Abstract
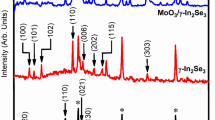
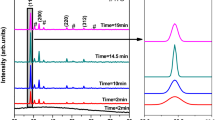
Indium selenide (γ-In2Se3) films were prepared using RF magnetron sputtering. Influence of deposition time on structural, optical, morphological, and photoelectrochemical (PEC) performance was studied. Formation of γ-In2Se3 is confirmed by low angle XRD, Raman spectroscopy, and XPS analysis. Surface morphology investigated using FE-SEM shows that γ-In2Se3 films are uniform and have a dense grain structure, without cracks and holes. Optical properties show that γ-In2Se3films absorb mainly in the UV region, and the bandgap energy decreases from 2.81 to 2.27 eV as deposition duration increases. Conduction and valance band-edge potential values show that γ-In2Se3 films are suitable for photoelectrochemical hydrogen evolution. PEC activity of γ-In2Se3 photoanodes was evaluated using linear sweep voltammetry (LSV), and there was an increase in photocurrent density with deposition time. Electron impedance spectroscopy (EIS) analysis revealed that γ-In2Se3 photoanodes had high charge transfer resistance, and it decreases with deposition time, which leads to improved PEC performance. Investigation of Mott Schottky's (MS) results shows a shifting of flat band potential towards negative potential, suggesting movement of fermi level towards conduction band edge. Carrier density increases from 3.7 × 1019 cm−3 to 8.9 × 1020 cm−3 and depletion layer width of γ-In2Se3 photoanodes are found in the range of ~ 2.67–9.10 nm. The gradual increase in electron lifetime indicates a decrease in the recombination rate of photo-generated charge carriers. An increase in time-dependent photocurrent density reveals that γ-In2Se3 films have effective electron–hole separation. Our work demonstrates that γ-In2Se3 can be a probable candidate for PEC water splitting and opto-electronic applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zou Z, Ye J, Sayama K, Arakawa H (2001) Direct splitting of water under visible light irradiation with an oxide semiconductor photocatalyst. Nature 414:625–627
Zhang H, Ming J, Zhao J, Gu Q, Xu C, Ding Z, Yuan R, Zhang Z, Lin H, Wang X, Long J (2019) High-Rate, Tunable Syngas Production with Artificial Photosynthetic Cells. Angew Chem 131(23):7800–7804
Holmes MA, Townsend TK, Osterloh FE (2012) Quantum confinement controlled photocatalytic water splitting by suspended CdSe nanocrystals. Chem Commun 48:371–373
Sharma KN, Joshi H, Singh VV, Singh P, Singh AK (2013) Palladium(II) complexes of pyrazolated thio/selenoethers: Syntheses, structures, single-source precursors of Pd4Se and PdSe nano-particles and potential for catalyzing Suzuki-Miyaura coupling. Dalton Trans 42:3908–3918
Monireh F, Yousefi M, Yousefzadeh S, Zirak M, Naseri N, Jeon T, Choi W, Moshfegh A (2019) Two-dimensional materials in semiconductor photoelectrocatalytic systems for water splitting. Energy Environ Sci 12:59–95
Hui C, Gu Y, Lin Y, Yu Y, Geohegan DB, Xiao K (2019) Synthesis and emerging properties of 2D layered III-VI metal chalcogenides. Appl Phys Rev 6:041312
Matthews P, McNaughter P, Lewis D, O’Brien P (2017) Shining a light on transition metal chalcogenides for sustainable photovoltaics. Chem Sci 8:4177–4187
Lin J, Bie M, Shang J, Tang X, Kou L (2020) Janus transition metal dichalcogenides: a superior platform for photocatalytic water splitting. Journal of Physics: Materials 3: 022004
Kumar G, Kumar J, Ilanchezhiyan P, Paulraj M, Jeon H, Kim D, Kang T (2020) Photoelectrochemical analysis of shape modified γ-phase In2Se3 nanostructures photoelectrodes. J Market Res 9:12318–12327
Procopio F, Pedrosa R, DeSouza F, Paz W, Scopel W (2020) Tuning the photocatalytic water-splitting capability of two-dimensional α-In2Se3 by strain-driven bandgap engineering. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 223520–3526
Yadav A, Salunke S (2015) Photoelectrochemical properties of In2Se3 thin films: Effect of substrate temperature. J Alloy Compd 640:534–539
Raval A, Saini L, Shah D, Patel S (2020) Synthesis and characterization of indium selenide thin films for solar cell application. AIP Conference Proceedings 2220:090029
Tanda M, Manaka S, Yamada KM, Takahashi K (1993) Photoluminescence studies and solar-cell application of CuInSe2 thin films prepared using selenization techniques. Jpn J Appl Phys 32:1913
Zhou J, Zeng Q, Lv D, Sun L, Niu L, Fu W, Liu F, Shen Z, Jin C, Liu Z (2015) Controlled synthesis of high-quality monolayered α-In2Se3 via physical vapor deposition. Nano Lett 15:6400–6405
Manolikas C (1988) New results on the phase transformations of ln2Se3. J Solid State Chem 74:319–328
Amory C, Bernede JC, Marsillac S (2003) Study of a growth instability of γ-In2Se3. J Appl Phys 94:6945–6948
Jasinski J, Swider W, Washburn J, Liliental-Weber Z, Chaiken A, Nauka K, Gibson G, Yang C (2002) Crystal structure of κ-In2Se3. Appl Phys Lett 81:4356–4358
Bhalerao A, Jambure S, Bulakhe R, Kahanda S l, Jagtap S, Banpurkar, Ansari A, In I, Lokhande C (2021) Substrate-Assisted Electrosynthesis of Patterned Lamellar Type Indium Selenide (InSe) Layer for Photovoltaic Application, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Advances in Energy Research, Springer Proceedings in Energy, M. Bose and A. Modi (eds.) pp. 837–845
Wu C, Kang J, Wang B, Zhu H, Li Z, Chen S, Wang L, Yang W, Xie C, Luo L (2019) Defect-induced broadband photodetection of layered γ-In2Se3 nanofilm and its application in near-infrared image sensors. Journal of Materials Chemistry C 7:11532–11539
Julien C, Hatzikraniotis E, Chevy A, Kambas K (1985) Electrical behavior of lithium intercalated layered In-Se compounds. Mater Res Bull 20:3287–3292
Lee H, Kang HD, Tran L (2005) Indium selenide (In2Se3) thin film for phase-change memory. Mater Sci Eng B 119:196–201
Li Q, Li Y, Gao J, Wang S, Sun X (2011) High performance single In2Se3 nanowire photodetector. Appl Phys Lett 99:243105
Panda R, Naik R, Mishra N (2018) Low-temperature growth of γ phase in thermally deposited In2Se3 thin films. Phase Transitions 91:862–871
Jiadong Z, Zeng Q, Lv D, Sun L, Niu L, Fu W, Liu F, Shen Z, Jin C, Liu Z (2015) Controlled synthesis of high-quality monolayered α-In2Se3 via physical vapor deposition. Nano Lett 15:6400–6405
Xiaoyan T, Zhou J, Yang Q (2011) Ascorbic acid-assisted solvothermal growth of γ-In2Se3 hierarchical flowerlike architectures. CrystEngComm 13:2792–2798
In-Hwan C (2011) The Preparation of CIS Absorber Layers by Using MOCVD with Two Different Methods. J Korean Phys Soc 59:80–84
Sylvie M, Sanchez S, Vedel J (1996) Electrodeposition of indium selenide In2Se3. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 412:1–295–101.
Takamasa K, Hiramatsu T, Onojima N (2011) Growth of γ-In2Se3 Thin Films by Electrostatic Spray Pyrolysis Deposition. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics 50:5S2 05FB11.
Li S, Yan Y, Zhang Y, Ou Y, Ji Y, Liu L, Yan C, Zhao Y, Yu Z (2014) Monophase γ-In2Se3 thin film deposited by magnetron radio-frequency sputtering. Vacuum 99:228–232
Yong Y, Li S, Ou Y, Ji Y, Yu Z, Liu L, Yan C, Zhang Y, Zhao Y (2014) Effects of pressure and deposition time on the characteristics of In2Se3 films grown by magnetron sputtering. Electron Mater Lett 10:1093–1101
Vaidyanathan R, Stickney JL, Cox SM, Compton SP, Happek U (2003) Formation of In2Se3 thin films and nanostructures using electrochemical atomic layer epitaxy. J Electroanal Chem 559:55–61
Ohtsuka T, Nakanishi K, Okamoto T, Yamada A, Konagai M, Jahn U (2001) Epitaxial growth of γ-In2Se3 films by molecular beam epitaxy. Jpn J Appl Phys 40:509
Hankare PP, Asabe MR, Chate PA, Rathod KC (2008) Structural, optical and microscopic properties of chemically deposited In2Se3 thin films. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 19:1252–1257
Mutlu IH, Zarbaliyev MZ, Aslan F (2007) Indium selenide thin film preparation by sol-gel technique. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 43:223–226
Sarmah PC, Rahman A (1998) Electrical and optical properties of RF sputtered CdTe films. Bull Mater Sci 21:149–154
Compaan AD, Gupta A, Lee S, Wang S, Drayton J (2004) High efficiency magnetron sputtered Cds/CdTe solar cells. Sol Energy 77:815–822
Li S, Yan Y, Deng Q, Yu Z, Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Song X, Zhao H, Su J, Lid J, Xia C (2020) Substrate-induced phase control of In2Se3 thin films. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 845:156270
Yan Y, Li S, Ou Y, Ji Y, Yu Z, Liu L, Yan C, Zhang Y, Zhao Y (2014) Effects of pressure and deposition time on the characteristics of In2Se3 films grown by magnetron sputtering. Electron Mater Lett 10:1093–1101
Jadhavar A, Bhorde A, Waman V, Pathan H, Jadkar S (2015) Synthesis of indium tin oxide (ITO) as a transparent conducting layer for solar cells by RF sputtering. Eng Sci 5:126–130
Nilanthy B, Steer ED, Smith EF, Kudrynskyi ZR, Kovalyuk ZD, Eaves L, Patanè A, Beton PH (2018) Epitaxial growth of γ-InSe and α, β, and γ-In2Se3 on ε-GaSe. 2D Materials 5: 035026
Cullity BD, Stock SR (2001) Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River NJ
Niranjan R, Padha N (2021) Growth of γ-In2Se3 monolayer from multifaceted InxSey thin films via annealing and study of its physical properties. Materials Chemistry and Physics 257:123823
Kite S, Chate P, Garadkar K, Sathe D (2017) Effect of annealing temperature on properties of molybdenum disulfide thin films. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28:16148–16154
Ke F, Liu C, Gao Y, Zhang J, Tan D, Han Y, Ma Y, Shu J, Yang W, Chen B, Mao HK, Chen XJ, Gao C (2014) Interlayer-glide-driven isosymmetric phase transition in compressed In2Se3. Appl Phys Lett 104/21: 212102
Weszka J, Daniel Ph, Burian A, Burian AM, Nguyen AT (2000) Raman scattering in In2Se3 and InSe2 amorphous films. J Non-Cryst Solids 265:98–104
Fang YX, Zhang H, Azad F, Wang SP, Ling FCC, Su SC (2018) Band offset and an ultra-fast response. UV-VIS photodetector in γ-In2Se3/p-Si heterojunction heterostructures. RSC Adv 8:29555–29561
Kursula PK (2000) Accuracy, precision and detection limits of SEM–WDS, SEM-EDS and PIXE in the multi-elemental analysis of medieval glass. X-Ray Spectrom 29:111–118
Yang S, Xu C, Yang L, Huabc SP, Zhen L (2016) Solution-phase synthesis of γ-In2Se3 nano-particles for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen generation under simulated sunlight irradiation. RSC Adv 6:106671–106675
Shi W, Yu S, Liu P, Fan W, Luo H, Song S (2013) Near-Infrared Photoluminescent Flowerlike α-In2Se3 Nanostructures from a Solvothermal Treatment. Chem Eng J 225:474–48029
Pei L, Yu S, Fan W, Shi W (2013) A new inorganic-organic hybrid In2Se3 as hollow nanospheres: hydrothermal synthesis and near-infrared photoluminescence properties. Dalton Trans 42:2887–2893
Kenneth B, William M, Wiley R, Venkatasubramanian E, Ohuchi F (2009) Vacancies ordered in screw form (VOSF) and layered indium selenide thin film deposition by laser back ablation. Appl Surf Sci 255:9707–9711
Tauc J (1970) Absorption edge and internal electric fields in amorphous semiconductors. Mater Res Bull 5:721–729
Hassanien AS, Akl AA (2016) Effect of Se addition on optical and electrical properties of chalcogenide CdSSe thin films. Superlattices Microstruct 89:153–169
Mott NF (1979) Davis E Electronics processes in non-crystalline materials. Clarendon, Oxford, p 428
Pathinettam PD, Marikani A, Murali KR (2002) Influence of thickness and substrate temperature on electrical and photoelectrical properties of vacuum deposited CdSe thin films. Mater Chem Phys 78:51–58
Hasegawa S, Kitagawa M (1978) Effects of annealing on localized states in amorphous Ge films. Solid State Commun 27:855–858
Abdel-Rahim FM, Hafiz MM, Alsorory H (2013) Thermal annealing effect on the structure and optical properties of Bi5Ge40Se55 thin films. J Alloys Comp 57076–80
Nang TT, Okuda M, Matsushita T, Yokota S, Suzuki A (1976) Electrical and optical properties of GexSe1-x amorphous thin films. Jpn J Appl Phys 15:849
Yang S, Xu CY, Yang L, Hu SP, Zhen L (2016) Solution-phase synthesis of γ-In2Se3 nano-particles for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen generation under simulated sunlight irradiation. RSC Adv 6:106671–106675
Caoa J, Li X, Lin H, Xu B, Chen S, Guan Q (2013) Surface acid etching of (BiO)2CO3 to construct (BiO)2CO3/BiOX (X = Cl, Br, I) heterostructure for methyl orange removal under visible light. Appl Surf Sci 266:294–299
Xi Z, Zhang L, Xie T, Wang D (2009) Low-temperature synthesis and high visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity of BiOI/TiO2 heterostructures. J Phys Chem C 113:7371–7378
Windisch C, Exarhos G (2000) Mott-Schottky analysis of thin ZNS films. J Vac Sci Technol A 18:1677–1680
Zhang H, Ma L, Ming J, Liu B, Zhao Y, Hou Y, Ding Z, Xu C, Zhang Z, Long J (2019) Amorphous Ta2OxNy-enwrapped TiO2 rutile nanorods for enhanced solar photoelectrochemical water splitting. Appl Catal B 243:481–489
Zhang H, Zhang P, Zhao J, Liu Y, Huang Y, Huang H, Yang C, Zhao Y, Wu K, Fu X, Jin S (2021) The Hole-Tunneling Heterojunction of Hematite-Based Photoanodes Accelerates Photosynthetic Reaction. Angew Chem Int Ed 60(29):16009–16018
Lin J, Heo Y, Nattestad A, Sun Z, Wang L, Kim JH, Dou SX (2014) 3D Hierarchical rutile TiO2 and metal-free organic sensitizer producing dye-sensitized solar cells 8.6 % conversion efficiency. Scientific Reports 4:5769
Rekha D, Baby LR, Gyu KH, Borse PH (2013) Enhanced solar photoelectrochemical conversion efficiency of ZnO:Cu electrodes for water-splitting application. International Journal of Photoenergy, Article ID 928321
Acknowledgements
Ashish Waghmare, Yogesh Hase, Vidya Doiphode, Shruti Shah, Pratibha Shinde, Subhash Pandharkar, Shruthi Nair, Ashvini Punde, and Bharat Bade are thankful to the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India, for the financial support under the National Renewable Energy Fellowship (NREF) program. Rahul Aher is thankful to Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune, for Bharat Ratna JRD Tata Gunwant Sanshodhak Shishyavruti. Vidhika Sharma, Mohit Prasad, and Sandesh Jadkar are grateful to Indo-French Centre for the Promotion of Advanced Research-CEFIPRA, Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, for special financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waghmare, A., Sharma, V., Shinde, P. et al. Preparation and characterization of γ-In2Se3 thin-film photoanodes for photoelectrochemical water splitting. J Solid State Electrochem 26, 219–232 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-021-05054-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-021-05054-1