse and bi-disperse granular gases in an equivalent compartmentalized system by molecular dynamics simulation. The simulation results are useful for quantitative comparison with an existing flux model that presents essential features of the oscillatory clustering behavior in a two-compartment system. By some minor improvement to one of the models, we show results of quantitative comparisons between predictions of the model and our simulation results. We also discuss the evolution of the system through oscillatory and degenerate oscillatory states using flux contour maps.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaeger H.M., Nagel S.R., Behringer R.P.: Granular solids, liquids, and gases. Rev. Mod. Phys. 68, 1259 (1996)
de Gennes P.G.: Granular matter: a tentative view. Rev. Mod. Phys. 71, 374 (1999)
Kadanoff L.P.: Built upon sand: theoretical ideas inspired by granular flows. Rev. Mod. Phys. 71, 435 (1999)
Aranson I.S., Tsimring L.S.: Patterns and collective behavior in granular media: Theoretical concepts. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 641 (2006)
Schlichting, H.J., Nordmeier, V.: Strukturen im Sand. Math. Naturwiss. Unterr. 49, 323 (1996) (in German)
Schinner, A.: Ein Simulationssystem fuer granulare Aufschuettungen aus Teilchen variable Form. Ph.D. thesis, University of Magdeburg (2000)
Mikkelsen R., van der Meer D., van der Weele K., Lohse D.: Competitive clustering in a bidisperse granular gas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 214301 (2002)
Mikkelsen R., van der Meer D., van der Weele K., Lohse D.: Competitive clustering in a bidisperse granular gas: Experiment, molecular dynamics, and flux model. Phys. Rev. E 70, 061307 (2004)
Liu R., Li Y., Hou M.: Oscillatory phenomena of compartmentalized bidisperse granular gases. Phys. Rev. E 79, 052301 (2009)
Costantinia G., Paolotti D., Cattuto C., Marconi U.M.B.: Bistable clustering in driven granular mixtures. Physica A 347, 411 (2004)
Lambiotte R., Salazar J.M., Brenig L.: From particle segregation to the granular clock. Phys. Lett. A 343, 224 (2005)
Hou M., Tu H., Liu R., Li Y., Lu K., Lai P., Chan C.K.: Temperature oscillations in a compartmentalized bidisperse granular gas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 068001 (2008)
Miao T., Liu Y., Miao F., Mu Q.: Oscillations of granular mixture gases with vertical vibration. Chin. Sci. Bull. 50, 740 (2005)
Viridi S., Schmick M., Markus M.: Experimental observations of oscillations and segregation in a binary granular mixture. Phys. Rev. E 74, 041301 (2006)
Chen K.C., Li C.C., Lin C.H., Guo G.H.: Clustering and phases of compartmentalized granular gases. Phys. Rev. E 79, 021307 (2009)
Eggers J.: Sand as Maxwells demon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 5322 (1999)
Brey J.J., Ruiz-Montero M.J., Moreno F.: Hydrodynamic Maxwell demon in granular systems. Phys. Rev. E 65, 011305 (2001)
van der Meer, D., van der Weele, K., Reimann, P., Lohse, D.: Compartmentalized granular gases: flux model results. J. Stat. Mech. P07021 (2007)
Li Y., Zhang Z., Tu H., Liu R., Hu H., Hou M.: The flux profile of granular gas in compartmentalized system. Acta Phys. Sin. 58, 5840 (2009)
Evesque P.: Are temperature and other thermodynamics variables efficient concepts for describing granular gases and/or flows. Poudres et Grains 13, 27 (2002)
Meerson B., Pöschel T., Bromberg Y.: Close-packed floating clusters: granular hydrodynamics beyond the freezing point?. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 024301 (2003)
Rouyer F., Menon N.: Velocity fluctuations in a homogeneous 2D granular gas in steady state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 3676 (2000)
van Zon J.S., MacKintosh F.C.: Velocity distributions in dissipative granular gases. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 038001 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Liu, R., Shinde, M. et al. Flux measurement in compartmentalized mono-disperse and bi-disperse granular gases. Granular Matter 14, 137–143 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-012-0344-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-012-0344-1